Chapter
13
Copyright © 2015 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without the prior written consent of McGraw-Hill Education.
Learning Objectives
1. Define programming of and describe the six steps of
2.
Computing Essentials 2015
3.
4.
5.
programming.
Compare design tools including top-down design, pseudocode,
flowcharts, and logic
structures.
Describe program testing and the tools for finding and removing
errors.
Describe CASE tools and object-oriented software development.
Explain the five generations of programming languages.
13-2
Introduction
• In this chapter, you focus on Phase 4, Systems Development, of the
Computing Essentials 2015
systems life cycle and learn about the programming process and some of
the programming languages that are available
• Competent end users need to
understand the relationship
between systems development
and programming
13-3
Computing Essentials 2015
Programs and Programming
Program
A problem-solving procedure
• A list of instructions to
accomplish a task
• Prewritten/packaged
• Custom-made
Programming
• A list of instructions for the
computer to follow to process
data
• Software Development Life
Cycle
Software Development Life Cycle
13-4
Step 1: Program Specification
Computing Essentials 2015
• Also called program definition or program analysis
• Five steps to complete in the process
13-5
Program Specification in Step 1
Computing Essentials 2015
• Program objectives
• Desired output
• Input data
• Processing requirements
• Program specifications document
13-6
Step 2: Program Design
• Plan a solution using structured programming techniques
Top-down design
Pseudocode
Flowcharts
Logic structures
Computing Essentials 2015
•
•
•
•
13-7
Top-Down Program Design
Computing Essentials 2015
• Identify the program modules required
Return
13-8
Pseudocode
Computing Essentials 2015
• Provide an outline of the logic and summarize the program you will write
Return
13-9
Flowcharts
• Graphically present the
Computing Essentials 2015
detailed sequence of steps
needed to solve a
programming problem
Flowchart Symbols
Return
13-10
Logic Structures
• Sequential structure
• Selection structure
• Repetition structure
Selection
Computing Essentials 2015
Sequence
Repetition
13-11
Step 3: Program Code
Computing Essentials 2015
Coding
• Writing the program
• Characteristics of a good program
• Reliable
• Produces the correct output
• Catches common input errors
• Well-documented and understandable
• Structured Programs
• Logic structures
13-12
Coding in Step 3
• Write the program
• Programming
Computing Essentials 2015
languages
13-13
Step 4: Program Test
• Debugging
• Test code
• Eliminate errors
Computing Essentials 2015
• Syntax errors
• Logic errors
• Testing process
13-14
Step 5: Program Documentation
• Written descriptions about a program
• Carried on throughout the programing
steps
• Important for people who will use
Computing Essentials 2015
and/or support the program
• Users
• Operators
• Programmers
13-15
Step 6: Program Maintenance
• 75% of total lifetime cost
• Ensures program is
• Error-free
• Effective
• Efficient
• Two activity categories
Computing Essentials 2015
• Operations
• Patches
• Software updates
• Changing needs
• Agile development
13-16
Case Tools and Object-Oriented Programming
• Computer-aided software
engineering (CASE)
• Automates portions of the
development process
• Object-oriented software –
OOP
Computing Essentials 2015
• Focuses less on procedures,
more on relationships
• Objects contain both the data
and the processing operations
needed to perform a task
CASE Tool: Providing code generation assistance
13-17
Generations of Programming Languages
• Levels or Generations
• Coding from machine languages to human or natural
languages
Computing Essentials 2015
• There are five distinct generations
• Lower level is closer to machine language
• Higher level is closer to human-like language
13-18
Generations of Programming Languages (Cont.)
• 1st Gen: Machine languages
• 2nd Gen: Assembly languages
Computing Essentials 2015
• 3rd Gen: High level procedural languages (3GLs)
• 4th Gen: Task-oriented languages (4GLs)
• 5th Gen: Problem and Constraint languages (5GL)
13-19
Careers In IT
• Computer programmers create, test,
troubleshoot, update and repair programs
• Employers seek individuals with
Computing Essentials 2015
• Degree in Computer Science or
Information Systems
• Desired traits include patience,
logical thinking, and attention
to detail
• Computer Programmers can expect to earn
$49,000 to $89,000 annually
13-20
A Look to the Future ~ Your Own Programmable Robot
• It may not be to much longer
Computing Essentials 2015
before you have your own robot
• Hardware components needed to
create are becoming cheaper
13-21
Open-Ended Questions (Page 1 of 2)
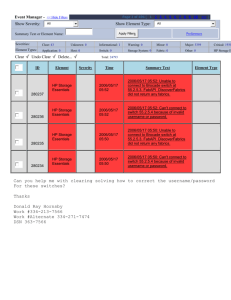
1. Identify and discuss each of the six steps of programming.
Computing Essentials 2015
2. Describe CASE tools and OOP. How does CASE assist programmers?
3. What is meant by “generation” in reference to programming languages? What
is the difference between low-level and high-level languages?
13-22
Open-Ended Questions (Page 2 of 2)
4. What is the difference between a compiler and an interpreter?
5. What are logic structures? Describe the differences between the three logic
Computing Essentials 2015
types.
13-23