Lesson 09 - L2L VPN - Stark State College

Lesson 9
Virtual Private Network
Configuration
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-1
Secure VPNs
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-2
VPN Overview
Intranet VPN has low-cost, tunneled connections with rich VPN services, which lead to cost savings and new applications
Remote Office
Home Office
POP
Main
Office
Extranet VPN extends WANs to business partners, which leads to new applications and business models
Business Partner
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
VPN
POP Remote access
VPN is cost-saving
Mobile Worker
SNPA v4.0
—11-3
IPSec Enables Security Appliance
VPN Features
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Internet
IPSec
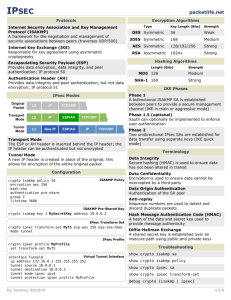
• Data confidentiality
• Data integrity
• Data authentication
• Anti-replay
SNPA v4.0
—11-4
What Is IPSec?
Internet
IPSec
IETF standard that enables encrypted communication between peers
• Consists of open standards for securing private communications
• Has network layer encryption that ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and authentication
• Scales from small to very large networks
• Is included in PIX Firewall v5.0 and later
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-5
IPSec Standards Supported by the
Security Appliance
• IPSec
– ESP
• IKE
• DES
• 3DES
• AES
• DH
• MD5
• SHA
• RSA Signatures
• CAs
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-6
How IPSec Works
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-7
Five Steps of IPSec
Host A Security
Appliance A
Security
Appliance B
Host B
• Interesting traffic: The VPN devices recognize the traffic to protect.
• IKE Phase 1: The VPN devices negotiate an IKE security policy and establish a secure channel.
• IKE Phase 2: The VPN devices negotiate an IPSec security policy to protect IPSec data.
• Data transfer: The VPN devices apply security services to traffic, then transmit the traffic.
• Tunnel terminated: The tunnel is torn down.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-8
Step 1: Interesting Traffic
Host A Security
Appliance A
10.0.1.3
Apply IPSec
Send in Clear Text
Security
Appliance B
Host B
10.0.2.3
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-9
Step 2: IKE Phase 1
Host A Security
Appliance A
Security
Appliance B
Host B
10.0.1.3
Negotiate the
Policy
IKE Phase 1:
Main Mode Exchange
Negotiate the
Policy
10.0.2.3
DH Exchange DH Exchange
Verify the Peer
Identity
Verify the Peer
Identity
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-10
IKE Phase 1 Policy Sets
Host A
10.0.1.3
Security
Appliance A
Negotiate IKE Proposals
Security
Appliance B
Host B
10.0.2.3
Policy Set 10
DES
MD5
Pre-share
DH1
Lifetime
Policy Set 20
3DES
SHA
Pre-share
DH1
Lifetime
IKE Policy Sets
Policy Set 15
DES
MD5
Pre-share
DH1
Lifetime
• Negotiates matching IKE transform sets to protect
IKE exchange
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-11
DH Key Exchange
Terry
Public Key B
+ Private Key A
Shared Secret
Key ( B A )
Key = Key
Alex
Public Key A
+ Private Key B
Shared Secret
Key ( A B )
Pay to Terry Smith $100.00
One Hundred and xx/100 Dollars
Encrypt Decrypt
Pay to Terry Smith $100.00
One Hundred and xx/100 Dollars
4ehIDx67NMop9eR
U78IOPotVBn45TR Internet
4ehIDx67NMop9eR
U78IOPotVBn45TR
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-12
Authenticate Peer Identity
Remote Office
Security
Appliance A
Internet
Peer
Authentication
Peer authentication methods
• Pre-shared keys
• RSA Signature
• DSA Signature
Corporate Office
Security
Appliance B
HR
Servers
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-13
Step 3: IKE Phase 2
Host A
10.0.1.3
Security
Appliance A
Negotiate IPSec
Security Parameters
Security
Appliance B
Host B
10.0.2.3
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-14
IPSec Transform Sets
Host A
10.0.1.3
Security
Appliance A
Negotiate Transform Sets
Security
Appliance B
Host B
10.0.2.3
Transform Set 30
ESP
3DES
SHA
Tunnel
Lifetime
IPSec transform sets
Transform Set 55
ESP
3DES
SHA
Tunnel
Lifetime
Transform Set 40
ESP
DES
MD5
Tunnel
Lifetime
• A transform set is a combination of algorithms and protocols that enacts a security policy for traffic.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-15
SAs
SAD
• Destination IP address
• SPI
• Protocol
SPD
• Encryption algorithm
• Algorithm Authentication
• Mode
• Key lifetime
192.168.2.1
SPI –12
ESP/3DES/SHA
Tunnel
28800
Internet
192.168.12.1
SPI –39
ESP/DES/MD5
Tunnel
28800
B A N K
SNPA v4.0
—11-16 © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SA Lifetime
Data-Based Time-Based
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-17
Step 4: IPSec Session
Host A
Security
Appliance A
Security
Appliance B
Host B
IPSec Session
• SAs are exchanged between peers.
