Functions
advertisement

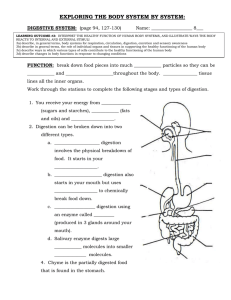
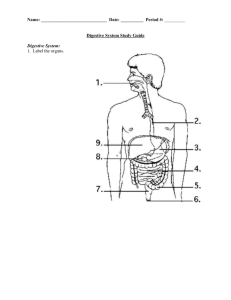
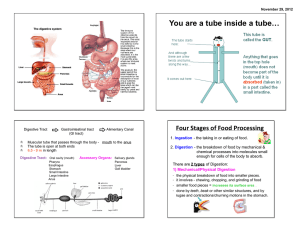
Digestion Functions Taelar Shelton, MS, ATC, AT/L Mouth Food is acted upon physically and chemically Papillae contain taste buds and are located on the tongue 32 teeth in mouth Tongue positions food toward basic of mouth to swallow Salivary Glands Parotid- secreation of saliva Sublingual- amylase is a digestive enzyme found in saliva Submandibular- provides digestive enzyme (amylase) to moisten food to make it easier to swallow Enzymes help begin the digestion of carbohydrates Pharynx Mouth to esophagus Trachea Respiratory system functions Esophagus About 10-12 inches long Peristalsis Heartburn in the burning sensation due to irritation caused by stomach aced backing up into the esophagus Cardiac Sphincter Allows food to enter the stomach Prevent stomach contents from backing up into esophagus Stomach Temporary storage of food Mix and churns food Secretes gastric juices for digestion (mucus, hydrochloric acid, enzymes) The major role of the stomach is not digestion Gastric ulcers can be caused by HCL irritation of the stomach lining Pyloric Sphincter Allows small amounts of food to intermittantly enter the duodenum “ski lift operator” Duodenum Can develop ulcers Length of all 3 portions of small intestines is about 20 feet Completes charbohydrate and protein digestion Villi help increase surface area Jejunum and Ilium Villi helps absorb products of digestion Completes digestion of protein, fats and carbohydrates Absorbs the end products of digestion into blood stream Carbohydrates – glucose Fats – fatty acid – glycerol Proteins – ammino acids Iliocecal Sphincter Regulates the passing of material from the small intestine to large intestine Cecum Collects waste products from digestive process Appendix Can become inlammed May need to be surgically removed Colon Ascending Colon- to absorb excess water from waste material Transverse Colon- peristalsis Descending Colon- about 5-6 feet Sigmoid Colon- cleans large intestine, prevents excess absorbtion of water Rectum Collects and eliminates waste Gall Bladder Collects and secretes bile Contracts to release bile into duodenum Liver Produces bile- helps digest fats Converts glucose into glycogen Acts on chyme as it passes through the duodenum Pancreas Secreates pancreatic juices to act on carbs, fats and proteins