Reading - Burlington-Edison School District

Second Grade Literacy Guide
Reading
Assessment
Timeline
DIBELS
Benchmark
(Report on SOAR) o
September o
January o June
DIBELS
Progress
Monitor
(
Report on SOAR) o October o November o December o
February o
March o April o May
R.B.A.
( Report on SOAR)
Assessments 2 nd Grade English Language Arts Common Core State Standards (ELA, CCSS)
Common Core (RL)
Reading Literature
Key Ideas and
Details
(RL.1, RL.2, RL.3)
Craft and
Structure
(RL.4, RL.5, RL.6)
Integration of
Knowledge and
Ideas
(RL.7, RL.9)
Range of Reading and Level of Text
Complexity
(RL.10)
Common Core (RI)
Reading Informational
RI.3)
(RI.10)
Text
Key Ideas and
Details (RI.1, RI.2,
Craft and Structure
(RI.4, RI.5, RI.6)
Integration of
Knowledge and Ideas
(RI.7,RI.8, RI.9)
Range of Reading and
Level of Text
Complexity
Common Core (RF)
Reading
Foundational
Skills
Phonics and Word
Recognition
(RF.3)
Fluency
(RF.4)
Common Core (W)
Writing
Text Types and
Purposes
(W.1.,W.2., W.3.)
Production and
Distribution of
Writing
(W.5., W.6.)
Research to
Build and
Present
Knowledge
(W.7., W.8.)
Common Core
(SP)
Speaking &
Listening
Comprehension and
Collaboration
(SL.1., SL.2,
SL.3.)
Presentation of
Knowledge and
Ideas
(SL.4., SL.5.,
SL.6.)
Common Core
(L)
Language
Conventions of
Standard
English
(L.1, L.2)
Knowledge of
Language
(L.3)
Vocabulary
Acquisition and
Use
(L.4, L.5, L.6) o November o
February o
April
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 1
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Burlington-Edison School District 2
nd
Grade Snapshot
(Review and refer to District Curriculum/Learning Guides/OSPI created for each subject to get additional descriptions, timelines, EALRS, CCSS, unit focus, etc.)
Reading (Harcourt, Daily 5, Café, F&P, Comp. Toolkit) Writing (Write Source, D Matteson) Math (TERC, Math Steps)
PHONICS/WORD RECOGNITION o Distinguish long and short vowels (RF) o Read common word families (-ack, -ock) o Know spelling-sound correspondences for vowel teams. (RF) o Blend onset and rime (make-take-rake) o Check for understanding/back up and reread (RF) o Sound it out/blend sounds/stretch & reread o Know common sight words
FLUENCY: 44 CWPM o 3 ways to read: pictures, words, retell o Choose “good fit” books o Build “Read to Self” Stamina o Use pictures…do words & picture match (RF) o Use Prior Knowledge (This reminds me of…) o Make Connections (Text to Self, schema) o Identify Genre (Fiction/Nonfiction) o Set reading goals o Author’s purpose o Make Predictions (before, during, after)/infer meaning o Read poetry (ongoing)
SPEAKING AND LISTENING o Responding to text (understand how to draw simple conclusions and give response to text) (SL)
LITERATURE/INFORMATIONAL TEXT o Ask questions throughout reading process (RL) o Compare and contrast (RL & RI) o Describe structure of a story (Beg/Middle/End) (RL) o Identify Story Elements (character/setting) (RL) o Nonfiction Text Features (captions, headings) (RI) o Purpose of Text (lists/signs/fairy tales/labels…) (RI) o Understand/analyze the relationship between literary and informational text (RL & RI) o Understand difference between main idea and supporting details, what the author wants to explain. (RI) o Story sequence (first, next, then, last)
Sept: DIBELS Benchmark (Record on SOAR)
Oct., Nov. Progress Monitor (Record on SOAR)
RBA (November)
Handwriting Without Tears
(letter/# formation)
REVIEW WRITING PROCESS
Comprehension Toolkit:
Book 2 Lessons 4 (Discover your passion) and
5(think about what you know) teach during writer’s workshop
Write narratives including details to describe actions, thoughts and feelings using event sequencing
(temporal words).
Write informative/explanatory texts in which they introduce a topic, use facts to develop points and provide a concluding statement.
O Uses planning strategy (web)
O Writes using Beg/Middle/End
O Identifies an audience
O Writes using 8-10 sentences
O Uses descriptive words
O Writes using dialogue
O Uses variety of punctuation
O Revises and edits with help
O Uses knowledge of more complex letter/sound relationships. Knows and uses 175-225 essential words
O Genres: Descriptive, Narrative
Nov: Narrative (Special Place)
(Record on SOAR)
Develop Daily Math Routines
(Ex. calendar activities, charts, # line, counting,
120’s chart, odd/even, place value, skip counting # patterns, quick images, telling time, coins, today’s number…)
Supplemental (1000s Book) o Unit 1: Counting, Coins, Combinations
-Digital and Analog Clock
- +/- within 10/using strategies
-Identifying name/value of coins
-Counting a set of objects
-Comparing Numbers >,<,=
-Use +/- within 100 to solve word problems o Unit 2: Shapes, Blocks and Symmetry
-Recognize shapes having specific attributes.
