Nursing Care of Clients with Gallbladder, Liver and Pancreatic
advertisement

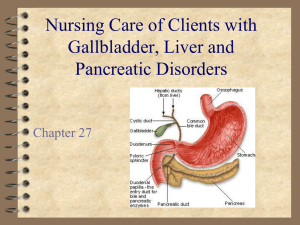
Nursing Care of Clients with Gallbladder, Liver and Pancreatic Disorders Chapter 27 Liver, Gallbladder and Pancreas Gallbladder Disorders Cholelithiasis and Cholecystitis Patho – gallstones form due to • abnormal bile composition • biliary statis • inflammation of gallbladder Risk factors – age, family hx., females - oral contraceptive Gallbladder Disorders Cholelithiasis Acute cholecystitis asymptomatic RUQ pain - back epigastric fullness after fatty meal a/n/v biliary colic jaundice fever with chills Gallbladder Disorders Treatment – laparoscopic cholecystectomy Nursing Diagnoses – Pain – Imbalanced Nutrition – Risk for Infection Let’s Review Liver Hepatitis Liver Disorders Hepatitis – inflammation of the liver due to virus, ETOH, drugs, toxins, may be acute or chronic Viral Hepatitis Hepatitis A - infectious hepatitis – fecal-oral route – benign, self-limiting Liver Disorders Hepatitis B – transmission - infected blood and body fluids • at risk - healthcare workers, drug users, multiple sexual partners, hemodialysis clients Hepatitis C – transmission - infected blood and body fluids – manifestations - mild, non-specific – world wide cause of chronic hepatitis Hepatitis Worldwide Liver Disorders Disease pattern – incubation – prodromal – icteric – convalescent Liver Disorders Nursing Care – teaching • handwashing • blood and body fluid precautions • vaccines for persons at high risk Advanced Cirrhosis Liver Disorders Cirrhosis – end state of chronic liver disease, progressive and irreversible • alcoholic cirrhosis, biliary, or secondary to hepatitis – Manifestations • liver enlg. Tender, wt loss, weakness, anorexia • ascites, gynecomastia, jaundice, edema, anemia, pancytopenia Liver Disorders Complications – portal hypertension – splenomegaly – ascites – esophageal varices – hepatic encephalopathy – hepatorenal syndrome What are your assessments, interventions? What are your goals? How would you chart this? Systemic effects of Cirrhosis Liver Disorders Liver Cancer – usually poor outcomes Liver Trauma – blunt or penetrating - hemorrhage Liver Abscess Hepatitis Nursing Care? Teaching needs? Complications? Pancreatitis Pancreatitis Pancreatitis – inflammation of pancreas characterized by release of pancreatic enzymes into pancreatic tissue itself leading to hemorrhage and necrosis Risk factors – alcoholism, gallstones Pancreatitis Manifestations – abrupt onset of severe epigastric/abdominal pain • relieved by leaning forward, sitting up • initiated by fatty meal or alcohol intake – n/v – abd. distention and rigidity, decreased b.s. – fever, 24 hours later jaundice Pancreatitis Pancreatitis Diagnostic tests – labs - amylase and lipase – Ultra sound, ERCP, C-T scan, needle bx Treatment – hydration, pain control and antibiotics Pancreatic Cancer Pancreatic Cancer Very lethal Risk factors – smoking, chemical or environmental toxins Manifestations – non-specific, a/n, wt. loss, dull epigastric pain Treatment – surgery - Whipple, radiation and chemotherapy