• The negotiated security services are applied to the traffic.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-18
Step 5: Tunnel Termination
Host A
Security
Appliance A
Security
Appliance B
Host B
IPSec tunnel
• A tunnel is terminated:
– By an SA lifetime timeout
– If the packet counter is exceeded
• Removes IPSec SA
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-19
Configure VPN
Connection Parameters
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-20
tunnel-group Command
• To create and manage the database of connection-specific records for IPSec, use the tunnel-group command in global configuration mode.
• The tunnel-group command has the following subcommands:
– tunnel-group general-attributes
– tunnel-group ipsec-attributes firewall(config)# tunnel-group name type type fw1(config)# tunnel-group training type ipsec-l2l
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-21
tunnel-group general-attributes Command
• The general-attribute sub-configuration mode is used to configure settings that are common to all supported tunneling protocols.
•
The tunnel-group general-attributes command has the following subcommands:
– accounting-server-group
– address-pool
– authentication-server-group
– authorization-server-group
– default-group-policy
– dhcp-server
– strip-group
– strip-realm firewall(config)# tunnel-group name general-attributes fw1(config)# tunnel-group training general fw1(config-general)#
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-22
tunnel-group ipsec-attributes Command
• The ipsec-attribute sub-configuration mode is used to configure settings that are specific to the IPSec tunneling protocol.
• The tunnel-group ipsec-attribute command has the following subcommands:
– authorization-dn-attributes
– authorization-required
– chain
– client-update
– isakmp keepalive
– peer-id-validate
– pre-shared-key
– radius-with-expiry
– trust-point firewall(config)# tunnel-group name ipsec-attributes fw1(config)# tunnel-group training ipsec-attributes fw1(config-ipsec) #
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-23
IPSec Configuration
Tasks
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-24
Configuring IPSec Encryption
• Task 1: Prepare to configure VPN support.
• Task 2: Configure IKE parameters.
• Task 3: Configure IPSec parameters.
• Task 4: Test and verify VPN configuration.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-25
Task 1: Prepare to
Configure VPN Support
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-26
Task 1: Prepare for IKE and IPSec
• Step 1: Determine the IKE (IKE Phase 1) policy.
• Step 2: Determine the IPSec (IKE Phase 2) policy.
• Step 3: Ensure that the network works without encryption.
• Step 4: (Optional) Implicitly permit IPSec packets to bypass security appliance ACLs and access groups.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-27
Determine IKE Phase 1 Policy
Parameter
Encryption algorithm
Hash algorithm
Authentication method
Key exchange
IKE SA lifetime
Strong
DES
MD5
Pre-share
DH Group 1
86,400 seconds
Stronger
3DES or AES
SHA-1
RSA Signature
DH Group 2 or 5
< 86,400 seconds
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-28
Determine IPSec (IKE Phase 2) Policy
Security
Appliance 1
Site 1
Security
Appliance 6
Internet e0 192.168.1.2
e0 192.168.6.2
10.0.1.11
10.0.6.11
Site 2
Policy Site 1
Transform set
Peer security appliance
IP address
Encrypting hosts
Traffic (packet type) to be encrypted
ESP-DES, tunnel
192.168.1.2
10.0.1.11
IP
Site 2
ESP-DES, tunnel
192.168.6.2
10.0.6.11
IP
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-29
Task 2: Configure Ike
Parameters
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-30
Task 2: Configure IKE
• Step 1: Enable or disable IKE.
• Step 2: Configure IKE Phase 1 policy.
