Comprehension and Fluency
advertisement

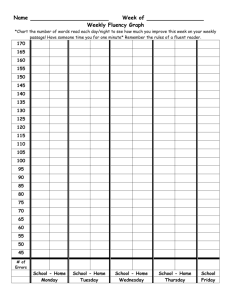
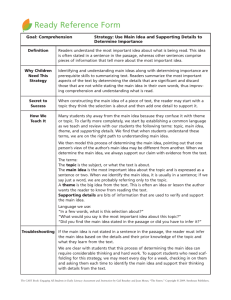
Comprehension and Fluency A house without books is like a room without windows. -Horace Mann Is Reading Still Important in the Video Age? The more you read, the more you know. The more you know, the smarter you grow. The smarter you are, the longer you stay in school. The longer you stay in school, the more diplomas you earn and the longer you are employed thus the more money you earn in a lifetime. The more diplomas you earn, the higher your children’s grades will be in school. The more diplomas you earn, the longer you live. The opposite would also be true: The less you read, the less you know. The less you know, the sooner you drop out of school. The sooner you drop out, the sooner and longer you are poor. The sooner you drop out, the greater your chances of going to jail. Some ways to have good conversations with your child: Encourage him to talk about what he is reading at school as well as at home; Also ask about the writing he is doing at school and/or at home; Share stories about your childhood and stories about other family members; Play word games. Talk with your child about the television programs he views; Ask your child his opinion about a variety of public issues; Encourage your child to make up stories to tell you; After your child tells you a story, ask him how he would change something in the story to make it different; Talk with your child about how the day went for him. The possibilities are endless! Reading At Home Hear the flow of language; Hear words that may be new to them and thus help to expand their vocabulary Get a chance to talk to you about the story that they may not be able to read by themselves; Expand their knowledge of the world; Simply enjoy hearing you read. Reading and Comprehension Reading refers to the ability to comprehend or make meaning from written text. What does it mean to comprehend? Definition: Reading comprehension is the construction of the meaning of a written communication through a reciprocal, holistic interchange of ideas between the interpreter and the message. Harris and Hodges Why is background knowledge key? Background Knowledge - What is it? Mike Piazza and Robin Ventura singled to start the eighth inning. After a Braves pitching change to bring in Mike Remlinger, Melving Mora-first of a series of pinch hitters- came to the plate for Benny Agbaynani. Mora bunted, moving Piazza and Ventura over. Kallis and Rhodes put on 84 but, with the ball turning, Mark Waugh could not hit with impunity and his eight overs cost only 37. The runs still had to be scored at more than seven an over, with McGrath still to return and Warne having two overs left, when Rhodes pulled Reiffel to Beven at deep square leg. Making Connections Text to Self Text to Text Text to World Show Your Child Your Connections Three-Level Taxonomy of Comprehension Literal Comprehension Lowest level Requires the reader to be able to retell of recall the facts Inferential Comprehension Refers to the ability of a reader to take in information that is implied within a text Requires the orchestration and manipulation of information Critical Comprehension Highest level in the taxonomy Involves making critical judgments about the information presented in the text Narrative Retelling Setting: When and where does the story take place? Characters: Who are the people in the story? Can you describe them? Plot: What is the story about? Events: What happened in the story? First, next, after that… How and why? Problem: What was the problem in the story? Solution: Was the problem solved? How? Theme: What do you think __ learned in the story? Why do you think author wrote the story? Connections: Does this story remind you of any other stories or a personal experience? Fluency Instruction Fluency is the ability to read a text accurately and quickly Fluency is important because it frees students to understand what they read Reading fluency can be developed by modeling fluent reading by having students engage in repeated oral reading More fluent readers: focus their attention on making connections among the ideas in a text and between these ideas and their background knowledge. Therefore, they are able to focus on comprehension. Less fluent readers: must focus their attention primarily on decoding individual words. Therefore, they have little attention left for comprehending the text. Independent level text Relatively easy text for the reader, with no more than approximately 1 in 20 words difficult for the reader (95 %) Instructional level text Challenging but manageable text for the reader, with no more than approximately 1 in 10 words difficult for the reader (90 % success) Frustrated level text Difficult text for the reader, with more than 1 in 10 words difficult for the reader (less than 90% success) How can I help my child become a more fluent reader? To understand a line or phrase that is difficult To get ready to talk about the book To follow a thread throughout the book To support a theory or prediction To study the author’s craft To think through an opinion about an issue in the text To think about how a word relates to others in the same genre par·ent·ing (pâr΄әn-tǐng) , n. 1. The most difficult and most important job you will ever have. 2. And, potentially, the most rewarding. A Village We have to work together in order for our children to grow and succeed so that they may become college and career ready.