Urine Production
advertisement

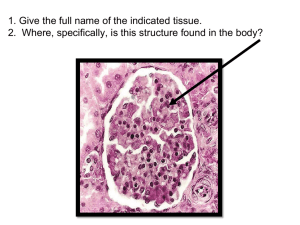
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name ____________________ Pd_____Date_________ Urine Production ❛❛The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.❜❜ Match these terms with the correct statement or definition Filtration, Tubular secretion, Tubular reabsorption ____________________1. Movement of plasma through the filtration membrane of the renal corpuscle. ____________________2. Movement of substances from the filtrate back into the blood of the peritubular capillaries. ____________________3. Transport of substances, usually waste products, into the filtrate. Using the terms provided, complete these statements: Blood cells and proteins, Filtration pressure, Bowman’s capsule, Increases, Decreases, Water, Filtration membrane ____________________1. The filtration membrane allows some substances, but not others, to pass from the blood ____________________2. into(1) (2) and small solutes readily pass through the filtration membrane, but (3) do not enter ____________________3.Bowman’s capsule. The formation of filtrate depends on a pressure difference called (4), which ____________________4. forces fluid from the glomerular capillaries, through the (5) into Bowman's capsule. When ____________________5. filtration pressure increases, the volume of the filtrate (6) , and the urine volume (7) . The ____________________6. filtration pressure is influenced by several factors. If the blood pressure in the glomerular ____________________7. capillaries increases, then filtration pressure (8) . Filtration pressure (9) when strong ____________________8. sympathetic stimulation produces constriction of renal blood vessels during excitement, ____________________9. vigorous physical activity, or emergencies. Also, decreases in the concentration of plasma ____________________10.protein (10) the filtration pressure.. Match these parts of the nephron with the correct function or description: Ascending limb, Distal tubule, Collecting duct, Proximal tubule, Descending limb ____________________1. Sixty-five percent of filtrate is reabsorbed here; proteins, sugars and ions are transported out of the tubule to the peritubular capillaries, and water follows by osmosis. ____________________2. Functions to concentrate the filtrate by removing water and adding solutes; 15 percent of filtrate volume is removed. ____________________3. Functions to dilute the filtrate by removing sodium and chloride ions; not permeable to water. ____________________4. Sodium ions and chloride ions are removed from the filtrate, and water follows by osmosis; 19 percent of the filtrate volume is removed, leaving only 1 percent of original volume. Urine Movement ❛❛The micturition reflex is initiated by stretching of the bladder wall.❜❜ Using the terms provided, complete these statements: Contract Relax, Higher brain centers Spinal cord, Irritation Stretch receptors, Parasympathetic Sympathetic ____________________1. As the bladder fills with urine, (1) in the wall of the bladder are stimulated. Action potentials ____________________2. travel to the (2) through the pelvic nerves, where integration of the reflex occurs. Action ____________________3. potentials then travel through (3) fibers back to the urinary bladder. Parasympathetic ____________________4. action potentials cause the urinary bladder to (4) and the internal urinary sphincter to (5) . Also ____________________5. because of the micturition reflex, action potentials to the external urinary sphincter decrease, ____________________6. which causes the sphincter to (6) . (7) can prevent or facilitate the micturition reflex by sending ____________________7. action potentials through the spinal cord to influence the intensity of the autonomic reflex and ____________________8. stimulate or inhibit the external urinary sphincter. Stretch of the urinary bladder also sends ____________________9. action potentials through afferent fibers to the brain, causing awareness of the need to urinate. ____________________ 10. (8) of the urinary bladder or urethra can also initiate the urge to urinate. Regulation of Acid-Base Balance ❛❛The mechanisms that regulate body pH are critical for survival.❜❜ Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: Bicarbonate buffer system, Protein buffer system, Phosphate buffer system ____________________1. Two that combine with the largest numbers of hydrogen ions. ____________________2. Amino acid side chains function as weak acids or weak bases. ____________________3. Can be regulated by the respiratory and urinary systems. Urine Movement ❛❛The micturition reflex is initiated by stretching of the bladder wall.