Chapters 12 thru 16 - the CLC Faculty and Staff Web Pages
advertisement

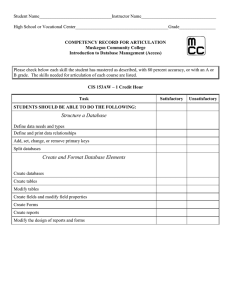
Review for Test 4 Chapters 12 and 13 – Information System and Application Development Information systems consist of hardware, software, data, people, and procedures MS .NET Framework and Sun/Oracle Java both provide virtual machines and thus are portable Java applets run inside webpages and often provide animation on these web pages Object-oriented development encapsulates both state (data or attributes) and behavior (methods or functions or processes) which manipulates the state Expert Systems are one aspect of AI and consist of 3 major components: knowledge base (rules and data), inference engine, and a user interface (to ensure knowledge transfer) AI uses neural networks as a mechanism similar to the human brain System Types – Office – o Document Management System o Content Management System o Communication System Transaction Processing System o Non-management users typically o Deals with action right now o Provided biggest bang for the development buck o Payroll, inventory control examples Management Information Systems o Short range – hour, day, week, month o Intended for low to middle management for controlling purposes o Often uses planned reports, queries, forms Decision Support Systems o Intended for middle to upper level management o Planning purposes o Uses statistical packages o Often done on data warehouse corporate data rather than transaction processing systems Executive Information Systems o Adds external data sources to DSS above System Development Life Cycle – provides checkpoints for the current phase and documentation for the next phase Preliminary investigation – feasibility System Analysis – determining the what System Design – determining the how System Acquisition – make or buy Implementation – deliver installation package, conversion, documentation John North 1 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Maintenance – fix broken items and gather information for next release Conversions are done Direct Parallel Phased Pilot Programs written in specialized languages – programming languages Statements must follow rules that constitute valid statements – the syntax of a programming language invalidly constructed program statements are considered syntax errors and logic errors occur when what was expected did not occur Programs have three types of control structures Sequential flow statements Selection or decision statements – if and select case Repetition or looping statements – while, for Program development uses an integrated development environment that provides for Editor to record program instructions Compiler to convert a specific programming language into machine code or intermediate language (.NET and Java for their virtual machines) Linker to combine programmer’s code with code from libraries or assemblies Loader to load program for testing Test generators to develop and run tests Debuggers to help isolate programming logic errors Interpreters convert one line of code at a time to executable machine code while a compiler converts the whole program into object code that will be executed as machine code when the program is run Interpreters good for debugging code Compilers can optimize code Language generations 1. Machine code 2. Assembly languages – intro to mnemonics for instruction codes and variable names for memory addresses Note: Machine code and assembly languages are referred to as low-level languages 3. Third generation languages – process oriented or functional decomposition Cobol, Fortran, PL/1, Pascal, Basic, C Object-oriented languages mistakenly included in this generation – Smalltalk, C++, Java, C#, Objective-C, Python 4. Fourth generation languages – generative languages especially DBMS software such as forms, queries, and reports to access databases Web based programs developed with Dreamweaver or MS Expression Web Specialized 4th generation languages – Progress, Focus John North 2 CIT120 Review for Test 4 5. Fifth generation languages – logic based Prolog, LISP, Scheme, Expert Systems, Automated Reasoning Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) deals with an application from creation to shelving Patches are sent out to fix bugs, security leaks, or misinterpreted procedures John North 3 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Chapter 14 – Databases Databases built to provide sharing of data Evolution of structured databases – hierarchical, network, relational, object-oriented, multi-dimensional The Web has made unstructured data more common today, primarily through its search engines Database consists of fields collected into a record, records collected into a table, tables collected into a database Fields in structured databases require both a field name and a data type Database data types include text, memo, number, autonumber or autoincrement, boolean or yes/no, date/time, objects, hyperlinks, attachments, and lookup Numbers include both integer – byte, integer, long decimal – single, double, decimal currency Tables are almost always given a primary key – a field or collection of fields that can uniquely define a record Secondary keys are used to speed up searches and sorting of data Database designers use normalization to