File
advertisement

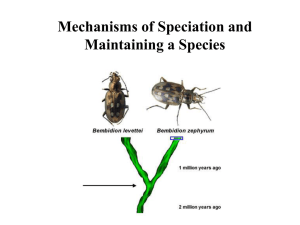
Speciation Outline • Marshmallow Challenge • Speciation Marshmallow Challenge • In science, scientists often work as a team – Able to work with all different people – To do research – Publish papers This activity will test your team-working skills Marshmallow Challenge • Purpose: build the tallest freestanding structure using the materials provided in 15 minutes • Materials: – 20 sticks of pasta – 1 meter of tape – 1 marshmallow Condition: the marshmallow has to be at the very top Species? • What is a species? – Difficult to define – Organisms that can interbreed under natural conditions and produce viable offspring Are lions and tigers the same species? Why? Speciation • Formation of new species • Modes: – Reproductive isolation – Allopatric speciation – Sympatric speciation Mechanisms of Reproductive Isolation • • Must evolve to become reproductive isolated from the original population Reproductive isolating mechanism: – Any factor that prevents two populations from interbreeding when living in the same region 1) Prezygotic mechanisms 2) Postzygotic mechanisms Prezygotic Mechanisms • 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Prevent fertilization and zygote formation Behavioural Temporal Ecological Mechanical Gametic • Behavioural – the behaviours of organisms are not recognized by each other – E.g. mating calls of frogs • Temporal – breed at different times of the year – E.g. flowering times of certain plants • Ecological – species are physically separated thus occupy different areas – E.g. birds that prefer higher or lower elevations • Mechanical – incompatible reproductive organs – E.g. different species of damselflies have uniquely shaped genitalia • Gametic – gametes do not recognize each other – E.g. sperms of clams will not fertilize sea cucumbers’ eggs Postzygotic Mechanisms • Prevent fertilized egg from growing into a viable and reproducing adult 1) Zygotic mortality 2) Hybrid inviability 3) Hybrid infertility • Zygotic mortality – after fertilization, zygote dies – Zygote of sheep and goat is not viable • Hybrid inviability – hybrid develops but dies before birth or cannot survive until maturity – Tigers and leopard hybrids ends in miscarriage or stillborn • Hybrid infertility – hybrid is healthy but infertile – Mules are infertile Examples of hybrids that are fertile! • • • • Wholphin Grizzly-polar bear Cama Coywolf Allopatric Speciation • Formation of new species due to long period of geographic isolation • Gradually become less and less alike – No genetic information exchange – No shared mutations – Experience different natural selection Examples • Finches on Galapagos Islands • Asian elephants – has 4 distinct subspecies Sympatric Speciation • Evolution of populations into separate species in the same geographic area • Example: – Hawthorn flies lay eggs in the fruits of hawthorn trees – After apple trees were introduced, some of the flies would lay eggs in the apples – Today, the species are now consist of two distinct populations Divergent Evolution • Evolution of a group into many forms • All come from a single common ancestor • Rodents: – Deer mouse – Flying squirrel – Porcupine – beaver Convergent evolution • Evolution of similar traits in distantly related species • Can be predicted like divergent evolution • Examples: – Euphorbia and cacti evolved similar features in response to hot, dry environments – Sharks and dolphins evolved similar stream-lined bodies Coevolution • One species evolves in response to the evolution of another species • Example: orchid and moth – Orchid require moth to pollinate the flowers – Moth depends on orchid for nectar – Over time, orchid evolved extremely long tubes and moth developed long tongue – Moth will spend more time obtaining nectar and thus making them more likely to pick up pollen Figure 8 on pg. 344 Homework Questions • Section 7.4: #4-8 • Section 8.2: #1-5 Exit Card • Come up with at least one question that you are not very clear about on speciation. Please make the question and the writing as clear as possible.