L1_L2Introduction
advertisement

Digital System Design
Subject Name
Course Code
: Digital System Design
: IT- 308
Instructor
: Amit Prakash Singh
Home page : www.worldcircle.org
course Key: ST4EW6F
1
Text-books
1. VHDL Primer by J. Bhasker; Addison Wesley
Longman Pub.
2. Introduction to Digital Systems by M.
Ercegovec, T. Lang and L.J. Moreno; Wiley
3. Digital System Design using VHDL by C.H.
Roth;Jyco Pub
4. Circuit Design with VHDL by Volnei A. Pedroni;
PHI
2
Reference Book
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
VHDL: Analysis & Modeling of Digital Systems by Z.
Navabi; MGH
VHDL Programming by Examples by Douglas L. Perry;
TMH
VHDL by Douglas Perry
The Designer Guide to VHDL by P.J. Ashendem; Morgan
Kaufmann Pub.
Digital System Design with VHDL by Mark Zwolinski;
Prentice Hall Pub.
Digital Design Principles and Practices by John F. Wakerly,
Prentice Hall (third Edition) 2001 includes Xilinx student
edition).
3
Overview
What is digital system design?
– Use of available digital components
• Microprocessor, e.g. Pentium
• Micro-controller, e.g. 8051
• Digital processing units, e.g. counters, shift registers.
– Combine them to become a useful system
4
Programmable logic
vs. microcontrollers in prototyping
• In some situation you can design a digital
system using programmable logic or
microcontrollers
• Programmable logic – more general and
flexible, economic for mass production
• Microcontrollers – more specific and less
flexible, cost more in mass production
5
Introduction
• VHDL is a hardware description language that can
be used to model a digital system
• VHDL is often quoted to be an acronym for Very
High Speed Integration Circuit Hardware
Description Language or VHSIC Hardware
Description Language
• VHDL is an IEEE standard as well as an ANSI
standard for describing digital systems
6
What is VHDL?
• VHDL = VHSIC Hardware Description
Language
• (VHSIC = Very High-Speed IC)
• Design specification language
• Design entry language
• Design simulation language
• Design documentation language
• An alternative to schematics
7
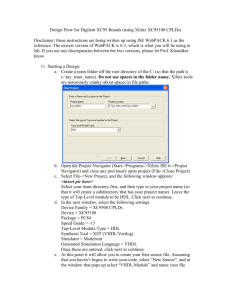
Design Flow
VHDL entry
(RTL Level)
Netlist
(Gate level)
Optimized netlist
(Gate level)
Physical Device
8
Synthesis
• Synthesis is the process of translating a
design from a hardware description into a
circuit design using a components from a
specified library.
• The standard of VHDL Register Transfer
Level Synthesis is available on following
site: http://stdsbbs.ieee.org
9
A Brief History
• Was developed in the early 1980s for managing design
problems that involved large circuits and multiple
teams of engineers.
• Funded by U.S. Department of Defence.
• The first publicly available version was released in
1985.
• In 1986 IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers, Inc.) was presented with a proposal to
standardize the VHDL.
• In 1987 standardization => IEEE 1076-1987
• An improved version of the language was relased in
1994 => IEEE standard 1076-1993.
10
VHDL Environment
11
Domains and Levels of Modeling
Functional
Structural
high level of
abstraction
low level of
abstraction
Geometric
“Y-chart” due to
Gajski & Kahn
12
Domains and Levels of Modeling
Functional
Structural
Algorithm
(behavioral)
Register-Transfer
Language
Boolean Equation
Differential Equation
Geometric
“Y-chart” due to
Gajski & Kahn
13
Domains and Levels of Modeling
Functional
Structural
Processor-Memory
Switch
Register-Transfer
Gate
Transistor
Geometric
“Y-chart” due to
Gajski & Kahn
14
Domains and Levels of Modeling
Functional
Structural
Polygons
Sticks
Standard Cells
Floor Plan
Geometric
“Y-chart” due to
Gajski & Kahn
15
Major Capabilities
• It contains elements that can be used to describe the
behavior, dataflow, and structure of the digital
systems
• It provides support for modeling the system
hierarchically and also supports top-down and
bottom-up design methodologies
• Models written by this language can be verified using
a VHDL simulator.
• The language is not technology-specific
• It supports both synchronous and asynchronous
timing models
• Test benches can be written using the same
language to test other VHDL models
16
Different Representation Models
• Some, Not Mutually Exclusive, Models
– Functional
– Structural
– Physical
17
Basic VHDL Concepts
•
•
•
•
•
•
Interface
Behavior
Structure
Test Benches
Analysis, elaboration, simulation
Synthesis
18
Modeling Interfaces
• Entity declaration
– describes the input/output ports of a module
entity name
port names
port mode (direction)
entity reg4 is
port ( d0, d1, d2, d3, en, clk : in std_logic;
q0, q1, q2, q3 : out std_logic );
punctuation
end entity reg4;
reserved words
port type
19
VHDL-87
• Omit entity at end of entity declaration
entity reg4 is
port ( d0, d1, d2, d3, en, clk : in bit;
q0, q1, q2, q3 : out bit );
end reg4;
20
Modeling Behavior
• Architecture body
– describes an implementation of an entity
– may be several per entity
• Behavioral architecture
– describes the algorithm performed by the module
– contains
•
•
•
•
process statements, each containing
sequential statements, including
signal assignment statements and
wait statements
21
Behavior Example
architecture name of the architecture of name of the entity is
{Declaration section of architecture body}
signal temp1,temp2,temp3 : std_logic;
component name of the component is
port(
);
end component;
begin
statement 1;
x<= sum(function)1;
process()1;
procedure;
process()2;
statement 2;
label : name of the comp port map (connectivity);
label2 : name of the comp port map (connectivity);
end architecture name of the architecture;
22
VHDL-87
• Omit architecture at end of architecture body
• Omit is in process statement header
architecture behav of reg4 is
begin
storage : process
...
begin
...
end process storage;
end behav;
23
Modeling Structure
• Structural architecture
– implements the module as a composition of
subsystems
– contains
• signal declarations, for internal interconnections
– the entity ports are also treated as signals
• component instances
– instances of previously declared entity/architecture pairs
• port maps in component instances
– connect signals to component ports
24