Empowered Not Devoured:
advertisement

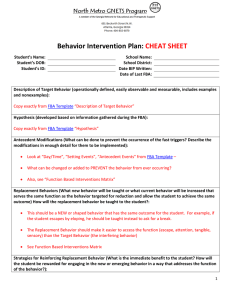
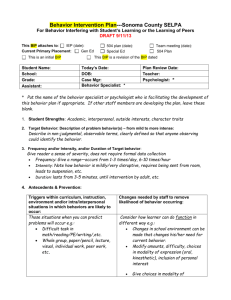
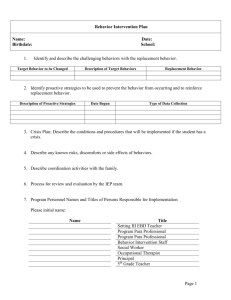
EMPOWERED NOT DEVOURED: What Can Behavior Services Do For You? Presented by: Amber Melton and Sarah Chandler June 2 & 3, 2014 Do You Know Your Superheroes? ` Objective: The participant will gain knowledge of resources and supports provided by the Behavior Services Staff and actively participate in the session as assessed through observation and performance. Please note… There will be a five-minute scheduled break in 45 minutes. At that time, you will be able to engage in an activity of your choice within the room. Electronic devices will be permitted at this time. Throughout the presentation, represents that a handout has been provided as a reference. Refer to the packet you were given. head banging fighting hitting yelling biting throwing things screaming crying non-compliant Cursing Getting out of seat Inappropriate sexual behavior running destroying property pushing Devoured ? Empowered ? Behavior Staff Purpose of the Behavior Support Services To collaboratively provide resources and support that will 1. Ensure safety of all staff and students 2. Align services and programming with federal and state guidelines 3. Allow teachers to focus on teaching and learning - Coordinator Positive Behavior Specialists Behavior Coaches SPED Social Worker Behavior Techs Why Involve The Behavior Staff • Support • Resources How To Involve The Behavior Staff • Complete a Behavior Support Services Request Form or a SPED Social Worker Request Form. • Be knowledgeable of the Behavior Specialist and Behavior Coach assigned to your school. When To Involve The Behavior Staff - As soon as there is a pattern of behavior with a student and strategies and reinforcements have not been successful at the school level. - After a BMP or BIP has been implemented and no progress is being made. Role of Coordinator • Supervise • Collaborate • Consult • Train Role of Positive Behavior Specialists • • • • • • • • • Write Attend Provide Monitor Lead Create Consult Train Input Role of Behavior Coaches • • • • • • • • Assist Model Observe Teach Provide Create Train Input Role of SPED Social Worker • As a social worker, I am here to provide a positive school-homecommunity connection. • I can provide resources to students and families such as Medicaid or SSI application help, Region IV or other Counseling Service referrals, Job Corp referrals, residential placement, Youth Services/Youth Court, Medication assistance, and other available community resources. • I can make referrals to the Mississippi Department of Human Services for suspected abuse, neglect, or exploitation of a child. I can follow up with our local DHS and their social workers. • I am involved with the DeSoto County MAP team. • I also provide Social Skills services to students and conduct group sessions for the students at Alpha and Omega. Request for Special Education Social Work Services Role of Behavior Techs and ABA Instructors • • • • • • Implement Assist Observe Communicate Provide Participate Region 4 Children’s Services Region IV Basic Information Region IV Services Include: • The main office is located in Hernando at 2725 Highway 51 South • The phone number is 662-4491808. The on call/after hours phone number is 1-888-287-4443. • Hours of operation are 8:00-5:00 Monday through Friday. • Children’s Services are reimbursed by most private insurances including Medicaid and CHIPS. Services may also be based on a sliding fee schedule that is determined by family size and income. • Individual, group, and family therapy • Case Management • Day Treatment-School Bases and Preschool • School Based Nursing Services • Psychiatric Services—Risk Assessments • MAP Team Region IV Children’s Services Counselors Case Managers • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Reginald Magee Tammara Armstrong Melissa Lyons Sommer Tubbs Monica Lemmons Amanda Beuning Carisha Williams Marc King Paula