-Draw shapes having specific attributes.
-Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons,
hexagons, and cubes.
-Partition a rectangle into rows and columns
of the same-size squares and count to find
the total number of them.
-Fluently add and subtract within 20.
-Ones, tens, hundreds place o Unit 3: Stickers, Number Strings & Story
Problems
-Use +/- within 100 to solve 1 and 2 step word
problems
-use words, pictures, and numbers
-Fluently +/- within 20 using strategies
-Even and Odd numbers
-Count by 2s, 5s, and 10s
-Mentally add 10 or 100 to a given #
Nov. Trimester 1 MBA
(Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 2
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Distr
Reading (Harcourt, Daily 5, Café, F&P, Comp Toolkit)
LITERATURE/INFORMATIONAL TEXT o Recount stories including fables/folktales and determine message, lesson, or moral (RL) o Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why
and how to demonstrate understanding of key details (RL & RI) o Acknowledge differences in points of view of characters (RL) o Fiction/Nonfiction Text features (table of contents, title, author) o Use information gained from the illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot. (RL) o Describe how words and phrases (alliteration/rhyme) supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem, or song. (RL) o Identify Main Topic of text as well as the focus of specific paragraphs within text. (RI) o Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas in a text. (RI) o Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic/subject. (RI) o Know and use various text features (captions, subheadings, glossaries) to locate key facts. (RI) o Explain how specific images (diagram) contribute/clarify. (RI) o Decode regularly spelled 2-syllable words with long vowels. (RF) o Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes. (RF) o Read grade level text with fluency and expression. (RL & RI) o Adjust reading rate to match text.
LANGUAGE o Use sentence-level context as a clue to meaning. (L) o Determine the meaning of the new word formed when a known prefix is added to a known word. (L) o Use a known root word as a clue to the meaning of an unknown word with the same root. (L) o Use knowledge of the meaning of individual words to predict the meaning of compound words. (L) o Read Voraciously (Don’t want to stop).
FLUENCY: 68 CWPM
Dec., Feb. Prog. Monitor (Record on SOAR) RBA (February)
Writing (Write Source, D Matteson) Math (TERC, Math Steps)
Handwriting Without Tears
(continue) o With guidance and support from adults, use a variety of digital tools to publish writing, including collaboration with peers. o Write opinion pieces and supply reasons using linking words
(because, and, also) that support the opinion with concluding statement. o Writes using 10-12 sentences, begins to organize ideas into a paragraph o All details are relevant to topic o Publishes own writing considering the audience o Includes detail and writes in 2 nd or 3 rd person o Uses dialogue o Selects from wide range of topics and writes for a variety of purposes o Writing includes more than one character o Uses knowledge of more complex letter sound relationships. Knows and uses 225-250 essential words. o Genres: Narrative, Expository,
Persuasive
Continue Daily Routines:
100’s chart, missing #’s, compare/order #’s o Unit 4:Pockets, Teeth and Favorite Things
-Grouping data into categories based on attributes
-Represent a set of data
-Comparing representations of a set of data
-Sorting the same set of data in a different way
-Use a Venn Diagram to sort 2 attributes at one time
-Choose a survey question and collect, sort and create representation of data
-Interpret and sharing results of data collection o Unit 9: Measuring Length and Time
-Compare 2 lengths
-Estimating and calculating lengths
-Solving comparison problems by finding the difference between 2 measurements
-Using a ruler (standard and metric) as a measuring tool
-Use inches, feet and yards to describe lengths
-comparing inches and centimeters, and understanding that difference size units yield different counts o Unit 5: How Many Floors? How Many Rooms?
-Using rows, columns
-Connecting numbers in a table to the situation they represent
Describing the pattern in numbers in column
-Use information in a table to determine the relationship between 2 quantities
-Create and/or extend a repeating pattern
-Even and odd numbers
Feb: Resp to Lit (Cool Ali Character) Feb: Trimester 2 MBA (Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 3
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Distr ict
Asse ss
Jan: DIBELS Benchmark (Record on SOAR)
Reading (Harcourt, Daily 5, Café, F&P, Comp. Toolkit)
LITERATURE/INFORMATIONAL TEXT o Read and comprehend literature, including stories and poetry, in the grades 2-3 text complexity band proficiently with scaffolding as needed.(RL) o Read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science and technical texts, in grades 2-3 text complexity band proficiently with scaffolding as needed. (RI) o Identify words with inconsistent but common spellingsound correspondences. (RF) o Recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words. (RF) o Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension using on-level text. (RF) o Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding. (RF)
LANGUAGE o Use glossaries and beginning dictionaries to determine/clarify meaning of words/phrases. (L) o Identify real-life connections between words and their use. (L) o Distinguish shades of meaning among closely related verbs and closely related adjectives. (L) o Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe. (L)
FLUENCY: 90+ CWPM
Mar/April/May: Progress Monitor May: RBA
June: DIBELS Benchmark (Record all on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
(Record on SOAR)
Writing (Write Source, D Matteson)
Handwriting Without Tears
(continue) o Participates in shared research and writing projects (read a number of books on a single topic to produce a report) o Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. o Writes a paragraph about 1 topic with supporting details o Adds, cuts, rewords and rearranges as needed o Selects from a wide range of topics and writes for a variety of purposes o Writes factual information o Spells unknown words using knowledge of word structures o Uses variety of sentence beginnings o Uses labeled illustrations
(captions, table of contents) o Plans for and creates a published piece that reflects the audience, form, and purpose o Genres: Responding to Literature,
Report Writing, Creative Writing
May: Summ. Expository (How to
Make Favorite Food) (Record on
SOAR)
Math (Terc, Math Steps)
Continue Daily Routines: # patterns, skip counting o Unit 6: How Many Tens? How Many Ones?
