Oct 26 to 30 - Cloudfront.net
advertisement

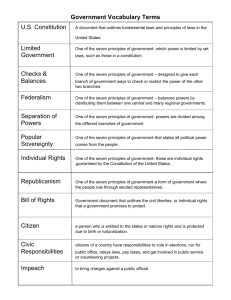
Oct 26 -30, 2015 WOD: • Bill of Rights -individual rights that are guaranteed (1st 10 amendments) • Amendment-a change • Due Process of Law-requires all states to respect the legal rights to all people WARM UP: •Which individual right is MOST important to you & why? • We Will summarize the rights guaranteed in the Bill of Rights • I Will demonstrate the Bill of Rights hand signs • Discuss Bill of Rights in depth-use pages 204-205 • BOK pg. 38 • Teach hand signs Why do you think the Founding Fathers included amendment 2? Bill of Rights 1. Freedom of speech, religion, assembly, petition, and press 2. 3. 4. 5. Right to bear arms No quartering (housing) of soldiers in private houses No unreasonable searches and seizures Due process of law 6. Right to a fair, speedy, and public trial 7. 8. 9. 10. Right to a trial by jury for civil cases No cruel and unusual punishment Rights of the people are not limited to the Constitution All powers not given to the National government are reserved to the state How do the Bill of Rights affect daily life? I Will demonstrate the Bill of Rights hand signs WOD: • Principle-main ideas/basic truth or law Warm Up: • Acrostic Poem Constitution • We Will identify how the U.S. Constitution reflects the 7 principles of government • I Will rank the 7 principles from most to least important and explain why for 1 and 7 • BOK page 36-top • Constitutional Analysis worksheet a system of government where power is shared among the central (or federal) government and the states • Federalism is a system of government in which the states and national government share powers. The Framers used federalism to structure the Constitution. • The Constitution assigns certain powers to the national government. These are delegated powers. • Powers kept by the states are reserved powers. • Powers shared or exercised by national and state governments are known as concurrent powers. the principle that requires all U.S. citizens, including government leaders, to obey the law • In the American government everyone, citizens and powerful leaders alike, must obey the law. Individuals or groups cannot twist or bypass the law to serve their own interests. • Article 1, Section 9, of the Constitution lists the powers denied to the Congress. Article 1, Section 10, forbids the states to take certain actions. • The 10th Amendment reserves for the states and people all powers not given to the national government nor denied to the state governments . a personal liberty and privilege guaranteed to U.S. citizens by the Bill or Rights • The first ten amendments to the Constitution shield people from an overly powerful government. These amendments are called the Bill of Rights. The Bill of Rights guarantees certain individual rights, or personal liberties and privileges. a government in which the people rule; a system in which the residents vote to decide an issue; REFLECTS THE WILL OF THE PEOPLE. • The power to rule comes from the people. • “Consent of the Governed” • The Constitution established popular sovereignty in the preamble, “We the People. . . establish this Constitution for the United States of America.“ REMEMBER WHEN YOU SEE THE TERM POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY YOU SHOULD BE THINKING…….. a belief that government should be based on the consent of the people; people exercise their power by voting for political representatives • Republicanism is based the belief that people exercise their power by voting for their political representatives. • Article 4, Section 4, of the Constitution also calls for every state to have a "republican form of government." • A republic is a form of government in which the supreme power rests in the body of citizens entitled to vote and is exercised by representatives chosen directly or indirectly by them. • In a republic, people elect others to represent them in the government. the ability of each branch of government to exercise checks, or controls, over the other branches • Based on the philosophy of Baron de Montesquieu, an 18th-century French thinker, "Power should be a check to power.“ • Each branch of government can exercise checks, or controls, over the other branches. Though the branches of government are separate, they rely on one another to perform the work of government. • This ensures that the branches work together fairly. the division of basic government roles into branches • Established in order to avoid having too much power might fall into the hands of a single group • This principle creates the division of basic government roles into 3 branches. No one branch is given all the power. • Articles 1,2, and 3 of the Constitution detail how powers are split among the three branches Which principle is the most important? Illustrate each principle to the side of notes • I Will rank the 7 principles from most to least important and explain why for 1 and 7 WOD: • Checks & Balances- system that does not allow any one branch of gov. have too much power • Separation of Power- the division of the 3 branches of gov. WARM UP ON THE NEXT SLIDE • We Will analyze how the U.S. Constitution reflects the 7 principles of government • I Will illustrate the 3 branches of government • BOK page 37-top Separation of Powers • Government Structure Worksheet Legislative, Executive, Judicial Legislative Executive Judicial Congress (Senate & House of Representatives) President Supreme Court Judges Can impeach the President. Write and pass laws. Approves Presidential appointments. Controls money. Declares War. Can veto acts of Congress. Commander of the US military Appoints federal judges. Grants reprieves and pardons for federal crimes Reviews laws. Can declare a law unconstitution al. Can declare executive acts unconstitution al. CW-Create a foldable with the 3 branches of government: Article I: Legislative-Congress (Senate and HoR) Article II: Executive- President, VP and Cabinet Article III: Judicial – Supreme Court and Municipal Courts (also judges) SGPT-tell one major detail of each branch of gov. AP: research 2 elected officials in each branch that currently hold a position and include it in the foldable • I Will illustrate the 3 branches of government • We Will use our GINORMOUS brains to ace Unit 4 Constitution Era test • I Will write a fact about the Constitution on the Parking Lot door • Predict how well you are going to do on your assessment on your TEST DATA TRACKING CHART • Rank and Justify the 3 branches of government OR • Elaborate on the 4 major weaknesses of the A.O.C • We Will review everything we have learned so far in U.S. History • I Will share with my partner 3 major facts I have learned Writing Prompt: • Write about EVERYTHING you have learned so far in US History this year