remove redundancy from the data tables Desktop to small workgroup databases include the dominant MS Access, Corel Paradox, and Lotus Approach, and Open Office Base Enterprise databases include dominant Oracle, IBM’s DB2 and Informix, MS SQL Server, Sybase, CA’s Ingres, open source MySQL and Postgres Queries are questions posed to the database looking for specific data that meet certain criteria People involved in databases include Data architects Data analysts Database administrators Application Programmers Users DP Director Database types Single user Client – server Multi-tiered Distributed – needs replication of shared data John North 4 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Moving from one version to another or changing database management software forces use to migrate the data from the old to the new database. John North 5 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Chapter 15 – Protection and Privacy Brownouts and blackouts Surge protectors, uninterruptable power supplies (UPS), and generators Dropping, spilling liquids, dust, static electricity Protecting the physical computers for individuals as well as data centers Ruggedized PCs – OLPC’s XO computer for kids in developing countries Green computing and the energy star rating scheme Specialized software for recovery of lost or stolen PCs Clearing a browser’s cache when working on a public computer Taking care of spam and spyware – Internet security packages, email filters Vaporware – software that never made it off the drawing boards Encryption software for files, logical disks, whole disks Wiping data off a disk drive removes any trace of it Information privacy – the rights of individuals or companies to control how information about them is collected and used. Electronic profiling of a person – marketing Identity theft Presence technology Digital surveillance Employee monitoring –employers tracking employee activity on the job Proximity cards – uses smart cards or RFID enabled cards to track location as well as video surveillance Throw-away email address for junk mail Besides backup/recovery procedures, companies need disaster recovery planning Off-site storage of critical data Recovery facilities – within organization or specialized companies John North 6 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Chapter 16 – Intellectual Property Copyrights – good for 70 years after person’s death Google books Project Gutenburg Digital watermarks Anticounterfeiting systems Holograms Traceless – system using invisible chemical markers that DRM software Trademarks: Registered, trademark, servicemark – good for 10 years but can be renewed Patents – most are good for 20 years can be read by special device Domain name squabbles can use WIPO (World Intellectual Property Organization) to resolve Plagiarism Fair use of copyrighted material – commentaries, news reporting, research, education Ethics vs law Code of conduct – written rules on what can and cannot be done Code of ethics – usually industry or organization based rules – Engineers, lawyers, doctors Whistle blowers Cheating and falsifying information Cheating is rampant; MBAs lead the way Resume padding vs Job requirements padding Computer hoaxes Digital manipulation Doctored photos US Gov releases new cash bills every 7 to 10 years to prevent counterfeiting Ethical Business practices Fraudulent reporting Pulling up sales Ethically questionable products Age verification Vaporware Workplace monitoring Cultural considerations Digital divide occurs in both developed and developing countries OLPC is attempting to address the digital divide through its XO computer for children; Intel is providing the Classmate computer as an alternative to the XO John North 7 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Ergonomics Repetitive Stress Syndrome and carpal tunnel syndrome Stress, burnout, addiction are emotional concerns with computer usage Green computing Energy Star rating More energy efficient processors, monitors Alternative energy – solar energy, fuel cells Getting rid of computer hardware and software Increased paper use e-trash - Toxic material needs to be recovered Assistive technologies provide accessibility to computers for users with disabilities Being driven by the Americans with Disabilities Act Legislation US Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act Digital Millennium Copyright Act – illegal to bypass DRM protection John North 8 CIT120 Review for Test 4 Access DB vs DBMS Structure – field, record, table, database Critical Objects o Table Fields and data types Text vs memo Number – byte, integer, long integer, single, double, currency Boolean (yes/no) OLE objects Attachments, hyperlinks Indexes Primary key – key symbol o Composite or concatenated Secondary keys Foreign keys Properties Validation rules and messages Default values Required fields Format / masks o Relationships 1-1, 1-M, M-M Intersection table Referential integrity Cascade update/delete o Forms – one record at a time Single record at a time Master / Child forms Hybrid forms o Queries – answering a question about the data Joins Aggregate (Totals) Wildcards - * and ? Criteria Parameterized queries o Reports Formalized tables and queries Detail / Summary Calculated fields Group breaks John North 9 CIT120