Notes
advertisement

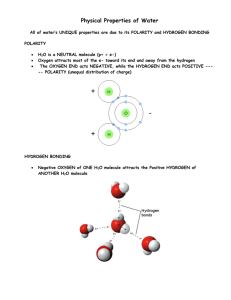
Objectives: Connect pH numbers to what they represent. Practice converting pH values. Evaluate strengths of acids & bases. What is the chemical equation for this beaker of distilled water? H2O + H2 ↔ H3O+ + OHor + H2O ↔ H + OH DEMONSTRATION Form water molecules Move around room Dissociate & ressociate randomly Equilibrium is a dynamic state It is rare for a hydrogen atom to leave the stability of the water molecule More likely to happen if water is heated or Influenced by other chemicals Chemical Equilibrium Is the concentration of water the same as the total concentration of H+ and OH-? No What does it mean to be at equilibrium? The reaction is still flowing back and forth, however, there is no net gain in either products or reactants H2O ↔ H+ + OH- Chemical Equilibrium Can an equation tend to one direction or the other? Yes (usually in the direction of the products) Which is in higher concentration in the beaker? H2O or [H+ + OH- ]? H2O pH Concentration How do you write the concentration of pH value 3? H+ = 1 x 10-3 How do you write pH 3 as a decimal? 0.001 How do you write pH 3 as a fraction? 1/1,000 What does this mean? If you reach into the beaker you would find only one dissociated H+ ion for every intact H2O molecules. Calculate the ratio of dissociated to intact water molecules in a beaker of distilled water of pH 7 at 25C pH 7, concentration of hydrogen [H+] = 1 x 10-7 Which is [H+] = 1/10,000,000 Which is one dissociated molecule of H2O for every 10 million intact H2O molecules What is the difference in hydrogen concentration between pH 5 and pH 2? How are the concentrations of [H+] and [OH-] related? What is the concentration of [OH-] if the pH is 3? What is the concentration of [OH-] if the pH is 13? Which of these two examples is more basic/alkaline? Electronegativity & pH Electronegativity can reveal the strengths of acids and bases If a hydrogen atom is in a molecule with other atoms that have a very strong ability to dominate the electrons, the the molecule will be polarized with hydrogen being stripped of its electron (think HCl) If the hydrogen does not have much association with its electron, then it leaves the molecule to become an ion and the solution is said to be more acidic QUESTIONS What is the difference between a strong acid/base and a weak acid/base? A strong acid/base dissociates readily Difference in electronegativity greater A weak acid/base dissociates less readily Minimal difference in electronegativity Which acids/bases are weaker and which are stronger – HCl, NH3, H2CO3, NaOH? Strong – HCl and NaOH Weak –NH3 and H2CO3