JB APUSH Unit VA
advertisement

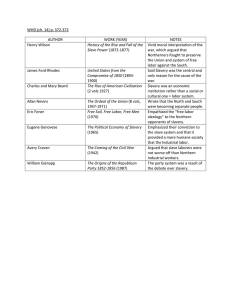
Antebellum Expansion Unit VA AP United States History Fundamental Questions ► Analyze American expansionism as a cause of sectional tension and conflict. ► Analyze how the national political system may have contributed to the cause of the Civil War. Democracy in America (1840) ► Impressed with American notion of equality More social mobility than Europe Success achievable for those willing and able ► “I sought for the greatness and genius of America in her commodious harbors and her ample rivers, and it was not there . . . in her fertile fields and boundless forests and it was not there . . . in her rich mines and her vast world commerce, and it was not there . . . in her democratic Congress and her matchless Constitution, and it was not there. Not until I went into the churches of America and heard her pulpits aflame with righteousness did I understand the secret of her genius and power. America is great because she is good, and if America ever ceases to be good, she will cease to be great.” Manifest Destiny ► “Away, away with these cobweb tissues of the rights of discovery, exploration, settlement,… [The American claim] is by the right of our manifest destiny to overspread and to possess the whole of the continent which Providence has given us for the development of the great experiment of liberty…” ► - John L. Sullivan, Democratic Review, 1845 American Progress Overland Trails Result of Manifest Destiny Texas Revolution ► American settlement Fueled by Manifest Destiny Encouraged by Mexican government ► Texas Revolution (1836) Santa Anna’s policies The Alamo (Feb-Mar 1836) Battle of San Jacinto (Apr 21, 1836) Second Party System (1828-1854) ► Democrats: States’ rights Limited government Laissez-faire Expansionism Pro-slavery Equal opportunity South and West Yeoman farmers, working class, southern planters, immigrants ► ► issue party concerned about Freemasons promoted economic nationalism and social conservatism ► Liberty Party: abolitionist party Andrew Jackson Whigs: American System Strong federal government Mixed on slavery Social conservatives New England Upper and middle class professionals, evangelical Protestants Anti-Masonic Party: Henry Clay ► Free Soil Party: Prevent expansion of slavery Taney Court ► Chief Justice Roger Taney Appointed by Andrew Jackson Slave owner ► Ideology States’ rights Limited government ► Major Cases Charles River Bridge v. Warren Bridge (1837) Scott v. Sandford (1857) Ex parte Merryman (1861) Election of 1840 ► William Henry Harrison (W) ► “Tippecanoe and Tyler Too” “Log Cabin and Hard Cider” Martin Van Buren (D) Suffers from Panic of 1837 Sectionalist Presidents William Henry Harrison (W) (1841) ► Campaign A war hero and hero of the common man ► Reality Wealthy plantation and slave owner ► Administration Intended to re-establish and promote American System policies Lasts one month after contracting pneumonia John Tyler assumes presidency Sectionalist Presidents John Tyler (W) (1841-1845) ► “His Accidency” Assumes full presidential powers ► A Democrat in Whig Clothing Slave owner from Virginia Rejects American System policies Passionately pursues Texas annexation ► Webster-Ashburton Treaty (1842) Settles boundary disputes with Great Britain Election of 1844 ► James K. Polk (D) Darkhorse candidate Expansion platform ► Henry Clay (W) Avoided direct expansionist rhetoric Sectionalist Presidents James K. Polk (D) (1845-1849) ► ► Jacksonian Democrat, slave owner, and ardent expansionist Agenda ► Independent national treasury Lower tariffs Oregon California Oregon “54’ 40 or Fight!” 49th Parallel ► Mexican-American War (1848) Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo Mexican Cession Oregon Country Mexican-American War (1846-1848) Thornton Affair (4/24/1846) ► War Plan and Execution ► ► John Fremont in California Stephen Kearny in New Mexico Zachary Taylor in Texas Winfield Scott in Veracruz and Mexico City Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) Rio Grande as Texas border Mexican Cession ► ► $15 million and assumption of claims against Mexico Wilmot Proviso Prohibit slavery in Mexican Cession lands Failed to pass Senate Election of 1848 ► Zachary Taylor (W) Slave owner War hero Lewis Cass (D) ► Martin van Buren (FSP) ► ► Sutter’s Mill California Gold Rush January 24, 1848 ► ► ► Massive migration to California Forty-Niners San Francisco 5,000 in 1848 25,000 in 1850 Compromise of 1850 ► Parameters Admit California as free state Mexican Cession ► Popular sovereignty Reinforced Fugitive Slave Law Texas boundary and debt disputes Slave trade abolished in D.C. ► “I trust we shall persist in our resistance [to the admission of California] until the restoration of all our rights, or disunion, one or the other is the consequence. We have borne the wrongs and insults of the North long enough.” - John C. Calhoun Fugitive Slave Law ► Enforcement of capturing and returning escaped slaves ► Slaves flee to Canada ► Right to trial by jury denied ► Special Commission $10 for those finding for slaveholder $5 for those finding for fugitive Underground Railroad ► Mostly run by free blacks and fugitive slaves Harriet Tubman ► Abolitionists and white supporters Few white families in South assisted Slave catchers knowledge Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852) ► Harriet Beacher Stowe ► Bestselling novel ► Adapted as a play ► Fuels abolitionist guilt and rhetoric in Northern free states Slavery and Literature Anti-Slavery Arguments ► Uncle Tom’s Cabin Pro-Slavery Arguments ► Harriet Beecher Stowe Moral and emotional argument against slavery ► Impending Crisis of the South (1857) Hinton Helper Empirical analysis of economic impact of slavery on the South “Freesoilers and abolitionists are the only true friends of the South; slaveholders and slavebreeders are downright enemies of their own section. Anti-slavery men are working for the Union and for the good of the whole world; proslavery men are working for the disunion of the States, and for the good of nothing except themselves." Sociology for the South (1854) George