Presenting
advertisement

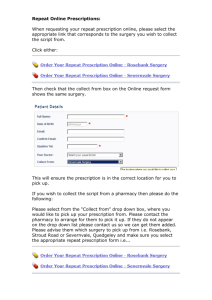
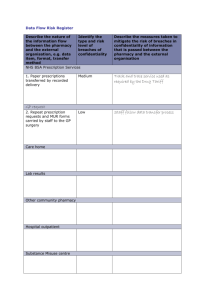
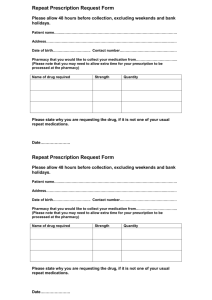
CHAPTER 15 COMMUNITY PHARMACY CHAPTER REVIEW • • • • • • • • • • Community Pharmacy Regulations Organization Customer Service Processing the Prescriptions Preparing the Prescription Customer Pick-up Using a Cash Register Other Duties Review COMMUNITY PHARMACY • The practice of providing prescription services to the public. • Almost 2/3 of all prescriptions drugs in the US are dispensed by community pharmacies. • One of the key characteristics of community pharmacy is the close interaction with patients. TYPES OF COMMUNITY PHARMACIES • Independent Pharmacies – individually owned local pharmacies • Food Store Pharmacies – A&P, Giant Eagle, Kroger, Pathmark and others • Chain Pharmacies – CVS, Walgreens, Rite-Aid and others • Mass Merchandiser Pharmacies – Wal-Mart, Kmart, Costco, Target and others RAPIDLY GROWING ASPECTS OF COMMUNITY PHARMACY • Disease State Management (DSM) • Medication Therapy Management (MTM) • Other Clinical services and Programs DSM • One-on-one pharmacist/patient consultation sessions – General medication advice and information – Diabetes education and monitoring – Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) education and monitoring – Anticoagualtion education and monitoring – Weight loss programs – Smoking cessation programs – Cholesterol reductions programs MTM • Tailored to provisions of Medicare Part D – 5 Core elements • Medication therapy review (MTR) • Personal medication record (PMR) • Medication-related action plan (MAP) • Intervention and/or referral • Documentation and follow-up CLINICAL SERVICES AND PROGRAMS • Walk in clinics staffed with nurse practitioners – Treatment for a limited number of conditions such as colds and minor injuries • Pharmacist or nurse vaccination programs – Influenza – Herpes zoster – Pnuemococcal HOW TECHNICIANS HELP WITH PHARMACY CLINICAL SERVICES & PROGRAMS • Coordinating billing • Scheduling appointments • Taking patient information REGULATIONS: FEDERAL REGULATIONS AFFECTING COMMUNITY PHARMACY • Omnibus Budget and Reconciliation Act (OBRA) • Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA) • Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act (Medicare Part D) • Combat Methamphetamine Epidemic Act (CMEA) REGULATIONS: WHAT STATES REGULATE • • • • • • Counseling Pharmacy technician certification Pharmacist to pharmacy technician ratios Scope of pharmacy technician practice Record keeping Required equipment in a pharmacy and work area requirements • Scope of medication compounding ORGANIZATION • Transaction windows for pick-up and drop-off of prescriptions • Pharmacist counselling area • Drug Storage areas – – – – – – – – – Tablets and capsules Syrups and suspensions Creams, ointments and other topicals Eye ad ear drops Rectal and vaginal preparations Injectibles Inhalers and nebulized medications Locked storage for controlled substances Refrigerated medications ORGANIZATION CONT. • Compounding area – sink • Prescription counter for preparing prescriptions – Counting trays – Vials – Labels • Prescription bins or shelves – Completed prescriptions arranged by customer’s last name CUSTOMER SERVICE • Presenting in a calm, courteous, professional manner – Listening carefully – Making eye contact – Repeating what the customer said – Calling patients by name • Knowing when to involve the pharmacist • Dealing with customer complaints – Positive responses vs. negative responses PROCESSING PRESCRIPTIONS • Prescription In-Take – Patient drop off – Faxed prescriptions – E-prescriptions or electronically transferred prescriptions – Telephone prescription orders ENTERING PATIENT PROFILE INFORMATION • • • • • • Patient name Date of birth Current address Telephone numbers Allergy information Insurance information ENTERING PRESCRIPTION INFORMATION • • • • • • Correct drug and strength Drug quantity Directions for use (the sig) Number of refills Dispense as Written (DAW) code Physician name, address, phone, and DEA number PROCESSING REFILL PRESCRIPTIONS • The prescription number • Availability of refills • Timeliness for refill Filing Hard Copy Prescriptions • By prescription number • By class – General prescriptions (non-controlled substances) – Class III, IV, V controlled substances – Class II controlled substances PREPARING PRESCRIPTIONS FOR DISPENSING • Generating a label • Retrieving the correct medication from stock • Counting or measuring – Using counting trays – Automated filling and measuring devices • Selecting a container – Safety caps – Easy open caps • Affixing the prescription label and auxiliary labels PHARMACIST FINAL CHECK • The final step of the prescription filling process before the prescription is bagged for patient pick up CUSTOMER PICK-UP • Alphabetized prescription bins • Signature logs USING A CASH REGISTER • Scanning a price • Handling payments – Cash – Checks – Credit cards – Gift cards – Coupons ORDERING STOCK • Transmitting drug orders to a drug wholesaler • Receiving drug orders from a drug wholesaler OTHER GENERAL DUTIES OF A PHARMACY TECHNICIAN • Assisting customers with where to find over-thecounter products • Keeping the pharmacy clean, neat and in working order – Cleaning counting trays and countertops – Keeping disposable supplies stocked • Bags, vials and bottles, labels, paper, cash register receipts – Facing stock bottles – Pulling soon to expire stock from shelves SEPARATION OF TRASH • Regular trash • Trash containing protected health information – Shredding or sending out for shredding