-Adding tens and ones to combine 2-digit #s
-write an equation that represents a problem
-Add 2-digit numbers by keeping 1 number whole
-compare strategies for adding 2-digit #s
-100s chart and sequence of numbers
-Place value and skip counting by 2s, 5s, 10s
-Solving Story Problems with missing number o Unit 7:Parts of a Whole, Parts of a Group
-fractions and fraction notation
-finding and showing ½ of a set (1/4, 1/3)
-solving problems about finding ½
-find equal parts of a whole & name them
-terms and notations for fractions that contain more than 1 part (2/3, ¾)
-finding fractions of sets o Unit 8:Partners, Teams and Paper Clips
-even and odd numbers
-adding even and odd numbers
-Developing fact fluency to and from 20
-Subtract amounts from 100, within 100
-Solving story problems o Unit 1 (Grade 3): Trading Stickers,
Combining Coins
-Place value of each digit in 2-3 digit #s
-+/- multiples of 10
-Solving story problems with 2 digit #s
May: Trimester 3 MBA
(Record on SOAR)
4
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Burlington-Edison School District 2
nd
Grade Snapshot
(Speaking, Listening, Science, and Social Studies can be integrated into many literacy lessons. Refer to CCSS, OSPI, Foss Kit Guides, etc. for additional information)
Speaking and Listening (CCSS) Science (Foss Kits) Social Studies (Harcourt, Read Alouds)
1.
Participate in collaborative conversations with diverse partners with peers and adults in small or larger groups. o Follow agreed upon rules for discussions. o Build on others’ talk in conversations by linking their comments to the remarks of others. o Ask for clarification and further explanation as needed about the topics and texts under discussion.
2.
Recount or describe key ideas or details from a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media.
3.
Ask and answer questions about what a speaker says in order to clarify comprehension, gather additional information, or deepen understanding of a topic or issue.
4.
Tell a story or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking audibly in coherent sentences.
5.
Create audio recordings of stories or poems; add drawings or other visual displays to stories or recounts of experiences when appropriate to clarify ideas, thoughts and feelings.
6.
Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation in order to provide requested detail or clarification.
Scientific Inquiry: ask questions, record observations, predict, collect data, explain, describe and draw, describe problem/solution
Question: What is a Scientist? What is an insect?
Insects(Life Science): o Identify, draw and label parts of insects (head, thorax, abdomen, 6 legs) o Observe and describe the life cycle of an insect (egg, larva, pupa, adult or egg, nymph, adult). o Observe that insects need water, food, air and space
(habitat) to live. o Describe how insects help the Earth/humans. o Explain how insects are similar and different.
Question: What does balance mean? How can you make an object move?
Balance and Motion (Physical Science): o Explore and investigate the concepts of balance, counterbalance, counterweight, and stability. o Describe objects and systems that turn on a central axis
(rotation). o Explain why force is needed to initiate rotational motion in objects. o Explore and describe wheels, spheres, and wheel-andaxle systems.
Question: What is a geologist? How do we use earth materials in our daily living?
Pebbles, Sand Silt (Earth Science): o Observe and compare properties of earth materials. o Identify that rocks are the solid material of the earth. o Investigate properties of pebbles, gravel, sand silt and clay particles, as well as how fossils are made. o Plan and conduct an investigation to demonstrate that soil is made up of different materials. o Explore places where earth materials are naturally found and ways that earth materials are used by humans.
Civics o Understands the key ideal of public or common good within the context of the community. o Understands the basic function and organization of government and laws in the community. o Understands that citizenship and civic involvement in the neighborhood and community are the rights and responsibilities of individuals.
Geography o Understands and applies basic mapping elements such as compass rose, labels, and a key to read and construct maps that display information about neighborhoods or local communities. o Understands the physical characteristics of places in the community. o Understands that people affect their environment as they meet their needs/wants.
History o Understands and creates timelines for events in a community to show how the present is connected to the past. o Understands individuals who have shaped history in the local community.
Economics o Understands the basic elements of a community’s economic system and that consumers make choices of products/services.
Social Studies Skills o Understands multiple points of view on community issues and engages in discussions about different points of view.