• Step 3: Configure a tunnel group.
• Step 4: Configure the tunnel group attributes pre-shared key.
• Step 5: Verify IKE Phase 1 policy.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-31
Enable or Disable IKE
Site 1
10.0.1.11
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6 e0 192.168.1.2
Internet e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
firewall(config)# isakmp enable interface-name
• Enables or disables IKE on the security appliance interfaces
• Disables IKE on interfaces not used for IPSec fw1(config)# isakmp enable outside
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-32
Configure IKE Phase 1 Policy
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6
Site 1 Site 2
Internet e0 192.168.1.2
e0 192.168.6.2
10.0.1.11
10.0.6.11
fw1(config)# isakmp policy 10 encryption des fw1(config)# isakmp policy 10 hash sha fw1(config)# isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share fw1(config)# isakmp policy 10 group 1 fw1(config)# isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400
• Creates a policy suite grouped by priority number
• Creates policy suites that match peers
• Can use default values
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-33
Configure a Tunnel Group
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6
Site 1 Site 2
Internet
10.0.1.11
Tunnel Group
192.168.6.2
L2L
192.168.1.2
IPSec
192.168.6.2
IPSec
10.0.6.11
Tunnel Group
192.168.1.2
L2L firewall(config)# tunnel-group name type type
• Names the tunnel group
• Defines the type of VPN connection that is to be established fw1(config)# tunnel-group 192.168.6.2 type ipsec-l2l
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-34
Configure Tunnel Group Attributes
Pre-Shared Key
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6
Site 1 Site 2
Internet
10.0.1.11
192.168.1.2
Tunnel Group
192.168.6.2
192.168.6.2
isakmp key cisco123 isakmp key cisco123
10.0.6.11
Tunnel Group
192.168.1.2
firewall(config)# tunnel-group name [general-attributes | ipsec-attributes]
• Enters tunnel-group ipsec-attributes subconfiguration mode firewall(config-ipsec)# pre-shared-key key
• Associates a pre-shared key with the connection policy fw1(config)# tunnel-group 192.168.6.2 ipsec-attributes fw1(config-ipsec)# pre-shared-key cisco123
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-35
Verify IKE Phase 1 Policy
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6
Site 1 Site 2
Internet
192.168.1.2
192.168.6.2
10.0.1.11
10.0.6.11
fw1# show run crypto isakmp isakmp identity address isakmp enable outside isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share isakmp policy 10 encryption 3des isakmp policy 10 hash sha isakmp policy 10 group 2 isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400
• Displays configured and default IKE protection suites
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-36
Task 3: Configure IPSec
Parameters
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-37
Task 3: Configure IPSec
Step 1: Configure interesting traffic: NAT 0 and ACL.
– access-list 101 permit
– nat 0
Step 2: Configure IPSec transform set suites.
– crypto ipsec transform-set
Step 3: Configure the crypto map.
– crypto map
Step 4: Apply the crypto map.
– crypto map map-name interface interface-name
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-38
Configure Interesting Traffic
Site 1
10.0.1.11
10.0.1.X
Security
Appliance 1
192.168.1.2
Security
Appliance 6
Internet
192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
Encrypt
10.0.6.X
Encrypt fw1(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 10.0.1.0
255.255.255.0 10.0.6.0 255.255.255.0
• permit = encrypt
• deny = do not encrypt
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-39
Example: Crypto ACLs
Security
Appliance 1
Site 1 e0 192.168.1.2
10.0.1.11
• Lists are symmetrical.
