2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions
advertisement

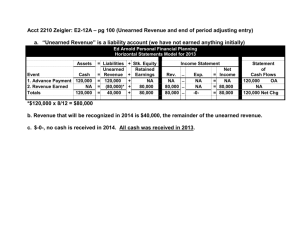
Chapter 2 Income Sources Copyright 2007 Thomson South-Western Types of Earned Income • Wages – Minimum wage – Overtime pay • Salaries • Tips and commissions Some workers make most of their earnings from tips rather than wages. 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 2 Self-Employment • An entrepreneur takes the risks of being selfemployed or owning a business • Advantages – You can make decisions about how to work or run the business – You can keep profits from your work or the business • Disadvantages – Involves high risk – Often requires long work hours 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 3 Employee Benefits • Forms of pay other than wages or salary – – – – – – – Pay without work Educational reimbursement Perks Insurance Retirement plans Profit-sharing and stock option plans Health flexible spending arrangements 2-1 Earned Income and Benefits Slide 4 Unearned Income • Is money received from sources other than working in a job • Is taxable • Comes from private and government sources – Examples from private sources: dividends and interest 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 5 Classification of Types of Income Earned Income Unearned Income Variable Income Salaries and wages Dividends Business profits Commissions Interest Royalties Bonuses Capital gains Rents Professional fees Gambling winnings Tips Alimony Social Security benefits Pensions Annuities Source: Internal Revenue Service, http://www.irs.gov/businesses/small/international/article/0,,id=96811,00.html (accessed March 6, 2006). 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 6 Government Transfer Payments • Money and benefits received from local, state, or federal governments • In-kind transfer payments – Examples: food stamps, rent subsidies, and Medicaid services • In-cash transfer payments – Examples: checks, debit cards, or other direct payments 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 7 Taxes • Are required payments to a government • Are collected from many sources – Examples: income taxes, use taxes, and excise taxes • Are paid on earned and unearned income 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 8 Costs of Paying Taxes • Paying taxes reduces disposable income • Less money is left to spend or save • Lower spending may affect the economy 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 9 Benefits of Paying Taxes • Taxes benefit taxpayers – Example: Social Security tax provides retirement benefits to workers • Taxes benefit all residents – Examples: Highways, parks, government transfer payments Taxes help provide parks for everyone to enjoy. 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 10 Focus on... Social Security Benefits • Workers pay into the Social Security fund and receive a statement each year • Payments are matched by employers • The worker receives monthly benefit checks when retired 2-2 Unearned Income Slide 11 Social Security Tax • Is withheld by the federal government • Provides a system of old-age, survivors, and disability insurance • Requires employers to verify that workers are eligible for employment • Requires workers to complete parts of Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 12 Taxes and Disposable Income • Wages, salaries, and business profits are taxable • Some unearned income is taxable • Lower taxes result in higher disposable income • Higher taxes result in lower disposable income 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 13 Required Deductions • Money withheld from a worker’s paycheck – Examples: income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax • Gross pay minus taxes and other deductions equals net pay 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 14 Sample Paycheck Stub 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 15 Income Taxes • Are withheld according to income amount and exemptions claimed on Form W-4 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 16 Medicare Tax • Is withheld by the federal government • Pays for medical care for retired persons and those who receive Social Security benefits • Is paid by workers and employers 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 17 Workers’ Compensation • An insurance plan • Pays medical and disability benefits to workers who are injured or contract diseases on the job • Laws and programs vary by state • Premiums are paid primarily by employers 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 18 Optional Deductions • Payments for items other than taxes that are subtracted from a worker’s pay – Examples: health insurance, vision insurance, savings plan, and retirement plan Retirement plans allow many retired workers to live comfortably. 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 19 Federal Tax Filing • Whether U.S. citizens must file a federal income tax return depends upon – Gross income – Filing status – Age – Whether you are a dependent 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 20 Tax Forms Form W-2 Used to report the taxable income a worker received during the calendar year Form 1040EZ Designed for use in filing income taxes by single and joint filers with no dependents Form 1040A A two-page form designed for use in filing income taxes Allows more options for income and deductions to be entered Form 1099-INT Shows the interest income earned during the year at one bank 2-3 Taxes and Other Deductions Slide 21