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 5
Second Grade Literacy Guide
LS
SP
HF
WM
September
2,3,4
1,3,5
WS
WSA
October
2,16
5,6,18,19 20
6, 7
9
16,17,21
9,16,25
9
10
18, 23, 25 13,15,21,22
9
10
Second Grade Comprehension Toolkit Lesson Sequence
September October November December January February March
1.Monitor
Comprehension
2.Activate and
Connect
3.Ask
Questions
4.Infer and
Visualize
5. Determine
Importance
6. Summarize
& Synthesize
1
6 7
12
Second Grade Fountas and Pinnell Phonics Lesson Sequence
November December January February March April
4,5
(writing)
13, 14,15
2 3
19,20
8,9 9,10,11
April
12
(revisit)
16
(Harcourt and Daily Café have additional comprehension lessons and resources)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
May/June
1,2,20
May/June
17,18
21,22
6
Second Grade Literacy Guide
# Title of Harcourt Anthology
Story
Genre Harcourt Spelling/Phonics focus
1 The Mixed Up Chameleon
2 Get Up and Go
Fantasy
Informational
3 Henry & Mudge Under Yellow Moon Realistic Fiction
4 Days with Frog and Toad Story
5 Wilson Sat Alone
6 The Enormous Turnip
7 Helping Out
8 Mr. Putter and Tabby Fly Plane
9 Hedgehog Bakes a Cake
10 Lemonade for Sale
Realistic Fiction
Folktale
Story
Realistic Fiction
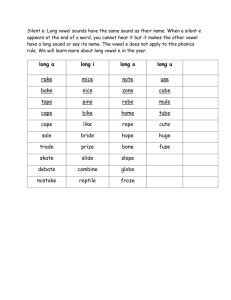
Long I __e, short i
Long a__e,
-ed ending
Changing y to I before adding ed
Long a__e, short a
-ack, -ock
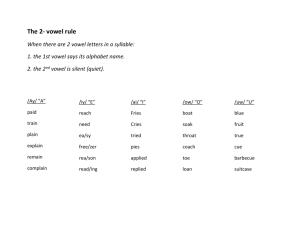
Nonfiction Photo Essay r-controlled vowel /ur/ ear
Realistic Fiction Abbreviations r-controlled vowel /or/ our ar, arm, ark
11 Johnny Appleseed
12 From Seed to Plant
13 Secret Life of Trees
14 Watermelon Day
15 Pumpkin Fiesta
16 The Day Jimmys Boa Ate the Wash
17 How I Spent My Summer Vacation
18 Dear Mr. Blueberry
19 Cool Ali
20 Emperor’s Egg
21 Pine Park Mystery
22 Goodbye Curtis
23 Max Found Two Sticks
24 Anthony Reynoso
25 Chinatown
Harcourt
Comprehension
Main Idea
Author’s Purpose
Narrative Elements
Compare/Contrast
Narrative Elements
Sequence
Main Idea
Predicting
Making Inferences
Compare/contrast
Play r-controlled: ear, eer
Expository Nonfiction spr, str, thr
Mental Image
Text features
Expository Nonfiction Vowel diagraphs /oo/
Realistic Fiction Consonant diagraphs /n/ gn, kn, /r/ wr
Fact/fiction
Making inferences
Story
Fantasy
Fantasy
Fantasy
Realistic Fiction
Informational
Inflections: -s, -es, ies
Vowel dipthongs: /ou/ ou, ow
Vowel Dipthongs: /oi/ oi, oy
Vowel digraphs: /oo/ oo, ue
Inflections: -es (f to v)
Suffixes: -ing, -ly
Predicting
Cause/effect
Cause/effect
Making Inferences
Creating Mental
Images
Fact/Fiction
Play
Realistic Fiction
Realistic Fiction
Personal Narrative
Realistic Fiction
Prefixes: pre-, re-
Contractions: ‘ll, n’t, ‘s
Vowel Digraphs: /oo/ ew, ui
Consonant Digraphs: /f/ gh, ph
Suffixes: -er, -est
Narrative Elements
Compare/Contrast
Multiple Meanings
Summarizing
Mental Images
26 Abuela
27 Beginner’s World Atlas
28 Dinosaurs Travel
Fantasy
Nonfiction Atlas
Informational Book r-controlled vowels: are, air
Vowel Variants: /oo/ oo, ou
Vowel Digraphs: /oo/ ou, ou(gh)
Making Inferences
Locate Information
Author’s Purpose
29 Montigue On the High Seas
30 Ruth Law Thrills a Nation
31 No More Harcourt Stories
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Story
Biography
Vowel Variants: /o/ aw, au(gh)
Prefixes: over-, un-
Narrative Elements
Predicting
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 1 Lesson 1-Metacognition
Book 2 Lesson 6-Make Connections
Book 2 Lesson 7-Merge Thinking
Book 4 Lesson 12-Inference
Book 4 Lesson 13-Visualizing
Book 4 Lesson 14-Inference
Book 4 Lesson 15-Infer/Visualize
Book 1 Lesson 2-Nonfiction Feat.
Book 1 Lesson 3-Nonfiction Feat.
