Security options and settings Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 connection types
advertisement

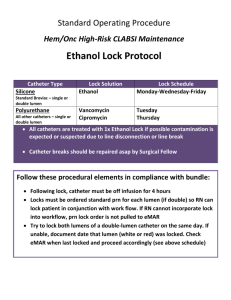
Topics 1. Security options and settings 2. Layer 2 vs. Layer 3 connection types 3. Advanced network and routing options 4. Local connections 5. Offline mode Lock security options – Admin password • The most important one! • The admin user can change all the security settings in the Lock, so the password should be changed from the default Lock security options – MAC/IP filter • Settings -> Industry settings -> Limit LAN traffic to certain MAC or IP addresses • Allowed targets can be specified either using MAC address or IP address • Useful especially in mode A Lock security options – “Do not enter” sign • Prevents new connections towards the Key from Lock’s LAN and other connected devices • Enabled by default and changeable in Edit Tosibox devices Lock security options – Prevent traffic between Sub Locks • Used for isolating Sub Lock networks from each other • Devices in each Sub Lock network can only access the “main” Lock’s LAN and the Internet, but not devices behind other Sub Locks • Helps also performance-wise because it reduces the broadcast traffic that would “leak” between the VPN connections Different connection types • Layer 2 – bridged, site-to-site • Creates a virtual network interface that appears to be residing in the remote network • Can be thought of as having a really long ethernet cable to the remote network • Each remote user gets its own address from the remote network • Works on the data link layer (MAC) • Layer 3 – routed, point-to-point • Tunnel end points have private addresses • Data is routed to the remote network via the remote end of the tunnel • Traffic in the remote network appears to be coming from the Lock device – no additional addresses need to be allocated • Works on the network layer (Internet Protocol) Changing the connection type • • The default connection type is • Layer 2 for Key-Lock connections • Layer 3 for Key-Central Lock connections and Mobile Clients The connection type can be changed in Lock’s web UI by clicking Edit Tosibox devices Advanced network options – Routing Key users’ Internet connection through Lock • Similar to traditional corporate VPN setups • Usually slows down the Internet access a bit • Can be useful for providing access to office/corporate network resources (via WAN) when Lock is deployed in mode B • Or forcing all traffic to go through the company’s proxy or firewall Advanced network options – Access to hosts through WAN • Used for providing access to only selected devices outside Lock’s WAN connection. Settings -> Industry settings • Other traffic (e.g. Internet) is not routed via the Lock Advanced network options – Static routes • Low-level configuration interface for more complex and rare cases • Needed e.g. if there are multiple routers in the LAN providing access to different destinations • Static routes are pushed also to Key users’ computers - requires Layer 3 connection • Configuration at Network -> Static routes Local connections • TOSIBOX Key periodically sends out messages in the local networks (LANs) to discover Locks or Central Locks • When a connection is requested to a Lock/Central Lock located in the same LAN, a direct connection is made locally, without MatchMaking service Offline mode • • It is also possible to disable Internet access in the Lock device so that only local connections are allowed (so-called Offline mode). The administrator can choose to block either: • All Internet access: both inbound VPN connections and outbound Internet access from LAN is blocked • VPN access from Internet (inbound) A temporary exception (timer) can be defined for both, e.g. to allow a technician to get remote access for one hour to perform maintenance work Offline mode • • It is also possible to disable Internet access in the Lock device so that only local connections are allowed (so-called Offline mode). The administrator can choose to block either: • All Internet access: both inbound VPN connections and outbound Internet access from LAN is blocked • VPN access from Internet (inbound) A temporary exception (timer) can be defined for both, e.g. to allow a technician to get remote access for one hour to perform maintenance work