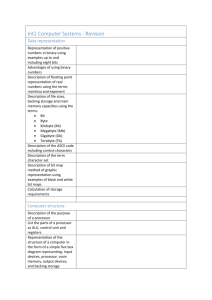
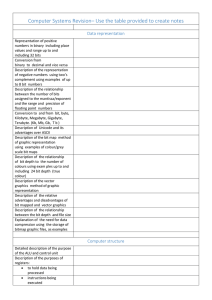
System Software
advertisement

System Software CS 1308 Computer Literacy and the Internet Introduction Von Neumann computer “Naked machine” Hardware without any helpful user-oriented features Extremely difficult for a human to work with An interface between the user and the hardware is needed to make a Von Neumann computer usable 2 System Software: The Virtual Machine System software Acts as an intermediary between users and hardware Creates a virtual environment for the user that hides the actual computer architecture Set of services and resources created by the system software and seen by the user 3 Figure 6.1 The Role of System Software 4 BIOS Basic Input/Output System The first piece of software that starts when the computer is turned on Stored in Flash Memory Power-on Self-test (POST) makes sure that all the system components are running properly (e.g. RAM check) Gets the keyboard, mouse, and other peripherals started Finds the “Boot” device and starts the operating system For more information (Google “How does the BIOS work”) 5 Types of System Software System software is a collection of many different programs Operating system Controls the overall operation of the computer Communicates with the user Determines what the user wants Activates system programs, applications packages, or user programs to carry out user requests 6 Functions of an Operating System Five most important responsibilities of the operating system User interface management Program scheduling and activation Control of access to system and files Efficient resource allocation Deadlock detection and error detection 7 The User Interface Operating system Waits for a user command If command is legal, activates and schedules the appropriate software package Types of User interfaces Text-oriented – DOS, Unix, Linux Graphical – Mac, Windows, Linux Hybrid – Cell phones, digital cameras, PDAs Embedded –Microwave ovens, cars, etc. 8 System Security And Protection The operating system must prevent Unauthorized people from using the computer User names and passwords Legitimate users from accessing data or programs they are not authorized to access Authorization lists 9 An OS provides security, e.g. against viruses! 0 Microsoft Word The virus code overwrites other programs in memory. Microsoft Word Doom the virus code Doom DOS OS DOS OS Shareware Game 16M 10 When an “infected program” is run, the program counter (PC) might take the value of the first address of the virus code. Should this happen, the virus code will be executed. Memory How might the OS prevent this? Shareware Game Memory Efficient Allocation Of Resources The operating system ensures that Multiple tasks of the computer may be underway at one time Processor is constantly busy Keeps a “queue” of programs that are ready to run Whenever processor is idle, picks a job from the queue and assigns it to the processor Memory and secondary storage devices are used efficiently. 11 An OS Allocates Resources Efficiently: It’s easy for an OS that supports a single user running a single program bus Doom Word Windows Netscape JAVA SPSS disk 12 ALU PC registers memory CPU Peripherals: •monitors •printers •network connections •etc. 1. User tells OS to execute program 2. OS finds the program on disk 3. OS copies the program into memory 4. OS initializes the PC to the beginning of the program 5. Program monopolizes all computer resources This wastes computer resources Input and Output are very slow Disk and peripherals are 10,000x slower than the CPU The user (typing on the keyboard) is even slower! CPU time is wasted while waiting for them During this time, CPU could be executing other programs! 13 Multitasking Although it seems like your computer is running many programs at once, including the OS, it is not. Your computer runs a bit of one program before switching to another. And then switching again, often because it is waiting for I/O. Because your computer is very fast, it seems like they are all running at the same time. 14 The Future Operating systems will continue to evolve Possible characteristics of fifth-generation systems Multimedia user interfaces Parallel processing systems Completely distributed computing environments – possibly over the internet (cloud computing) 15 Summary System software acts as an intermediary between the users and the hardware Your computer would be useless without an operating system and system software. 16