white blood cells
advertisement

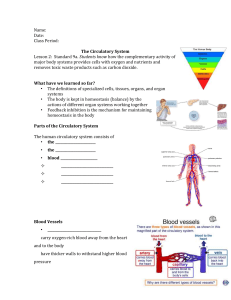
Circulatory System The circulatory system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body Functions of the Circulatory System • The human circulatory system, or cardiovascular system, has the great job of transporting oxygen and nutrients to the organs and tissues of the body, and to carry away waste products. • It regulates the body’s temperature and increases blood flow to meet demands during exercise. • This system also sends parts of the immune system (white blood cells and antibodies) to fight off foreign substances upon their invasion. • Should injury or bleeding occur, it sends clotting cells and proteins to help stop bleeding and promote healing. Major Components • Pump (heart) – Continuously circulates blood • Network of tubes – Arteries- blood away from heart – Veins- blood back to the heart • Blood – Fluid that fills the circulatory system Types of Circulation • Coronary Circulation -the movement of blood through the tissues of the heart • Pulmonary Circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, to the lungs, and returns oxygenated (oxygen-rich) blood back to the heart • Systemic Circulation carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body, and returns deoxygenated blood back to the heart. The flow of blood through the heart to the lungs and back to the heart Coronary circulation Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation The flow of blood to and from the heart Coronary circulation Pulmonary circulation Systemic circulation Click on heart for Pumps Your Blood Song Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Comparison The inside space of a tube Blood Pressure • Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood on the wall of the arteries. • There are two numbers (systolic pressure/diastolic pressure • Systolic pressure is the result of the contraction of the ventricles (normal 110-140) • Diastolic pressure is during the ventricle relaxation (normal 70-90) Functions of the Blood • Carries oxygen from the lungs to the body. • Carries carbon dioxide to the lungs • Carries waste products from cells to the kidneys • Carries nutrients ad other substances to the cells • Cells and molecules in blood fight infection and help heal wounds Parts of the Blood • RED BLOOD CELLS produced in the bone marrow and contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells. • WHITE BLOOD CELLS – fight bacteria, viruses and other invaders of the body • PLASMA – This is the yellowish liquid portion of blood that contains electrolytes, nutrients and vitamins, hormones, clotting factors, and proteins such as antibodies to fight infection. • PLATELETS (Thrombocytes) – irregularly shaped cell fragments that help clot blood. Blood Types Blood Types AA or AO = Type A BB or BO = Type B OO = Type O AB = Type AB Antigen- chemical identification tag on red blood cells Antibodies-found in plasma Destroy or neutralize substances that do not belong. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/blood/types.cfm Blood Transfusion • Who can give you blood? • People with TYPE O blood are called Universal Donors, because they can give blood to any blood type. • People with TYPE AB blood are called Universal Recipients, because they can receive any blood type. • People with Rh + can receive + or • People with Rh - can only receive - RH Factor • Rh Factor is the presence of a specific protein in the blood • It was discovered while studying Rhesus monkeys. • Rh+ means the protein is present in the blood • Rh- means the protein is not present in the blood • This is important in transfusions and in a pregnant women with Rh- carrying a baby with Rh+. • When this happens the blood can clump. Blood Diseases • Anemia-disease of red blood cells -body tissue cannot get enough oxygen. • Causes-not enough iron in the diet; loss of large amount of blood; inherited • Sickle cell anemia- misshaped red blood cells that can clog capillaries • Leukemia-one or more types of white blood cells are made in excessive amounts.