Book 6 Lesson 19-summarize
Book 6 Lesson 20-Main Idea
Book 3 Lesson 8-Questioning
Book 3 Lesson 9-Questioning
Book 3 Lesson 10-Questions
Book 3 Lesson 11-Questions
Book 5 Lesson 16-Determine
Importance
Revisit Book 4 Lesson 12 Infer.
Book 5 Lesson 17-Paraphrase
Book 5 Lesson 18-Organize
Thinking
Book 6 Lesson 21 and 22
7
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Phonics and Word Recognition
STANDARD
Common Core
RF3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words. a.
Distinguish long and short vowels when reading regularly spelled one-syllable words. b.
Know spelling-sound correspondences for additional common vowel teams. c.
Decode regularly spelled two-syllable words with long vowels. d.
Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes e.
Identify words with inconsistent but common spelling-sound correspondences. f.
Recognize and read grade appropriate
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How do sounds form words?
I can read the short vowel sounds in words.
I can read long vowel sounds in words.
I can read consonant clusters at the beginning of words.
I can recognize a word pattern and use it to make other words.
Why are sight words important?
I can read sight words. irregularly spelled words.
Vocabulary
Short vowel
Long Vowel
Consonant clusters
Sight words
Past tense
Word families
Assessment: Optional: High Frequency Word Lists (See Appendix)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: September/October
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
Long/Short Vowels
LS2, LS3, LS4, SP1, SP3,
SP5
Fountas & Pinnell
-ed endings
WS5/WS6/WS18
Changing y to I before adding ed
WS18/WS19
-ack, -ock
SP2/SP16
Harcourt stories
Harcourt leveled library
Harcourt decodable books
Comprehension Toolkit
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Can use Daily 5 and
Daily Café as guides for building independence and to organize strategies for reading workshop.
SEE APPENDIX FOR K-3
SIGHT WORD LIST
8
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Fluency
STANDARD
Common Core
RF4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a.
Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b.
Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c.
Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, reread as necessary.
Fluency Benchmark: 44 WCPM
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How should reading sound?
* I can read fluently.
* I can read with expression.
* I can match my reading rate to the type of text.
* I can recognize when I need to self correct.
Vocabulary
Fluent
Fluency
Expression
Sight words
Accuracy
Timeline: September/October
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Assessment: DIBELS Benchmark and Monthly Progress Monitoring: Nonsense Words, Oral Reading Fluency (44 WCPM), Accuracy (Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 9
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Vocabulary
STANDARD
Common Core
RI4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
L4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies. (A-
E)
L5 Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
(A-B)
L6 Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
What is Vocabulary?
How does Vocabulary Grow?
* I can use context clues to figure out new words.
* I can use familiar word parts to figure out new words.
* I can use new vocabulary words
I have learned in stories read and in conversations.
Vocabulary vocabulary context clue strategy
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: September/October
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Teacher’s
Guide integrates vocabulary building within each story
CAFÉ vocabulary lessons build strategies
Notes
10
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Literature
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Recount stories, including fables and folktales from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson or moral.
3. Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges.
4. Describe how words and phrases supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem or song.
5. Describe the overall structure of a story, including describing how the beginning introduces the story and the ending concludes the action.
6. Acknowledge differences in the points of view of characters, including by speaking in a different voice for each character when reading dialogue aloud.
7. Use information gained from illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot.
9. Compare and contrast two or more versions of the same story.
10. By end of year, read and comprehend literature including stories and poetry in grades 2-3 text complexity proficiently with scaffolding as needed at the high end of range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
*I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
*I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
*I can choose good fit books.
*I can read poetry.
*I can identify Narrative
Elements (characters, plot, setting, theme).
*I can retell stories.
*I can compare/contrast two stories.
Vocabulary schema prior knowledge activate connection
Text to Text
Text to Self
Text to World
Metacognition
Fiction
Main Idea
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Genres:
Fantasy
Informational
Realistic Fiction
Story
Folktale
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: September/October
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Main Idea
Author’s Purpose
Narrative Elements
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 1 Lesson 1
Book 2 Lesson 6
Book 2 Lesson 7
Book 4 Lesson 12
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
11
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Informational
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as focus of specific paragraphs within text.
3. Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text.
4, Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
5. Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently.
6. Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe.
7. Explain how specific images (e.g. Diagram) contribute to and clarify a text.
8. Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text.
9. Compare and contrast the most important points presented by 2 texts on the same topic.
10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in grades 2-3 complexity proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
*I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
*I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
*I can choose good fit books.
*I can read informational text.
*I can tell what the main idea is in the story.
*I can find facts in the story.
Assessment:
Vocabulary schema prior knowledge activate connection
Text to Text
Text to Self
Text to World
Metacognition
Nonfiction
Main Idea
Author’s purpose
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Informational
Realistic Fiction
Story
Folktale
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: September/October
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies: Main Idea and Author’s Purpose
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 1 Lesson1
Book 2 Lesson 6
Book 2 Lesson 7
Book 4 Lesson 12
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
12
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Phonics and Word Recognition
STANDARD
Common Core
RF3 Know and apply grade-level phones and word analysis skills in decoding words a.
Distinguish long and short vowels when reading regularly spelled onesyllable words. b.
