Document
advertisement
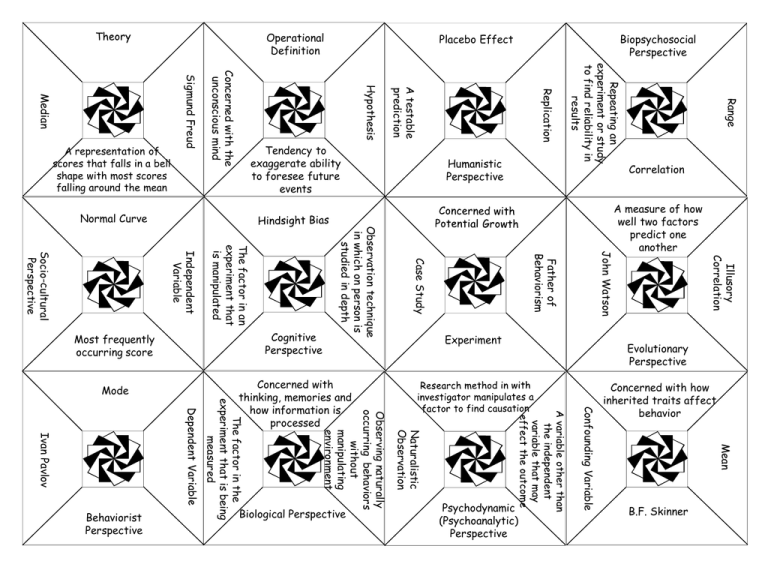
Operational Definition Illusory Correlation Concerned with how inherited traits affect behavior Mean Psychodynamic (Psychoanalytic) Perspective Evolutionary Perspective Confounding Variable Naturalistic Observation Observing naturally occurring behaviors without manipulating environment Biological Perspective John Watson Father of Behaviorism Experiment Concerned with thinking, memories and how information is processed The factor in the experiment that is being measured Ivan Pavlov Behaviorist Perspective Case Study Mode Observation technique in which on person is studied in depth The factor in an experiment that is manipulated Independent Variable Socio-cultural Perspective Cognitive Perspective Correlation A measure of how well two factors predict one another Normal Curve Most frequently occurring score Range Humanistic Perspective Repeating an experiment or study to find reliability in results Tendency to exaggerate ability to foresee future events Biopsychosocial Perspective Replication A testable prediction Hypothesis Concerned with the unconscious mind Sigmund Freud Median A representation of scores that falls in a bell shape with most scores falling around the mean Placebo Effect B.F. Skinner Somatic Nervous System Neurotransmitters Electrochemical messengers Reabsorption of remaining neurotransmitters in the synapse Reuptake Epinephrine Sympathetic Nervous System System that arouses body for “fight or flight” Endorphins Pain Controlling Neurotransmitters Axon Located in the Brain and Spinal Cord Extension of the neuron that carries messages away from cell body Resting Potential Antagonist Hormones The Endocrine System The slow chemical communication system System that calms the body and conserves energy GABA Afferent Neurons Efferent Neurons Agonist Glutamate Dendrite Receive incoming signals from other neurons Refractory period Multiple Sclerosis Junction between the sending neuron and the receiving neuron Increases the speed of the neural impulse The cells support center Interneurons Myelin Sheath Soma The Nervous System Caused by the degradation of the axon’s protective casing The fast electrochemical communication system Action Potential Level of stimulation required to create a neural impulse Motor Neurons Sensory Neurons Autonomic Nervous System Parietal Lobe Pons Tissue damage in the brain Lesion Imperative for Sight Occipital Lobe Emotional control specifically Aggression and Fear Amygdala Reticular Formation Frontal Lobe Plasticity Old belief that bumps on the skull effected personality Phrenology Shows the effects of the two hemispheres working separately from one another Split Brain Studies Voluntary Motor Movement Cerebellum Thalamus Corpus Callosum Detects brain waves Wernicke’s Area Hippocampus Explicit Memories Damage to left hemisphere causing permanent language impairment Limbic System Lateralization Temporal Lobe Broca’s Area Brain Stem Sensory Cortex Decision making and judgments Shows the importance of the frontal lobe being in communication with the inner brain Outer layer of the brain responsible for higher level functioning Medulla Oblongata EEG Phineas Gage Cerebrum Fibrous connective tissue between the right and left hemisphere CT Scan PET Scan MRI Hypothalamus Lens The laboratory device that tests the depth perception of infants Visual cliff Outer Ear Optic Nerve Carries the neural impulse from the eye to the brain Difference Threshold The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye Receptor cells in the eye that convert light energy into neural signals The retina contains only red, green, and blue color detectors The conversion of one form of energy into another – sensation to electrochemical message Rods and Cones When one sense influences another (taste and smell) Hammer Sensitive to color, clarity, and are in the very center of the eye Young Hemholtz (Trichromatic) Theory Diminished sensitivity to constant stimulation Transduction Perception Organizing and interpreting information Stirrup The retina contains three color detectors for opposing colors (red-green, blue-yellow, whiteblack) Sensory Interaction Sensory Adaptation Sensation Receiving information from the environment Color Constancy Absolute Threshold ESP Pupil Anvil Opponent Process Theory Proximity The coiled, bony, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear The brains ability to adapt to an inverted or distorted visual field Cochlea Controls the amount of light entering the eye The light sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing rods and cones Perceptual Adaptation Figure-ground Binocular cues Monocular cues Psychoactive Drug Uncontrollable sleep attacks – sending sufferer straight to REM Narcolepsy A very powerful stimulant Methamphetamine When hypnagogic sensations happen NREM-1 Physical dependence Dream The body’s biological wakefulness cycle Circadian Rhythm REM When memories are consolidated Sleep Apnea Characterized by temporary bouts of stopped breathing 4 Night Terrors Opiate Reoccurring inability to fall asleep Nicotine Addictive and stimulating substance in cigarettes Number of NREM sleep stages Consciousness Sleep Hypnosis Activation Synthesis Theory Depressant Hallucinogen A powerful hallucinogen Withdrawal Manifest Content Slows down brain and body functioning Speeds up brain and body functioning Causes loss of touch with reality through delusions and hallucinations LSD Discomfort or distress after a user stops taking a drug Latent Content Delta Waves The story of the dream – what’s usually remembered NREM-2 Theta Waves Tolerance Fixed-Ratio A learned response to a neutral stimulus Conditioned Response Classical Conditioning Type of learning where two stimuli are linked together to anticipate events A relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience Learning Associative Learning Variable-Interval Giving a reinforcement every time the participant gets closer and closer to the desired behavior Unconditioned Stimulus Something that naturally