Fitzhugh Capitalism and liberalism virtually enslaved the lower classes ► Cannibals All! (1857) George Fitzhugh "the unrestricted exploitation of so-called free society is more oppressive to the laborer than domestic slavery." Sectionalist Presidents Zachary Taylor (W) (1849-1850) ► ► ► War hero of Mexican-American War States’ rights, but no secession Views on Slavery Slave owner No expansion of slavery Refused to sign Compromise of 1850 ► Died after a year in office Sectionalist Presidents Millard Fillmore (W) (1850-1853) ► ► ► ► Assumes the presidency after Taylor’s death Anti-slave moderate Signs Compromise of 1850 Perry Expedition to Japan (1853-1854) The Death of Compromising? ► The Great Triumvirate was no more by 1852 ► A new generation of sectional and ambitious politicians assume leadership roles William Seward (W, R) Stephen Douglas (D) Jefferson Davis (D) Election of 1852 ► Franklin Pierce (D) “Doughface” ► Winfield Scott (W) Sectionalist Presidents Franklin Pierce (D) (1853-1857) ► ► Jackson Democrat from New Hampshire Doughface Supported Compromise of 1850 Gadsden Purchase Ostend Manifesto (1854) Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854) William Walker and Nicaragua Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854) ► ► Stephen Douglas and Chicago Parameters Separate Nebraska Territory into Nebraska and Kansas Each territory voted for slavery based on popular sovereignty ► Impact Douglas won his railroad and Southern support Virtually repealed the Missouri Compromise Ended the Whig Party and Second Party System Bleeding Kansas (1854-1861) ► Kansas Territory settled by two groups ► A virtual civil war between anti-slave and pro-slave local governments ► A Tragic Prelude, John Steuart Curry, 1937 Free-Soilers Border Ruffians Sacking of Lawrence Pottawatomie Massacre Pierce and federal government barely addressed the issue Brooks-Sumner Incident May 22, 1856 ► Senator Charles Sumner (R) (MA) ► ‘Crime Against Kansas’ Speech Rep. Preston Brooks (D) (SC) Becomes a Southern hero The Republican Party ► Makeup Disillusioned Northern Democrats Frustrated Conscience Whigs Free Soil Party members ► Platform: Increasingly against expansion of slavery Protective tariffs Homestead Act/sale of federal lands Funding for transcontinental railroad Scott v. Sandford (1857) ► ► ► ► ► “[Blacks] had for more than a century before been regarded as beings of an inferior order, and altogether unfit to associate with the white race, either in social or political relations, and so far unfit that they had no rights which the white man was bound to respect.” " . . . We think they [people of African ancestry] are . . . not included, and were not intended to be included, under the word "citizens" in the Constitution, and can therefore claim none of the rights and privileges which that instrument provides for and secures to citizens of the United States. . . ." “For if they were so received, and entitled to the privileges and immunities of citizens, it would exempt them from the operation of the special laws and from the police regulations which they considered to be necessary for their own safety. It would give to persons of the negro race, who were recognized as citizens in any one State of the Union, the right to enter every other State whenever they pleased...to go where they pleased at every hour of the day or night without molestation, unless they committed some violation of law for which a white man would be punished; and it would give them the full liberty of speech in public and in private upon all subjects upon which its own citizens might speak; to hold public meetings upon political affairs, and to keep and carry arms wherever they went. And all of this would be done in the face of the subject race of the same color, both free and slaves, and inevitably producing discontent and insubordination among them, and endangering the peace and safety of the State.” “. . . [T]he rights of private property have been guarded with . . . care. Thus the rights of property are united with the rights of person, and placed on the same ground by the fifth amendment to the Constitution, which provides that no person shall be deprived of life, liberty, and property, without due process of law. And an act of Congress which deprives a citizen of the United States of his liberty or property, merely because he came himself or brought his property into a particular Territory of the United States, and who had committed no offence against the laws, could hardly be dignified with the name of due process of law.” “Upon these considerations, it is the opinion of the court that the act of Congress which prohibited a citizen from holding and owning property of this kind in the territory of the United States north of the line therein mentioned, is not warranted by the Constitution, and is therefore void; and that neither Dred Scott himself, nor any of his family, were made free by being carried into this territory; even if they had been carried there by the owner, with the intention of becoming a permanent resident.” Election of 1856 ► James Buchanan (D) “Doughface” ► John Fremont (R) Election results establish Republican Party as legitimate national party ► Millard Fillmore (KNP) Sectionalist Presidents James Buchanan (D) (1857-1861) ► “Doughface” Supported KansasNebraska Act Involved himself in Dred Scott decision Lecompton Constitution (Kansas) Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) ► Freeport Doctrine Dred Scott decision and popular sovereignty ► “A house divided against itself cannot stand. I believe this government cannot endure, permanently half slave and half free.” John Brown and Harpers Ferry (1859) ► "I, John Brown, am now quite certain that the crimes of this guilty land will never be purged away but with blood. I had, as I now think, vainly flattered myself that without very much bloodshed it might be done." Election of 1860 Abraham Lincoln (R) ► Stephen Douglas (D) ► ► ► Northern Democrats Southern Democrats Coalition of Cotton Whigs and Know-Nothing John Breckinridge (D) John Bell (CU) Union vs. Confederacy Free and Slave States (1789-1861)