Calvin Cycle: Carbon Fixation in Photosynthesis
advertisement

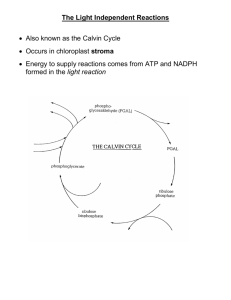
The Calvin Cycle Also known as the dark reaction Carbon Fixation by the Calvin Cycle From the light reaction, NADPH, ATP and oxygen was produced. Carbon fixation: C is bonded, or fixed, into an organic compound Calvin cycle has 3 major steps occurring in the stroma Step One Carbon dioxide diffuses into the stroma from the surrounding cytosol An enzyme combines CO2 with RuBP, a 5 carbon molecule The 6 carbon molecules splits into two 3-C molecules called PGA Step Two PGA is converted into another 3C molecule called PGAL Each PGA gains a phosphate from a molecule of ATP This compound receives a proton (H+) from NADPH, then releases the phosphate group. The resulting NADP+, ADP and phosphate go back to the light reaction Step Three Most of the PGAL is converted back to RuBP by using up a phosphate from ATP, making ADP So RuBP actually begins and ends the Calvin Cycle. Where’d that other Carbon go Some PGAL and other molecules made in the Calvin cycle are used to make amino acids, lipids, and carbohydrates. Carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, sucrose, glycogen, starch, and cellulose. How Many? PGAL is a 3-C molecule, and one turn of the Calvin cycle fixes one carbon, so it takes 3 turns of the cycle to make 1 PGAL. For 3 turns, 9 molecules of ATP and 6 molecules of NADPH are used. Equations + H2O + light energy (CH2O) + O2 CO2 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 light-independent reactions in stroma of chloroplast light-dependent reactions at thylakoids of chloroplast light 12H2O LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS ADP + ATP Pi 6CO2 6O CO2 into leaf O2 out 2 NADP NADPH + PGA CALVIN- PGAL BENSON CYCLE RuBP 6H2O P C6H12O 6 (phosphorylated glucose) end product (e.g. sucrose, starch, cellulose) Fig. 6.17, p. 127 Rate of Photosynthesis Rate is affected by the environment As light increases, the rate increases then levels off. As temperature increases, the rate increases, hits a peak, then declines. As CO2 levels increase, the rate increases then levels off Conclusion and Dark Reaction Chart Location – Stroma, fluid in the chloroplast surrounding the Thylakoid membranes Function – produce carbohydrates, (glucose) Reactants – Carbon Dioxide, RuBP, ATP and NADPH+ Products – Glucose, ADP and NADP