Bio Honors Aerobic Cell Respiration Notes What is the site of
Bio Honors
Aerobic Cell Respiration Notes
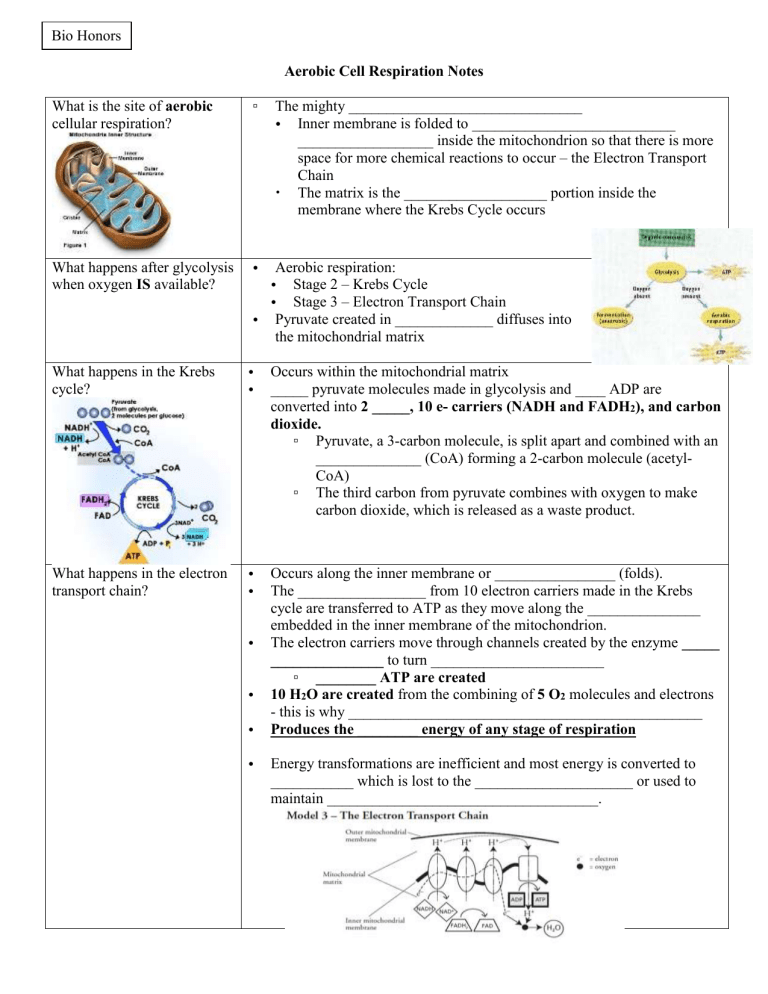
What is the site of aerobic cellular respiration?
▫
The mighty _______________________________
•
Inner membrane is folded to ___________________________
__________________ inside the mitochondrion so that there is more space for more chemical reactions to occur – the Electron Transport
Chain
The matrix is the ___________________ portion inside the membrane where the Krebs Cycle occurs
What happens after glycolysis when oxygen IS available?
What happens in the Krebs cycle?
•
Aerobic respiration:
•
Stage 2 – Krebs Cycle
•
Stage 3 – Electron Transport Chain
•
Pyruvate created in _____________ diffuses into the mitochondrial matrix
•
Occurs within the mitochondrial matrix
•
_____ pyruvate molecules made in glycolysis and ____ ADP are converted into 2 _____, 10 e- carriers (NADH and FADH
2
), and carbon dioxide.
▫
Pyruvate, a 3-carbon molecule, is split apart and combined with an
______________ (CoA) forming a 2-carbon molecule (acetyl-
CoA)
▫
The third carbon from pyruvate combines with oxygen to make carbon dioxide, which is released as a waste product.
What happens in the electron transport chain?
•
Occurs along the inner membrane or ________________ (folds).
•
The _________________ from 10 electron carriers made in the Krebs cycle are transferred to ATP as they move along the _______________ embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
•
The electron carriers move through channels created by the enzyme _____
_______________ to turn _______________________
▫
________ ATP are created
•
10 H
2
O are created from the combining of 5 O
2 molecules and electrons
- this is why _______________________________________________
•
Produces the ________ energy of any stage of respiration
•
Energy transformations are inefficient and most energy is converted to
___________ which is lost to the _____________________ or used to maintain ____________________________________.
Cellular Respiration
Summary
Notice anything about the photosynthesis and respiration equations?
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + ATP
•
In the anaerobic process of _________________ , organic compounds are converted into ________________________, producing a small amount of ATP and e-carriers
•
In aerobic respiration, pyruvic acid is broken down using _________ to produce ________ and _____________, which produces a large amount of ATP
•
This process is ___% efficient (means _____% of the stored energy in your food is used)
_____________________________________________
Comparing Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis
•
Food __________________
•
Energy from _______ stored in glucose
•
CO
2
and H
2
O __________
•
O
2
given off
•
______________ glucose
•
Goes on only in light
•
Occurs ________ in presence of chlorophyll
“The Powerhouse of the Cell” video questions
1. What are the two different types of fibers in skeletal muscle?
2. What makes the “slow twitch” fibers “dark”?
3. How do reserves of mitochondria provide energy for endurance?
Cellular Respiration
Food ___________________
•
Energy of _____________ released
•
H
•
O
2
2
O and CO
2
_____________
taken in
•
___________ glucose
•
Goes on day and night
•
Occurs in _____ living cells
4. What are the three main metabolic pathways?
5. _______________ occurs outside the mitochondria, uses ________ oxygen, and quickly produces only
_______ ATP. It also produces a ____________ that ________ the Krebs Cycle.
6. Both the __________ and __________ happen inside the mitochondria, use _______ and produce as many as _____ ATP.
7. After a minute or two (of exercise), depending on the amount of ___________________ we have, we need to switch into other fuels, fuels that get ______________________ through the mitochondria.
8.
We actually have a ______________ of muscle cells, so in exercise training, we’re ______________ the number of mitochondria.
Modeling Respiration:
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle
ETC
Aerobic Respiration Makes ______ ATP
Reactants
2 ATP
Glucose
2 ADP + P
NAD+
2 Pyruvate e- carriers
2 ADP + P
10 e- carriers
Oxygen
ADP + P
Products
4 ATP
2 Pyruvate
2 NADH
6 CO
2
2 ATP
10 e- carriers NADH and FADH2
Water
32 ATP
Key Questions to study:
1.
Trace the carbon beginning with one glucose molecule all the way through each of the three stages of aerobic respiration.
2.
What occurs when there is oxygen available?
3.
Which pathway creates more ATP: anaerobic or aerobic? Explain why.
4.
What are the inputs and outputs of each stage of respiration?
5.
Where does each stage of cellular respiration occur within the cell?
6.
How efficient is aerobic respiration? What happens to the “lost” energy?




