Introduction to Education
advertisement

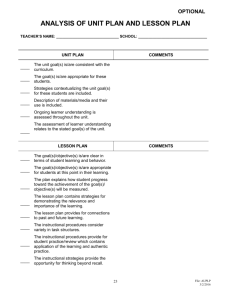
INTRODUCTION TO INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN August 2011 In-Service Information taken from “Real World Instructional Design” by Katherine Cennamo and Debby Kalk. Wadsworth, Cengage Learning. 2005. INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN (ID) What is it? A plan for delivering the content, lessons, and/or activities necessary for students to reach a goal within the curriculum Curriculum – subjects taught or element of the subject at an educational institution Instructional Designers work with Subject Matter Experts to build course content for Instructors. At STI, instructors are both the Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) and Instructional Designers for their subjects ADDIE MODEL BASIC INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN MODEL Analysis – learner needs assessment so know where they may be at and where need to be Design – making objective lists and framing assessments Development – making media, storyboards, instructional materials Implementation – plan and manage delivery of instruction; make teaching support materials Evaluation – Formative and summative evals help identify where revisions needed ESSENTIAL TRIANGLE OF ID Usual order of preparation/considerations: Learners Needs Outcomes and Objectives Assessments Activities Can start with any step, as will be aligning anyway LEARNERS’ NEEDS AND CHARACTERISTICS How do we find out? We usually anticipate informally, but advisory boards and industry help too Learners may not know their learning needs Checklists, Likert Scales, Questionnaires (p. 4) What do they know? Learning Context Peers & Learning Rewards Equipment, Where will they Learn? STI Labs, clinical sites and classrooms are the “where” Application Context Support materials, exercises you develop, labs you make LEARNER NEEDS EXAMPLES Employees have trouble understanding when to use email, phone or in person communication New office professional employees lack soft skills in professionalism and communications Girls need encouragement to enter careers dominated by males PRACTICE What are the learner characteristics of STI employees who need a lesson on email vs phone or personal contact in communications? Generational Skill Level Values Motivations Attitudes Pre-req Skills Needed OUTCOMES, ACTIVITIES AND ASSESSMENTS MUST ALIGN Outcomes detail the results that are desired from the instruction. Activities – enhance learners’ ability to achieve Assessments measure whether those results occurred GOALS, OUTCOMES AND OBJECTIVES Goals are the “big picture” Outcomes give details to translate goals into something measurable Objectives describe the assessment and criteria for acceptable performance Behavior learner will exhibit Conditions under which the behavior must occur Criteria that must be met for acceptable performance • Broad goal statement first, then define specific learning outcomes, then objectives WRITING OBJECTIVES PERFORMANCE TERMS STUDENT is SUBJECT VERB – ACTION Add Modify Solve Analyze Operate Specify Build Organize State Choose Plot Subtract Correct Predict Suggest Defend Prepare Tabulate Demonstrate Present Translate Evaluate Read Verbalize Generate Reconstruct Write Illustrate Revise Label Select Measure Sketch Some are definitely “hands-on”, but what mental processing needs to happen first??? GOAL: TEACHING PRESCHOOL CHILDREN TO CARE FOR EYEGLASSES Learning Outcomes: After participating in the program, youngsters should be able to: Demonstrate the proper way to care for their eyeglasses Choose to care for their glasses properly List the steps in the proper care of glasses Objectives: Using a set of 3 pictures, the learner will order the steps for proper care of their eyeglasses with pictures with 100% accuracy. Given a moistened wipe and eyeglass case, the learner will demonstrate how to clean and store their eyeglasses 2 out of 3 times. Note: Each outcome is different and requires different activities and assessments SAMPLE ASSESSMENTS FOR VARIOUS LEARNING OUTCOMES Outcome Assessment Verbal Information Short Answer, Matching, M/C, Free Recall Intellectual Skills Application in Varied Situations Motor Skills Demonstration Attitudes Determination of New Attitude Frequency Cognitive Strategies Reflective Journal ASSESSMENT TIME TO MAKE, ADMINISTER AND CORRECT Time required to complete and score various Assessments DEVELOPING SCORING KEYS What criteria will you be using to score the work and in what order are you looking for them? To what degree will criteria be met? See Examples on pages 9-11 in Handout Answer Keys Checklists Rating Scales Rubrics LEARNING ACTIVITIES “STRATEGIES” Deliberate arrangement of events to facilitate learning What changes in thinking/performance should occur? How will you know the changes occurred? What activities will help facilitate these changes in thinking or performance? Chunking Content then Develop Learning Events Sequencing Those Learning Events (prioritize & think first) Learning Activities Learning Objects – in online learning, these are the electronic files, links or images that assist in the activities Learning Events EVENTS OF LEARNING & INSTRUCTION Design Sheet on page 15 Focus on goals Connect to prior knowledge Gain and integrate content knowledge Take action and monitor learning progress Synthesize and evaluate Extend and Transfer LEARNING EVENTS PREPARING SALES TEAM FOR NEW PRODUCT LEARNING THEORIES DEFINING THE DELIVERY CONTEXT Delivery Context: Conditions under which the instruction will be delivered Delivery Options and Delivery Modes on Next Slide DELIVERY OPTIONS AND MODES Delivery Options Synchronous vs Asynchronous – learners progress together at same pace or not? Distance vs Face to Face – learners location in comparison to others in class Formal vs Informal – subtle like a museum or structured like a class Delivery Modes Classroom – typical and best for presenting basic skills; easier to develop/deliver Telecourse – video-based distance learning class Teleconference – Interactions with 2-way audio/video Web – synchronous – webinars – no “anytime, anywhere” Print – workbook, supplements Video – Tape or DVD as a self-paced. Expensive if don’t have developing skills. Online – web-based (LMS) discussions; group work CD Rom – media-rich content; reliable; Overcome Internet/download issues Blended Learning Example: Supplement a textbook with a website Most courses use 2 or more delivery modes (use each optimally) BLENDED LEARNING EXAMPLE CHUNKING THE LEARNING INSTRUCTIONAL PACKAGE COMPONENTS WHAT DOES PUBLISHER GIVE ME? Learner’s Materials Lots of Variety in How Packaged Web, print, CD Instructor’s Guides Tips & Lesson Plans Worksheets, Activities Pre and Post Tests Answer Keys Glossary Test Bank Table of Contents Everything to Prepare and Should we use only publisher provided materials? Follow-up with After If instructor alters learning materials, will need to alter these too Licensing and Fair Use –some protection for educators who make copies of copyrighted materials for teaching purposes. How much, and is the copyright holder deprived of royalties if you do so? EVALUATING CURRICULUM AND MATERIALS Formative Evaluation Done before teaching/presenting the first time Who do you get to do this? Summative Evaluation After final product or test has been used With actual learners Develop a system whereby you can note changes for next time On lesson plans? On a copy of the materials? TERMS Activities Answer key Application Context Assessment Asynchronous Attitudes Blended Learning Broad Goal Statement Cases CD Rom Checklist Chunking Content Classroom Cognitive and Physical Abilities Cognitive Strategies Delivery modes Media Assets Motivations Evaluation Motor Skills Extend and Transfer Objectives Formal Instruction Online Formative Evaluation Outcomes Goals Performance based Informal Instruction Portfolio Instructional Design Prior Knowledge and Experiences Instructor Guides Project based Intellectual Skills Rating Scale Interactive Programs Reflections Learner Rubrics Learner’s Materials Summative Evaluation Learning Activities Synchronous Learning Context Synthesize and evaluate Learning Events Teleconference Learning Objects Telecourse Lesson Plans Verbal Information Video Web