Know spelling-sound correspondences for additional common vowel teams. c.
Decode regularly spelled two-syllable words with long vowels. d.
Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes e.
Identify words with inconsistent but common spelling-sound correspondences. f.
Recognize and read grade appropriate irregularly spelled words.
Recognize and read grade-appropriate irregularly spelled words.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How do sounds form words?
I can read the short vowel sounds in words.
I can read long vowel sounds in words.
I can read words with vowel teams.
I can read consonant clusters at the beginning of words.
I know common abbreviations.
I can recognize a word pattern and use it to make other words.
Why are sight words important?
I can read sight words.
Vocabulary
Abbreviations
Vowel Combinations
Vowel Teams
Consonant Clusters
Timeline: November/December
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
Common Abbreviations
Consonant Clusters
Vowel Teams
WS20, LS6, LS7, LS9
Harcourt r-controlled vowels
/ur/ear r-controlled vowels
/or/our
Abbreviations ar,arm, ark spr, str, thr
Harcourt stories
Harcourt leveled library
Harcourt decodable books
Comprehension Toolkit
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Can use Daily 5 and
Daily Café as guides for building independence and to organize strategies for reading workshop.
SEE APPENDIX FOR K-3
SIGHT WORD LIST
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 13
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Fluency
STANDARD
Common Core
RF4 Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a.
Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b.
Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings.
Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, reread as necessary.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How should reading sound?
I can read fluently.
I can read with expression.
I can match my reading rate to the type of text.
I can recognize when I need to self correct.
Vocabulary fluent expression sight words accuracy
Assessment: DIBELS Progress Monitoring: Nonsense Words, Oral Reading Fluency, Accuracy (Record on SOAR)
Timeline: November/December
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 14
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Vocabulary
STANDARD
Common Core
RI4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
L4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies. (A-
E)
L5 Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
(A-B)
L6 Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
What is Vocabulary?
How does Vocabulary Grow?
I can use context clues to figure out new words.
I can use familiar word parts to figure out new words.
I can use new vocabulary words I have learned in stories read and in conversations.
I can understand words with several meanings.
Vocabulary vocabulary context clue strategy
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: November/December
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Teacher’s
Guide integrates vocabulary building within each story
CAFÉ vocabulary lessons build strategies
Notes
15
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Literature
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Recount stories, including fables and folktales from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson or moral.
3. Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges.
4. Describe how words and phrases supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem or song.
5. Describe the overall structure of a story, including describing how the beginning introduces the story and the ending concludes the action.
6. Acknowledge differences in the points of view of characters, including by speaking in a different voice for each character when reading dialogue aloud.
7. Use information gained from illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot.
9. Compare and contrast two or more versions of the same story.
10. By end of year, read and comprehend literature including stories and poetry in grades 2-3 text complexity proficiently with scaffolding as needed at the high end of range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
*I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
*I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
*I can choose good fit books.
*I can read poetry.
*I can identify Narrative
Elements (characters, plot, setting, theme)
*I can retell stories
*I can compare/contrast two stories
Vocabulary
Metacognition
Fiction
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Genre:
Nonfiction Photo Essay
Realistic Fiction
Story
Play
Expository Nonfiction
Assessment: RBA
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: November/December
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Main Idea
Predicting
Making Inferences
Compare/Contrast
Mental Image
Text Features
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 4 Lesson 13
Book 4 Lesson 14
Book 4 Lesson 15
Book 1 Lesson 2
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
16
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Informational
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as focus of specific paragraphs within text.
3. Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text.
4, Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
5. Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently.
6. Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe.
7. Explain how specific images (eg. Diagram) contribute to and clarify a text.
8. Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text.
9. Compare and contrast the most important points presented by 2 texts on the same topic.
10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in grades 2-3 complexity proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
I can choose good fit books.
I can read informational text.
I can tell what the main idea is in the story.
I can find facts in the story.
I can read diagrams, charts and graphs.
Assessment: RBA
Vocabulary
Metacognition
Fiction
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Genre:
Nonfiction
Nonfiction Photo Essay
Realistic Fiction
Story
Play
Expository Nonfiction
Timeline: November/December
Resources and
Materials
Notes
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Main Idea
Predicting
Making Inferences
Compare/Contrast
Mental Image
Text Features
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 4 Lesson 13
Book 4 Lesson 14
Book 4 Lesson 15
Book 1 Lesson 2
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 17
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Phonics and Word Recognition
STANDARD
Common Core
RF3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words a.
Distinguish long and short vowels when reading regularly spelled onesyllable words. b.
Know spelling-sound correspondences for additional common vowel teams. c.
Decode regularly spelled two-syllable words with long vowels. d.
Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes e.
Identify words with inconsistent but common spelling-sound correspondences. f.
Recognize and read grade appropriate irregularly spelled words.
How do sounds form words?
I can read words with suffixes.
I can read words with prefixes.
I can use prefixes and suffixes correctly.
I can read words with vowel combinations.
I know how to use plurals.
I can count the number of syllables in a word.
I can recognize a word pattern and use it to make other words.
Why are sight words important?