Clay Belinda Lundford Lashundra Jones Tessica Eckford Yoko Montgomery Rochelle McGee Shakebra Young Tina Dow Earline Jordan Chris McClinton Kristen Merritt Delcenia Pegues Sylvia Lindsey Tanya Redmond Miranda Roberts Training Opportunities • • • • • • Understanding Data from FBA to Implement BIP Got Behavior? Are you Programming for it? Avoiding a Meltdown: Autism & EMD behavior Social Skills Training Paraprofessional Behavior Module A Guide to Writing a Behavior Modification Plan: Getting Answers • CPI • Teaching Social Skills in the Classroom • How to Teach Replacement Behaviors While Teaching To schedule professional development sessions during planning times, LSC meetings, or afterschool professional development please call Peggy Darnell. Preventing and Encouraging Positive Student Behavior CPI Crisis Development Model CPI Verbal Escalation Continuum Creating and Implementing School-Based Behavior Modification Plans - Target Behavior(s) - Function/Hypothesis - Replacement Behaviors - Strategies/Interventions - Positive Reinforcement/Natural Consequences - Progress Monitoring Target Behaviors • Observable • Measureable Examples… Which is best? 1. Ally is defiant. 2. Ally stays at the computer to continue playing after her time is up and requires prompting to end and move to the next activity. Function/Hypothesis Sensory Stimulation Attention Escape/ Avoid Access to Tangibles What’s the Function? Ally stays at the computer to continue playing after her time is up and requires prompting to end and move to the next activity. Ally wants to continue engaging in a preferred activity. Escape/Avoid non-preferred activity TOOL Replacement Behaviors • Must serve the same function as the problem behavior • Be proactive, not reactive • Be efficient and effective • If we do not teach a new behavior, the student will come up with a new way to get what he/she wants. Examples of Replacement Behaviors • • • • • • • Use a schedule Say “all done” Ask for a break, help, a turn, a hug Identify feelings Say “no” Take turn Express feelings using words Strategies/Interventions 3 Common Research-Based Strategies - Check-in and Check-out - Token Economy - Scheduled Breaks Check-in and Check-out • Why • When • How Token Economy • What is it? • What are the benefits Scheduled Breaks Why What does it look like? Positive Reinforcement/ Natural Consequences • Occurs when a reward, sometimes called a reinforcer, is given for a specific desired behavior. • Over time, this will lead to an increase in the desired behavior. • Many experts believe that reinforcement is more effective than punishment in shaping long term behavior. • Should be age appropriate and something valued by the student, Tool • Forced –Choice Menu • Picture Menu Progress Monitoring • How • How often • By whom - Is the replacement behavior increasing? - Is the target behavior decreasing? - Is the reinforcement decreasing? Plans should be reviewed two to three weeks after implementation and monthly following. FBA Functional Behavioral Assessments (FBA) identify the function(s) of an individual student’s behaviors and provide information leading to effective interventions and needed supports. Purpose of FBA: An FBA allows educators to better understand the following areas of concern: • Skill deficits (academic and behavioral) • Performance deficits (academic and behavioral) • Student preferences • Reinforcement that is maintaining appropriate and/or challenging behavior. • For a student who becomes subject to disciplinary action a functional behavioral assessment is used to develop a behavior intervention plan within the context of the IEP process. BIP • Same components as a BMP but driven by the FBA • Must be progress monitored • Must be reviewed three weeks after implementation • Must be revised if progress is not being made by the student YOU are We appreciate you! What can the Behavior Services Staff do for YOU? Amber Melton, Positive Behavior Specialist amber.melton@dcsms.org Sarah Chandler, Sped Social Worker sarah.chandler@dcsms.org