Internet
Security
Appliance 6 e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
Security Appliance 1 (fw1) fw1# show run access-list access-list 101 permit ip 10.0.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.6.0
255.255.255.0
Security Appliance 6 (fw6) fw6# show run access-list access-list 101 permit ip 10.0.6.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.1.0
255.255.255.0
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-40
Configure Interesting Traffic: NAT 0
Security
Appliance 1
Site 1
192.168.1.2
10.0.1.11
10.0.1.11
Do Not
Translate
Internet
Security
Appliance 6
192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
Do Not
Translate
10.0.6.11
fw1(config)# nat (inside) 0 access-list 101
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-41
Configure an IPSec Transform Set
Security
Appliance 1
Site 1
Security
Appliance 6
Internet e0 192.168.1.2
e0 192.168.6.2
10.0.1.11
10.0.6.11
Site 2 firewall(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set transform-set-name transform1 [transform2]
• Sets are limited to two transforms
• Default mode is tunnel
• Configures matching sets between IPSec peers fw1(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set fw6 esp-des esp-md5-hmac
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-42
Available IPSec Transforms
Site 1
10.0.1.11
Security
Appliance 1
Security
Appliance 6 e0 192.168.1.2
Internet e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
esp-des ESP transform using DES cipher (56 bits) esp-3des ESP transform using 3DES cipher(168 bits) esp-aes ESP transform using AES-128 cipher esp-aes-192 ESP transform using AES-192 cipher esp-aes-256 ESP transform using AES-256 cipher esp-md5-hmac ESP transform using HMAC-MD5 auth esp-sha-hmac ESP transform using HMAC-SHA auth esp-none ESP no authentication esp-null ESP null encryption
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-43
Configure the Crypto Map
Security
Appliance 1
Site 1
10.0.1.11
e0 192.168.1.2
Internet
Security
Appliance 6 e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
fw1(config)# crypto map FW1MAP 10 match address 101 fw1(config)# crypto map FW1MAP 10 set peer 192.168.6.2
fw1(config)# crypto map FW1MAP 10 set transform-set pix6 fw1(config)# crypto map FW1MAP 10 set security-association lifetime seconds 28800
• Specifies IPSec (IKE Phase 2) parameters
• Maps names and sequence numbers of group entries into a policy
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-44
Apply the Crypto Map to an Interface
Site 1
10.0.1.11
Security
Appliance 1 e0 192.168.1.2
Internet
Security
Appliance 6
Site 2 e0 192.168.6.2
10.0.6.11
firewall(config)# crypto map map-name interface interface-name
• Applies the crypto map to an interface
• Activates IPSec policy fw1(config)# crypto map FW1MAP interface outside
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-45
Example: Crypto Map for Security
Appliance 1
Site 1
10.0.1.11
Security
Appliance 1 e0 192.168.1.2
Security
Appliance 6
Internet e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
Security Appliance 1 (fw1) fw1# show run crypto map crypto map FW1MAP 10 match address 101 crypto map FW1MAP 10 set peer 192.168.6.2
crypto map FW1MAP 10 set transform-set pix6 crypto map FW1MAP interface outside
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-46
Example: Crypto Map for Security
Appliance 6
Site 1
10.0.1.11
Security
Appliance 1 e0 192.168.1.2
Internet
Security
Appliance 6 e0 192.168.6.2
Site 2
10.0.6.11
Security Appliance 1 (fw6) fw6# show run crypto map crypto map FW1MAP 10 match address 101 crypto map FW1MAP 10 set peer 192.168.1.2
crypto map FW1MAP 10 set transform-set pix1 crypto map FW1MAP interface outside
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-47
Task 4: Test and Verify
VPN Configuration
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-48
Task 4: Test and Verify VPN Configuration
• Verify ACLs and interesting traffic.
– show run access-list
• Verify correct IKE configuration.
– show run isakmp
– show run tunnel-group
• Verify correct IPSec configuration.
– show run ipsec
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-49
Task 4: Test and Verify VPN Configuration
(Cont.)
• Verify correct crypto map configuration.
– show run crypto map
• Clear IPSec SA.
– clear crypto ipsec sa
• Clear IKE SA.
– clear crypto isakmp sa
• Debug IKE and IPSec traffic through the security appliance.
– debug crypto ipsec
– debug crypto isakmp
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-50
Scale Security
Appliance VPNs
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-51
CA Server Fulfilling Requests from IPSec Peers
CA Server
• Each IPSec peer individually enrolls with the
CA server.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-52
Enroll a Security Appliance with a CA
• The security appliance generates public and private key pair.
• The security appliance obtains public key and certificate from the CA.
• The security appliance requests signed certificate from the CA.
• The CA administrator verifies request and sends signed certificate.
CA Server
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-53
Summary
• A VPN is a service that offers secure, reliable connectivity over a shared public network infrastructure such as the Internet.
• Cisco security appliances enable a secure VPN.
• IPSec configuration tasks include configuring IKE and IPSec parameters.
• CAs enable scaling to a large number of
IPSec peers.
© 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SNPA v4.0
—11-54