I can read sight words.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
Vocabulary
Vowel Combinations
Vowel teams
Consonant clusters
Prefixes
Suffixes
Past tense
Plurals
Timeline: January/February
Resources and
Materials
Notes
Fountas & Pinnell
Vowel Combinations
Plurals
Suffixes
Past Tense
Adding s, ed, ing
LS16, LS17, LS21, WS9,
WS16,WS25, LS9, SP10,
WS18, WS23, WS25
Harcourt
Vowel digraphs
Consonant digraphs
Inflections: s, es, ies
Vowel dipthongs /ou/
Vowel digraphs /oo/
Inflections: es (f to v)
Harcourt stories
Harcourt leveled library
Harcourt decodable books
Comprehension Toolkit
6 Minute Solutions
Can use Daily 5 and
Daily Café as guides for building independence and to organize strategies for reading workshop.
SEE APPENDIX FOR K-3
SIGHT WORD LIST
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 18
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Fluency
STANDARD
Common Core
RF 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a.
Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b.
Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c.
Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Fluency Benchmark: 68 WCPM
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How should reading sound?
I can read fluently.
I can read with expression.
I can match my reading rate to the type of text.
I can recognize when I need to self correct.
Vocabulary fluent expression sight words accuracy
Timeline: January/February
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Assessment: DIBELS Benchmark and Monthly Progress Monitoring: Nonsense Words, Oral Reading Fluency(68 CWPM), Accuracy (Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 19
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Vocabulary
STANDARD
Common Core
RI4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
L4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies. (A-
E)
L5 Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
(A-B)
L6 Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
What is Vocabulary?
How does Vocabulary Grow?
* I can use context clues to figure out new words.
* I can use familiar word parts to figure out new words.
* I can use new vocabulary words
I have learned in stories read and in conversations.
Vocabulary vocabulary context clue strategy
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: January/February
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Teacher’s
Guide integrates vocabulary building within each story
CAFÉ vocabulary lessons build strategies
Notes
20
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Literature
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Recount stories, including fables and folktales from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson or moral.
3. Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges.
4. Describe how words and phrases supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem or song.
5. Describe the overall structure of a story, including describing how the beginning introduces the story and the ending concludes the action.
6. Acknowledge differences in the points of view of characters, including by speaking in a different voice for each character when reading dialogue aloud.
7. Use information gained from illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot.
9. Compare and contrast two or more versions of the same story.
10. By end of year, read and comprehend literature including stories and poetry in grades 2-3 text complexity proficiently with scaffolding as needed at the high end of range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
*I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
*I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
*I can choose good fit books.
*I can read poetry.
*I can identify Narrative
Elements (characters, plot, setting, theme)
*I can retell stories
*I can compare/contrast two stories
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Genre:
Expository Nonfiction
Realistic Fiction
Story
Fantasy
Assessment: RBA
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: January/February
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Fact/Fiction
Making Inferences
Predicting/Inferences
Cause/Effect
Creating Mental Images
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 1 Lesson 3
Book 6 Lesson 19
Book 6 Lesson 20
Book 3 Lesson 8
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
21
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Informational
STANDARD
Common Core State
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as focus of specific paragraphs within text.
3. Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text.
4, Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
5. Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently.
6. Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe.
7. Explain how specific images (e.g. Diagram) contribute to and clarify a text.
8. Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text.
9. Compare and contrast the most important points presented by 2 texts on the same topic.
10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in grades 2-
3 complexity proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
I can choose good fit books.
I can read informational text.
I can tell what the main idea is in the story.
I can find facts in the story.
I can read diagrams, charts and graphs.
Assessment: RBA
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Genre:
Expository Nonfiction
Realistic Fiction
Story
Fantasy
Timeline: January/February
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Fact/Fiction
Making Inferences
Predicting/Inferences
Cause/Effect
Creating Mental Images
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 1 Lesson 3
Book 6 Lesson 19
Book 6 Lesson 20
Book 3 Lesson 8
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
22
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Phonics and Word Recognition
STANDARD
Common Core
RF3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words a.
Distinguish long and short vowels when reading regularly spelled onesyllable words. b.
Know spelling-sound correspondences for additional common vowel teams. c.
Decode regularly spelled two-syllable words with long vowels. d.
Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes e.
Identify words with inconsistent but common spelling-sound correspondences. f.
Recognize and read grade appropriate irregularly spelled words.
How do sounds form words?
I can read words with suffixes.
I can read words with prefixes.
I can add –er and –est to words correctly.
I can read words with vowel combinations.
I can read contractions.
I know how to read words with past tense.
I can count the number of syllables in a word.
I can recognize a word pattern and use it to make other words.
Why are sight words important?
I can read sight words.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
Vocabulary
Vowel Combinations
Vowel teams
Consonant clusters
Prefixes
Suffixes
Past tense
Plurals
Timeline: March/April
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
-er, -est
Vowel teams
Past Tense
WS13, WS15, WS21,
LS9, SP10, WS22
Harcourt
Suffixes: -ing, -ly
Prefixes: pre-, re-
Contractions
Vowel Digraphs
Consonant Digraphs
Suffixes: -er, -est r-controlled vowels: are, air
Harcourt stories
Harcourt leveled library
Harcourt decodable books
Comprehension Toolkit
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Can use Daily 5 and
Daily Café as guides for building independence and to organize strategies for reading workshop.