triggers a response Secondary Reinforcer Discouraging a behavior by taking away a desired stimulus Variable-Ratio The reappearance of a diminished conditioned response Spontaneous Recovery An unlearned naturally occurring response to a certain stimulus Unconditioned Response Conditioned Stimulus Originally neutral stimulus that with association creates a conditioned response Chaining Fixed-Interval Skinner’s Box Pavlov’s Dogs Thorndike’s Puzzle Box Primary Reinforcer Negative Punishment Negative Reinforcement Learning by use of reinforcements and punishments Positive Punishment Operant Conditioning Discouraging behavior by adding an undesired stimulus Encourages behavior by adding a desired stimulus Observational Learning Positive Reinforcement Generalization Extinction Learning by watching others Insight Latent Learning Learned helplessness Babble Syntax Language rules Early speech in which child speak with mostly nouns and verbs like “go car” Telegraphic Speech Language Meaning Semantics Decision Making Two-Word Stage Insight A sudden realization of the solution to a problem The way an issue is posed, which has the ability to effect the decision Framing Heuristics Simple thinking strategies that allow us to solve problems efficiently Problem Solving One-Word Stage A mental image or best representation of a category The Mind Intuition The smallest unit of speech that carries meaning Morpheme A methodical step-bystep processes that guarantees an accurate solution Babbling Stage Speech Thinking Thoughts Prototype Mental activities associated with thinking The tendency to search of ideas that support personal ideas and disregard contrary evidence Availability Heuristic Confirmation Bias Making decisions based on how readily available information is in memory A mental grouping of similar objects Making judgements based on how well things match our prototypes Concept The smallest distinctive sound unit in a word Creativity Representative Heuristic Language Fixation Functional Fixedness Elizabeth Loftus The most immediate and brief recording of information that is usually lost Echoic Memory The Spacing Effect Forgetting 7 bits of information The tendency for practicing retrieval to yield better retention Sensory Memory The tendency for distributed study to yield better retention Flashbulb Memory Exceptionally clear memories of emotionally significant events The disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information Mnemonic Devices Serial Position Effect The Testing Effect The relatively permanent limitless storehouse of the memory system Long Term Memory The process of getting memory into storage Encoding Semantic Encoding Tendency to remember when in the same mood as information was encoded Proactive Interference The increase of synaptic firing after brief stimulation (thought to be the biological basis of memory) Long Term Potentiation Retrieval The process of getting memory out of storage Effortful Processing Mood-Congruent Memory Iconic Memory Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon Explicit Memories Implicit Memories Chunking The disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information The incorporation of misleading information into one’s memory of an event Retroactive Interference Storage Persistent learning over time and storing and retrieving of that information Misinformation Effect Source Amnesia Amnesia Automatic Processing Abilities The Mind Asked to create a mental age test in Paris for school children Thoughts Emotional Intelligence Disability dealing with an extra copy of the chromosome 21 The chronological age given after assessments based on mental ability Binet Condition where a person has an exceptional skill our ability but is very low in all other intellectual areas Mental Age Normal Curve Thought Processes MENSA Bell-shaped curve showing distribution of data where most scores fall along the mean Down Syndrome A test yielding consistently similar scores Reliability The average IQ 100 Decision Making Test measuring what it is supposed to measure Savant Syndrome The mental ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and adapt to new situations Intelligence An assessment that measures mental aptitudes Intelligence Test Memory Validity WAIS WISC Stanford-Binet Gardner Testing Designed to predict a person’s future performance General Intelligence Aptitude Tests IQ Achievement Tests According to Spearman, there was only one underlying mental ability Content Validity Standardization Predictive Validity Harry Harlow’s Monkeys Children become increasingly likely to react to newcomers with tears and distress Embryo An experiment created by Mary Ainsworth to test attachment styles The Strange Situation Attachment When cheek is touched, infant instinctively opens mouth to feed Erik Erikson Believed that development was shaped by changes or crises throughout life The transition from childhood to adulthood marked by the entrance of puberty Adulthood Sane people are tested over a period of years The inability to see from another’s perspective Stranger Anxiety Object Permanence Understanding an object still exists even without seeing it Cross-sectional Study Adolescence Study in which people of different ages are tested and compared Emerging Adulthood Though an object may change shape or sixing understanding that its properties remain the same Egocentricism Piaget’s Theory as to How Children learn to Understand the World Schema, Assimilation, and Accommodation Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Development Conservation Diana Baumrind’s Parenting Styles Lev Vygotsky Insecure attachment Secure Attachment Childhood Sensorimotor, Preoperational, Concrete Operational, and Formal Operational Elizabeth Kubler-Ross Critical Period Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development Optimal time for exposure to a particular stimulus in order to develop a certain ability Preconventional, Conventional, and Postconventional Agents that can harm prenatal development Zygote Babinski Reflex Fetus Moro Reflex