PHOTOSYNTHESIS
advertisement

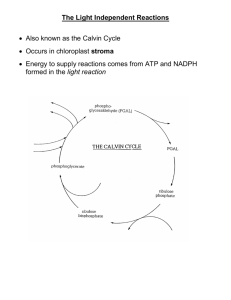
Photosynthesis Reactants Products carbon + water + energy glucose + oxygen dioxide 6CO2 + 6H2O + light C6H12O6 + 6O2 energy Review: Light reactions • Convert solar energy to chemical energy – ATP energy ATP – NADPH electron donator • What can we do now? build stuff !! photosynthesis The second phase of photosynthesis is called the Calvin Cycle (Light-Independent phase) LIGHT-DEPENDENT PHASE (Requires Sunlight) LIGHT-INDEPENDENT PHASE (Does Not Require Sunlight) REMEMBER: This is when the chemical energy produced in the first phase is combine with Carbon Dioxide to create sugar. LIGHT-INDEPENDENT REACTIONS/ Calvin Cycle SUGAR ASSEMBLY- SECOND PHASE The light-INDEPENDENT reactions (or Calvin cycle) use the chemical energy produced in the light-dependent reactions (ATP and NADPH) and carbon dioxide to create sugar. The Calvin Cycle 5 The Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. STROMA (Fluid interior) Carbon Dioxide enters the plant leaf through openings called stomata. THE CALVIN CYCLE At the beginning of the Calvin Cycle, six CO2 molecules bond with six 5-carbon sugar called RuBP (Ribulose Biphosphate) to form an six unstable 6-carbon sugar. (An enzyme called Rubisco is responsible for joining these molecules.) O C C C C O RuBP CARBON DIOXIDE C C C C C C UNSTABLE 6-CARBON SUGAR C C THE CALVIN CYCLE This step is called Carbon Fixation, because a carbon is “fixed” onto the RuBP. O C C C C O RuBP CARBON DIOXIDE C C C C C C UNSTABLE 6-CARBON SUGAR C C THE CALVIN CYCLE (CO2) (RuPB) 6 carbon sugar THE CALVIN CYCLE C C C C C C C C C C C C UNSTABLE 6-CARBON SUGAR PGAs The unstable 6-carbon sugars immediately split to form twelve stable 3-carbon molecules. These molecules are called PGA’s (phosphoglycerate) THE CALVIN CYCLE (CO2) 6 Carbon sugar (RuPB) (PGA) 3 Carbon molecules THE CALVIN CYCLE 12 NADPH and 12 ATP (from the light dependent reactions) then give their energy to turn the 3carbon PGA molecules into PGALs (3-carbon sugars called glyceride tri-phosphate with higher energy bonds). ADP, P, and NADP+ are released and then return to the thylakoid membrane to be re-energized. C C C ADP + ATP C C C NADPH NADP+ C C C C C C 2 PGAL molecules THE CALVIN CYCLE (CO2) 6 carbon sugar (RuPB) 3 carbon molecules (PGA) ATP ADP + NADPH NADP+ (PGAL) 2 PGALs are transferred out of the chloroplast to the cytoplasm of the cell where they are combined to make a six-carbon glucose. (CO2) (RuPB) 6 carbon sugar 3 carbon molecules (PGA) ATP ADP + NADPH NADP+ (PGAL) (2 PGAL) (Sugar) (CO2) (RuPB) 6 carbon sugar 3 carbon molecules ADP + ATP ATP ADP + NADPH NADP+ (PGAL) (PGAL) (Sugar) The ten remaining PGAL molecules each with 3-carbon atoms, reorganize using 6 ATP molecules to make 6 molecules of RuBP (the 5-carbon sugar) to start the cycle all over again. Question 3 A molecule of adenosine that has two phosphate groups bonded to it is ______. A. AMP B. ADP C. ATP D. ACP The answer is B. ADP is adenosine diphosphate. Adenosine P P P Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) P P Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) Adenosine P P Question 4 What is the function of the protein molecule shown in this diagram? ATP Protein P ADP ADP Energy This protein molecule has a specific binding site for ATP. In order to access the energy stored ATP, the protein molecule binds the ATP and uncouples one phosphate group. This action releases energy that is then available to the cell. ATP Protein P ADP ADP Energy Question 6 The function accomplished by the light-dependent reactions is ________. A. energy production B. sugar production C. carbon fixation D. conversion of sugar to PGAL The answer is A. The light-dependent reactions transfer energy from the sun to chlorophyll, and pass energized electrons to proteins embedded in the thylakoid membrane for storage in ATP and NADPH molecules. Sun Light energy transfers to chlorophyll. Chlorophyll passes energy down through the electron transport chain. Energized electrons provide energy that splits H2 O H+ NADP+ bonds P to ADP forming oxygen ATP released NADPH for the use in light-independent reactions Question 7 The first step in the Calvin cycle is the ________. A. replenishing of RuBP B. production of PGAL C. Splitting of six-carbon sugar into two three-carbon molecules D. Bonding of carbon dioxide to RuBP The answer is D. The carbon atom from CO2 bonds with a five-carbon sugar to form an unstable six-carbon sugar. This molecule then splits to form two three-carbon molecules. Photosynthesis Overview copyright cmassengale 25