COMPUTER BLOCK DIAGRAM, HARDWARE
DEVICES, SYSTEM SOFTWARE AND
APPLICATION SOFTWARE
1
Manesh T
Faculty In 111charge:
101CS
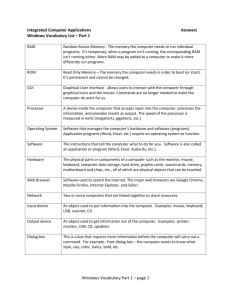
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
Parts of computer system
1. INPUT UNIT
Mouse, keyboard
2. OUTPUT UNIT
Printer, monitor, audio speakers
3. CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
It is the heart of computer system.
All calculations and other operations are performed in this unit.
3 Parts
1. Control Unit (CU)
It controls and coordinates the activities of all other units.
2. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
All the arithmetical and logical activities are performed in the ALU.
3. Registers/Memory
The processor contains special storage locations called registers.
2003 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved.
2
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF COMPUTER
System Unit
Storage
HD
RAM
Registers
CU
ALU
CPU
3
4. STORAGE UNIT
Store processed information
Primary storage unit
RAM,ROM
Secondary storage unit
Hard drives, floppy drives
4
COMPUTER BLOCK DIAGRAM
5
HARDWARE DEVICES
6
IMPORTANT INPUT DEVICES:
Keyboard
Mouse
Other Pointing
Devices
Slide
7
KEYBOARD
Slide
8
THE MOUSE
The mouse is the most widely used pointing device.
A mouse is palm sized.
As the mouse is moved, its movements are mirrored
by the on-screen pointer.
Slide
9
TYPES OF MICE
Wheel
Mouse
Cordless
Mouse
Wheel mouse – Contains a rotating wheel used to
scroll vertically within a text document; connects to
PS/2 port or USB port
Cordless mouse – Uses infrared signals to connect to
the computer’s IrDA port; it must be within sight of
the receiving port
Optical Mouse-
Slide
10
OTHER TYPES OF POINTING DEVICES
Trackball
Touch
Screen
Pointing
Stick
Joystick
Touch Pad
Pen
AUDIO INPUT: SPEECH RECOGNITION
Speech recognition is a
type of input in which the
computer recognizes
words spoken into a
microphone.
Special software and a
microphone are required.
Latest technology uses
continuous speech
recognition where the
user does not have to
pause between words.
Slide
12
DIGITAL INPUT: DIGITAL CAMERAS AND
DIGITAL VIDEO
Digital Cameras
Digital Video
Click on the
picture to play
the video.
Slide
13
ALTERNATIVE INPUT DEVICES
Scanners
Flatbed
Fax Machines
Barcode reader
Slide
14
DIGITAL CAMERAS
The image’s light falls on a charge-coupled device
(CCD) which transforms the light’s patterns into
pixels (individual dots).
Images are stored in the camera using flash memory.
The most popular types are CompactFlash and
SmartMedia.
Photo-editing programs enable the user to edit the
images.
Slide
15
DIGITAL VIDEO
A video capture board transforms analog video into
digital video.
Digital video cameras use digital technologies to
record video images.
A Web cam is a low resolution video camera.
Web cam
Digital video
camera
Slide
16
OUTPUT DEVICES: ENGAGING OUR
SENSES
Output devices are peripheral devices that enable us
to view or hear the computer’s processed data.
Visual output – Text, graphics, and video
Audio output – Sounds, music, and synthesized speech
Slide
17
MONITORS
CRT
LCD
A monitor is a peripheral device which displays
computer output on a screen.
Screen output is referred to as soft copy.
Types of monitors:
Cathode-ray tube (CRT)
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD or flat-panel)
Light Emitting Diode(LED)
Plasma
Slide
18
PRINTERS
A
printer is a peripheral
device that produces a
physical copy or hard
copy of the computer’s
output.
Slide
19
TYPES OF PRINTERS
Inkjet
Laser
20
STORAGE DEVICES
MEMORY VS. STORAGE
Hard Drive – storage
RAM – memory
Storage, also known as mass media or auxiliary
storage, refers to the various media on which a
computer system can store data.
Storage devices hold programs and data in units called
files.
Memory is a temporary workplace where the
computer transfers the contents of a file while it is
being used.
Slide
21
HARD DISKS
Platter
Read/Write
head
Hard disks are high-speed, high-capacity storage
devices.
They contain metal disks called platters.
They contain two or more stacked platters with
read/write heads for each side.
Hard disks can be divided into partitions to enableSlide
22
computers to work with more than one operating
system.
23
IDENTIFY FOLLOWING HARDWARES
EXERCISE
24
MOUSE
25
KEYBOARD
26
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
27
INSIDE CPU
28
MOTHER BOARD
29
RAM (RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY)
ROM (READ ONLY MEMORY)
30
HARD DISK
31
VIDEO CARD
32
PROCESSOR
33
BLUETOOTH CARD
34
SOUND CARD
35
NETWORK CARD
36
CD/DVD DRIVE
37
WEB CAMERA
38
SCANNER
39
PRINTER
40
JOY STICK
41
MICROPHONE AND SPEAKERS
42
SOFTWARE
Software: Software is a set of programs
Basic
applications
Specialized
applications
43
1. APPLICATION SOFTWARE
Definition
Application software is end user software that
is used to accomplish a variety of tasks
Example: MS word, MS Excel, MS PPT, etc…
44
SYSTEM SOFTWARE
Master program
Controls all hardwares connected to computer
Collection of programs
Application
software
Operating
System/
system
software
Users
Hardware
45
Application
Software
Computer/ System
Software
Interaction:
Users always interact
with application
software while doing
different activities.
Generally, users do not
interact with system
software as it works in the
background.
Dependency:
Application software
cannot run without the
presence of the system
software.
System software can run
independently of the
application software.
46
SESSION 3
END
47