Iran
advertisement

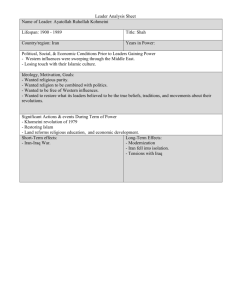
• Historically known as Persia • Persia derived from ancient Greek name for Iran, Persis – Name comes from a region in southern Iran called Pars • 1935, the Shah, Reza Shah Pahlavi, asked for the country to be called by its native name – Iran means “Land of the Aryans” • Known as the Islamic Republic of Iran since 1979 o Tehran is the capital of Iran • The economy is heavily energy based, with oil exports comprising 85% of all export revenues and up to 70% of government income. o World’s second largest oil producer behind Saudi Arabia o World’s second largest natural gas producer behind Russia • Has maintained its own distinct cultural identity in the Islamic world o Most of the population are not descendants of Arabs o Own language—Persian (called Farsi) o Abides by the Shia interpretation of Islam Believe that Mohammad’s son-in-law Ali and his son Hussein are the rightful heirs of Mohammad. Believe that the Koran and the Prophet’s intentions may be interpreted by special clerics who derive their legitimacy from divine appointment, lifelong study, and prayer. • Being a Muslim country, women suffer legal and cultural discrimination, but differ in treatment from the women in other Muslim countries • 94% of all Iranian women attend school and 60% of college graduates are women • Segregation of the sexes from educational institutions is still widely practiced • Some Iranian women who are Muslim wear the chador. o The chador is the black, full-body covering. o It satisfies the requirements of a strict interpretation of hajib or Islamic dress where a woman’s hair and skin must be concealed in public, with the exception of her hands and face. • Others adhere to a minimalist version of hajib, covering only their hair with veils of different color and lengths • Despite their education and relatively good health, women in Iran experience significant discrimination in employment. o Husbands can prevent wives from working o Cannot hold public office above the municipal level and traditionally earn less than their male counterparts in similar jobs. o Only 15% of women are in the working population despite the high rate of them being educated • Iranian women also face discrimination in family matters. – Not only can women be compelled into marriage at age 13, but they also have few rights in the areas of divorce, custody, and inheritance. – Domestic violence generally goes unpunished. A woman’s testimony in court is technically worth just half of a man’s, and a woman may still be stoned for adultery. – Women cannot obtain a passport without the permission of a husband or male relative. • Ta’arof is a system of politeness that includes both verbal and non-verbal communication. o It stems from the cultural obligation to put others, especially guests, if not above all else, at least before oneself. o it is of utmost importance to make the guests feel welcomed. Drastic measures are taken to ensure company's comfort: Saving the best room in the house, delicacies, the most ornate dishes and even fancy beddings for that accidental guest. o For the sake of Ta'arof, a lie is no longer considered a sin when hospitality is the intention. In fact, when an Iranian offers something, they may assure the guest by adding, 'Honestly, I'm not Ta'arofing!' which insinuates that there is some dishonesty in ta'arof? • Mohammad Reza Pahlavi came to power during WWII after an Anglo-Soviet invasion forced the abdication of his father Reza Shah. • After WWII, United States took over Britain’s role as leading foreign player in Iranian politics. • Muhammad Mossadeq became Prime Minister in 1951. • Nationalized the foreign oil companies. • Got rid of corrupt military officials. • Instills distrust and animosity toward Americans (and the west) • Was toppled in a coup aided by the America CIA in 1953. • The Shah of Iran returns to power and the oil once again flowed westward I’m backkk… • In 1963, the Shah attempted to modernize Iran by promoting some democratic and social reforms that became known as The White Revolution. Women’s rights- right to vote, more freedom in divorce, and allowed to wear Western attire. Education- more modern and secular Land- took some of the clergy’s land holdings • The above reforms and undermined the religious leaders authority and were greatly criticized by them. • The United States helped the Shah establish a brutal secret security force (SAVAK) that employed torture and murder to any opponents • Because of the United States involvement with the SAVAK and the Shah, a wave of antiAmericanism spread throughout Iran. The clerics exploited the situation, rallying support from the poor on religious grounds and the wealthy land owners and merchants for financial reasons • The Shah had a number of clerics arrested, while a number of them fled including the Ayatollah Khomeini. • Fled to Iraq and remained there until… • In the late 1970’s, the Shah became extremely unpopular in his own kingdom. Reforms did very little to help the poor. • In September 1978, The Shah instituted martial law because of the widespread unrest in the country. Recession and inflation plaguing the country. SAVAK continued to repress dissidents Shah was fighting a losing bout with lymphatic cancer and was not focused on resolving the issues • Ayatollah Khomeini (in exile) seized the moment to convince Iranians that all the nation’s ill could be traced to sources The Shah’s secular practices and policies Influence of the “ Great Satan” ( the United States) • Khomeini’s solution was to kick the Shah to the curb and give him the power • The Shah knew his days were numbered, so he boarded a plane with his wife and never returned home. • With the Shah gone, Khomeini flew home to Tehran to throngs of adoring fans. • He announced that he would establish the Islamic Republic of Iran • First truly Islamic state in modern history • Reinstitute pure Islam as it was in the golden days of the Prophet Muhammad I’m a ROCK STAR!!! …Wait! I hate the West! • Khomeini set up a theocracy (a government ruled by or subject to religious authority) • Stated that the rest of the regimes in the Muslim world were corrupt because of their relations with the “Great Satan” • He established this Islamic state by rigid enforcement of Iran’s Shiite version of Sharia (Islamic law) • The following measures were implemented: • • • • • Purged Iran of all un-Islamic influences ( ex. Bankinginterest is forbidden) Purged Iran of all Western influences ( ex. Prohibited music and dancing) Enforced the revolution’s new Islamic regulations (streets policed to watch for cultural violations) Persecuted all non-Muslims and secular nationalists Imposed strict regulations on women including the mandatory use of the veil and covered from head to toe • For Westerners, he earned the reputation as an evil Islamic madman that wouldn’t be matched until Osama bin Laden • Khomeini’s regime wanted to put the Shah on trial. • In November 1979, President Jimmy Carter invited the Shah to New York for medical attention. • With Khomeini’s blessing a group of approximately 500 students demonstrated outside the U.S. embassy in Tehran and demanded that the U.S. extradite The Shah. • Your are a CIA agent and your job today is going to examine primary source documents from throughout the crisis in an attempt to reconstruct the event. • In essence you will be working backwards, trying to decipher what documents are more important than others as you construct a debriefing of the event.