1948 US Presidential Election
advertisement

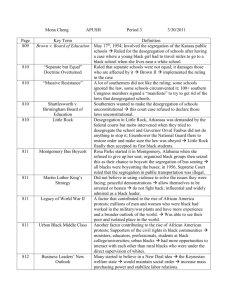
1950s TX: Political Changes Essential Questions: – Analyze the political, economic, and social impact of political controversies such as desegregation and communism – Identify the different points of view of political parties in the 1950s Political Parties Divide After WWII, Republicans and Democrats both had members who disagreed on world affairs, New Deal programs, and segregation. New political stances liberal (loose on tradition), conservative (strong on tradition), and moderate (in the middle) emerged. – Ex: “Conservative Democrats” The Dixiecrats Southern Democrats were not happy with President Harry S. Truman, a moderate Democrat, when he desegregated the military in 1948. Those favoring segregation nominated Strom Thurmond of S. Carolina to run against him in 1948. – Formed the States’ Rights Democratic Party, or “Dixiecrats”; won 4 states, but party later dissolved. 1948 U.S. Presidential Election The “Tidelands” Controversy Texans were upset that the federal government refused to allow Texas’s sovereignty beyond 3 miles from the coast—where potential of oil and gas was worth billions! Dwight Eisenhower, a Republican running for President in 1952, promised Democrat Governor Allan Shivers he would sign a bill giving the tidelands to Texas if money from the tidelands went to support Texas schools. Shivers-Eisenhower Connection Governor Shivers organized “Democrats for Eisenhower” in 1952. Shiver’s name was on the ballot for both parties—he won the election. “Ike” also won and became president. Shivers helped modernize Texas government by supporting funding for state hospitals, retired teachers and state employees, and roads and bridges. 1952 U.S. Presidential Election New Highways and Suburbs President Eisenhower supported an interstate highway system to connect states with quality roads. The Gulf Freeway, or I45, in Houston was the first interstate in TX. Developers purchased property miles from the city and began building residential areas called suburbs (ex: Kingwood). Houston Suburban Areas Drought in 1950s Texas An extended drought began drying up reservoirs, wells, and rivers causing extensive damage and destruction. It ended in 1957, but: – cities built new reservoirs – ranchers built more stock ponds – farmers turned more to irrigation – the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers built more dams across Texas rivers The Warren Court President Eisenhower appointed Earl Warren Chief Justice of the Supreme Court. In the 1950s and 1960s the court consistently decided in favor of those seeking to end discrimination. In 1967, President Lyndon B. Johnson appointed Thurgood Marshall, the first African American justice to the Supreme Court. School Desegregation In Plessy vs. Ferguson (1896), the Supreme Court ruled that racial segregation was legal as long as facilities of both races were equal. In the Brown vs. Board of education of Topeka, Kansas case (1954), the Court ruled racial segregation in public schools was unconstitutional— schools were ordered to desegregate. Mansfield ISD in TX was the last to integrate in 1965. It took 20 years for desegregation to fully occur. Desegregation of Public Facilities Minorities were still denied access to public facilities, parks, libraries, and swimming pools even though their taxes helped them. They sued to gain access. A popular way to resist court desegregation orders was to turn operation of city facilities over to private clubs that maintained discrimination. The “Red Scare” The fear about the rise of communism led to many people, including labor unions and civil rights workers, being accused of Communist ties. Senator Joseph McCarthy of Wisconsin accused many U.S. military leaders and politicians of being Communists. “McCarthyism” spread as some Hollywood stars were blacklisted too. John Henry Faulk, an Austin native and radio star for CBS, was accused and fired. But he sued for libel and won!