❜❜ Using the terms provided, complete these statements: Contract Relax, Higher brain centers, Spinal cord, Irritation, Stretch receptors, Parasympathetic, Sympathetic ____________________1. As the bladder fills with urine, (1) in the wall of the bladder are stimulated. Action potentials ____________________2. travel to the (2) through the pelvic nerves, where integration of the reflex occurs. Action ____________________3. potentials then travel through (3) fibers back to the urinary bladder. Parasympathetic action ____________________4. potentials cause the urinary bladder to (4) and the internal urinary sphincter to (5) . Also ____________________5. because of the micturition reflex, action potentials to the external urinary sphincter decrease, ____________________6. which causes the sphincter to (6) . (7) can prevent or facilitate the micturition reflex by sending ____________________7. action potentials through the spinal cord to influence the intensity of the autonomic reflex and ____________________8. stimulate or inhibit the external urinary sphincter. Stretch of the urinary bladder also sends action potentials through afferent fibers to the brain, causing awareness of the need to urinate. (8) of the urinary bladder or urethra can also initiate the urge to urinate. Regulation of Urine Concentration and Volume ❛❛The volume and composition of urine changes, depending on conditions in the body.❜❜ Using the terms provided, complete these statements: Concentrated Increases, Dilute Large, Decreases Small ____________________1. If body fluid concentration increases above normal levels, the kidneys produce a (1) amount of ____________________2. (2) urine, which eliminates solutes and conserves water. This helps to return the body fluid ____________________3. concentration to normal. If body fluid concentration decreases, the kidneys produce a (3) ____________________4. amount of (4) urine. As a result, water is lost and solutes conserved, and body fluid ____________________5. concentration increases. Urine production also maintains blood volume and therefore blood ____________________6. pressure. When blood volume increases above normal, the kidneys produce a (5) amount of ____________________7. (6) urine. The loss of water (7) blood volume and also (8) blood pressure. Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: Ascending limb, Glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, Nephron, Collecting duct, Podocytes, Descending limb, Renal corpuscle Filtration membrane ____________________1. Functional unit of the kidney. ____________________2. Duct into which the distal tubule empties. ____________________3. Enlarged end of nephron; Bowman's capsule and glomerulus. ____________________4. Tuft of capillaries surrounded by Bowman's capsule. ____________________5. Specialized cells that surround the glomerulus and form the inner layer of Bowman's capsule. ____________________6. Composed of glomerular capillary walls, podocytes, and the basement membrane between them. ____________________7. Part of Henle’s loop; very permeable to water and solutes. Place these vessels in the correct sequence that blood would pass through them, from abdominal aorta to renal veins. Arcuate artery, Interlobar artery, Afferent arteriole, Interlobular artery, Efferent arteriole, Peritubular capillaries, Glomerular capillaries, Renal artery 1. Abdominal aorta 5. ____________________ 9. ____________________ 2. ____________________ 6. ____________________ 10. Renal veins 3. ____________________ 7. ____________________ 4. ____________________ 8. ____________________ Urine Production ❛❛The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.❜❜ Match these terms with the correct statement or definition: Filtration, Tubular secretion, Tubular reabsorption ___________________1. Movement of plasma through the filtration membrane of the renal corpuscle. ___________________2. Movement of substances from the filtrate back into the blood of the peritubular capillaries. ___________________3. Transport of substances, usually waste products, into the filtrate. C. Match these terms with the correct parts labeled in figure 18.1: Renal calyx, Renal capsule, Renal cortex, Renal medulla, Renal pelvis, Renal pyramid, Ureter ____________________1 ____________________2 ____________________3 ____________________4 ____________________5 ____________________6 ____________________7 Match these terms with the correct parts labeled in figure 18.2: Collecting duct, Distal tubule, Loop of Henle, Proximal tubule, Renal corpuscle ____________________1 ____________________2 ____________________3 ____________________4 ____________________5