Outer planets
advertisement

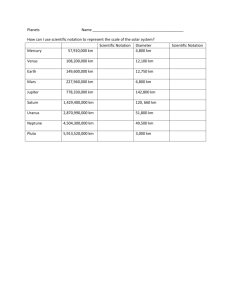
Bell work Every planet that has an atmosphere has weather. Jupiter's Great Red Spot appears to be very similar to a hurricane system on Earth, but it has lasted for centuries, driven by the planet's internal thermal energy. Write a humorous but accurate weather forecast for one of the outer planets that has an atmosphere. Write your report in your science journal, but be prepared to present it to the class. Outer planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Objectives for today! Explain how gas giants are different from terrestrial planets. Describe the individual characteristics of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Jupiter Distance from sun43.3 light-minutes Period of rotation9 h, 54 min Period of revolution11 years, 313 days Temperature−110°C oGravity-236% of Earth's Jupiter Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system. Like the sun, Jupiter is made mostly of hydrogen and helium. The outer part of Jupiter's atmosphere is made of layered clouds of water, methane, and ammonia. At a depth of about 10,000 km into Jupiter's atmosphere, the pressure is high enough to change hydrogen gas into a liquid. Deeper still, the pressure changes the liquid hydrogen into a liquid, metallic state. Jupiter Unlike most planets, Jupiter radiates much more energy into space than it receives from the sun. The reason is that Jupiter's interior is very hot. Another striking feature of Jupiter is the Great Red Spot, a storm system that is more than 400 years old and is about 3 times the diameter of Earth! Distance from sun 1.3 light-hours Period of rotation 10 h, 42 min Period of revolution 29 years, 155 days Diameter 120,536 km Temperature −140°C Gravity 92% of Earth's Saturn Saturn Saturn is the second-largest planet in the solar system. Saturn has roughly 764 times the volume of Earth and is 95 times more massive than Earth. Its overall composition, like Jupiter's, is mostly hydrogen and helium. But methane, ammonia, and ethane are found in the upper atmosphere. Saturn's interior is probably much like Jupiter's. Saturn Also, like Jupiter, Saturn gives off much more energy than it receives from the sun. Scientists think that Saturn's extra energy comes from helium falling out of the atmosphere and sinking to the core. In other words, Saturn is still forming! Although all of the gas giants have rings, Saturn's rings are the largest. Saturn's rings have a total diameter of 272,000 km. Yet, Saturn's rings are only a few hundred meters thick. The rings are made of icy particles that range in size from a few centimeters to several meters wide. Objectives for today! Explain how gas giants are different from terrestrial planets. Describe the individual characteristics of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Uranus Distance from sun 2.7 lighthours Period of rotation 17 h, 12 min (R) Period of revolution *83 years, 273 days Diameter 51,118 km Temperature −195°C Gravity 89% of Earth‘s Uranus Uranus was discovered by the English amateur astronomer William Herschel in 1781. The atmosphere of Uranus is mainly hydrogen and methane. Because these gases absorb the red part of sunlight very strongly, Uranus appears blue-green in color. Uranus and Neptune have much less mass than Jupiter, but their densities are similar. This suggests that their compositions are different from Jupiter's. They may have lower percentages of light elements and a greater percentage of water. Uranus A Tilted Planet Unlike most other planets, Uranus is tipped over on its side. So, its axis of rotation is tilted by almost 90° and lies almost in the plane of its orbit. For part of a Uranus year, one pole points toward the sun while the other pole is in darkness. At the other end of Uranus's orbit, the poles are reversed. Some scientists think that early in its history, Uranus may have been hit by a massive object that tipped the planet over. Neptune Distance from sun 4.2 lighthours Period of rotation 16 h, 6 min Period of revolution163 years, 263 days Diameter 49,528 km Temperature −200°C Gravity 112% of Earth's Neptune Irregularities in the orbit of Uranus suggested to early astronomers that there must be another planet beyond it. They thought that the gravity of this new planet pulled Uranus off its predicted path. By using the predictions of the new planet's orbit, astronomers discovered the planet Neptune in 1846. Neptune The Atmosphere of Neptune The Voyager 2 spacecraft sent back images that provided much new information about Neptune's atmosphere. Although the composition of Neptune's atmosphere is similar to that of Uranus's atmosphere, Neptune's atmosphere has belts of clouds that are much more visible. At the time of Voyager 2's visit, Neptune had a Great Dark Spot like the Great Red Spot on Jupiter. And like the interiors of Jupiter and Saturn, Neptune's interior releases thermal energy to its outer layers. This release of energy helps the warm gases rise and the cool gases sink, which sets up the wind patterns in the atmosphere that create the belts of clouds. Voyager 2 images also revealed that Neptune has a set of very narrow rings. Objectives for today! Explain how gas giants are different from terrestrial planets. Describe the individual characteristics of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto.