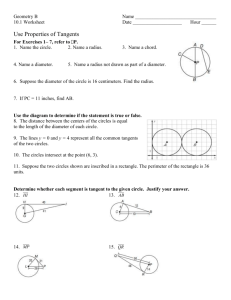
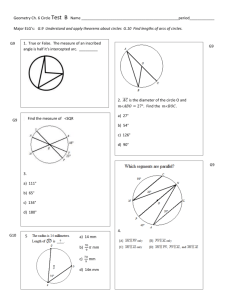
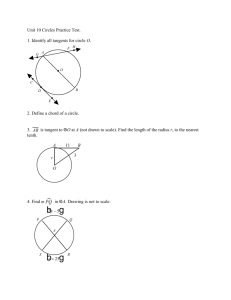
CIRCLES
advertisement

CIRCLES Unit 3-2 Equations we’ll need: Distance formula d x1 x2 y1 y2 2 2 Midpoint formula x1 x2 y1 y2 M ( x, y ) , 2 2 Definitions Circle: Set of all points in a plane that is a fixed distance from a fixed point Center: The fixed equidistance point of the circle Radius: The fixed equidistance length of the circle Circle Equation ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 Center (h, k ) Radius r 2 2 Example 1 Name the center and the radius of this circle, ( x 2)2 ( y 3)2 16 and graph it ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 r 16 r4 2 2 2 c (2,3) r4 Example 1 Name the center and the radius of this circle, ( x 2)2 ( y 3)2 16 and graph it ( x 2) ( y 3) 4 2 c (2,3) r4 2 2 Example 2 Write an equation of the circle with its center at (–3, 5), the radius is 5 and graph it. ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 2 2 Example 3 Name the center and the radius of this circle, x 2 y 2 25 and graph it ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 2 2 YOUR TURN! Graph the equation ( x 3)2 ( y 2)2 9 ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 Example 4 2 2 Find the radius, graph the circle, and write the equation in standard form with the given center of (2, -3) and the point (1, 0). x1 x2 y1 y2 2 d d 2 1 3 0 2 d 1 3 2 2 radius 2 d 1 9 10 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2 radius 2.3 - Circles C 10 ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 Example 4 2 2 Find the radius, graph the circle, and write the equation in standard form with the given center of (2, -3) and the point (1, 0). r 10 C (2, 3) ( x 2) ( y (3)) 2 2 10 2 ( x 2) ( y 3) 10 2 3/23/2016 8:52 PM radius = 10 2 C 2.3 - Circles 11 Example 5 ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 2 2 Write a circle equation whose center is at the origin and passes through (1, –6). 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 12 YOUR TURN! ( x h) ( y k ) r 2 2 2 Write a circle equation whose center is at (1, 0) and passes through (-2, 3) 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 13 Example 6 ( x h) ( y k ) r Write a circle equation whose endpoints of a diameter are (-5, 2) and (3, 6). 2 2 2 x x y y2 MP 1 2 , 1 2 2 5 3 2 6 MP , 2 2 Diameter MP 1, 4 Center 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 14 Example 6 ( x h) ( y k ) r Write a circle equation whose endpoints of a diameter are (-5, 2) and (3, 6). 2 2 MP 1, 4 2 d x1 x2 y1 y2 d 5 (1) 2 4 d 4 2 2 2 2 d 16 4 20 3/23/2016 8:52 PM Radius Center 2 Center 2 2 Radius 2.3 - Circles 15 Example 6 ( x h) ( y k ) r Write a circle equation whose endpoints of a diameter are (-5, 2) and (3, 6). 2 2 2 r 20 C (1, 4) ( x (1)) ( y 4) 2 2 20 2 ( x 1) ( y 4) 20 2 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2 2.3 - Circles 16 d YOUR TURN! x1 x2 y1 y2 2 2 x1 x2 y1 y2 MP , 2 2 ( x h) ( y k ) r Write a circle equation whose endpoints of a diameter are (5, 4) and (-1, -6). 2 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2 2 2.3 - Circles 17 Example 7 Determine the equation of this circle by the graph given 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 18 YOUR TURN! Determine the equation of this circle by the graph given 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 19 Assignment WORKSHEET! 3/23/2016 8:52 PM 2.3 - Circles 20