SEE APPENDIX FOR K-3
SIGHT WORD LIST
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 23
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Fluency
STANDARD
Common Core
RF 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a.
Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b.
Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c.
Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How should reading sound?
I can read fluently.
I can read with expression.
I can match my reading rate to the type of text.
I can recognize when I need to self correct.
Vocabulary fluent expression sight words accuracy
Timeline: March/April
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
6 Minute Solutions
Assessment: DIBELS Benchmark and Monthly Progress Monitoring: Nonsense Words, Oral Reading Fluency, Accuracy (Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Notes
24
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Vocabulary
STANDARD
Common Core
RI4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
L4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies. (A-
E)
L5 Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
(A-B)
L6 Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
What is Vocabulary?
How does Vocabulary Grow?
* I can use context clues to figure out new words.
* I can use familiar word parts to figure out new words.
* I can use new vocabulary words
I have learned in stories read and in conversations.
Vocabulary vocabulary context clue strategy
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: March/April
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Teacher’s
Guide integrates vocabulary building within each story
CAFÉ vocabulary lessons build strategies
Notes
25
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Literature
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Recount stories, including fables and folktales from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson or moral.
3. Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges.
4. Describe how words and phrases supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem or song.
5. Describe the overall structure of a story, including describing how the beginning introduces the story and the ending concludes the action.
6. Acknowledge differences in the points of view of characters, including by speaking in a different voice for each character when reading dialogue aloud.
7. Use information gained from illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot.
9. Compare and contrast two or more versions of the same story.
10. By end of year, read and comprehend literature including stories and poetry in grades 2-3 text complexity proficiently with scaffolding as needed at the high end of range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
I can choose good fit books.
I can read poetry.
I can identify Narrative
Elements (characters, plot, setting, theme).
I can retell stories.
I can compare/contrast two stories.
Assessment: RBA
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Summarize
Mental Image
Genre:
Informational
Play
Realistic Fiction
Personal Narrative
Fantasy
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: March/April
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Fact/Fiction
Narrative Elements
Compare/Contrast
Multiple Meanings
Summarizing
Mental Images
Making Inferences
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 3 Lesson 9
Book 3 Lesson 10
Book 3 Lesson 11
Book 5 Lesson 16
Revisit Book 4Lesson 12
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
26
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Informational
STANDARD
Common Core State
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as focus of specific paragraphs within text.
3. Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text.
4, Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
5. Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently.
6. Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe.
7. Explain how specific images (e.g. Diagram) contribute to and clarify a text.
8. Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text.
9. Compare and contrast the most important points presented by 2 texts on the same topic.
10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in grades 2-
3 complexity proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
I can choose good fit books.
I can read informational text.
I can tell what the main idea is in the story.
I can find facts in the story.
I can read diagrams, charts and graphs.
Assessment: RBA
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Summarize
Mental Image
Genre:
Informational
Play
Realistic Fiction
Personal Narrative
Fantasy
Timeline: March/April
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Fact/Fiction
Narrative Elements
Compare/Contrast
Multiple Meanings
Summarizing
Mental Images
Making Inferences
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 3 Lesson 9
Book 3 Lesson 10
Book 3 Lesson 11
Book 5 Lesson 16
Revisit Book 4Lesson 12
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
27
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Phonics and Word Recognition
STANDARD
Common Core
RF3 Know and apply grade-level phonics and word analysis skills in decoding words a.
Distinguish long and short vowels when reading regularly spelled onesyllable words. b.
Know spelling-sound correspondences for additional common vowel teams. c.
Decode regularly spelled two-syllable words with long vowels. d.
Decode words with common prefixes and suffixes e.
Identify words with inconsistent but common spelling-sound correspondences. f.
Recognize and read grade appropriate irregularly spelled words.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How do sounds form words?
I can read words with suffixes.
I can read words with prefixes.
I can read compound words.
I can read words with vowel combinations.
I know common abbreviations.
I can count the number of syllables in a word.
I can recognize a word pattern and use it to make other words.
Why are sight words important?
I can read sight words.
Vocabulary
Vowel Combinations
Vowel teams
Prefixes
Suffixes
Abbreviations
Compound Words
Timeline: May/June
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
Compound Words
Abreviations
WS1, WS2, WS20
Harcourt
Vowel Variants /oo/ ou
Vowel Digraphs /oo/ ou
Vowel Variants /o/ aw,au
Prefixes: over-, un-
Harcourt stories
Harcourt leveled library
Harcourt decodable books
Comprehension Toolkit
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Can use Daily 5 and
Daily Café as guides for building independence and to organize strategies for reading workshop.
SEE APPENDIX FOR K-3
SIGHT WORD LIST
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 28
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Fluency
STANDARD
Common Core
RF 4. Read with sufficient accuracy and fluency to support comprehension. a.
Read on-level text with purpose and understanding. b.
Read on-level text orally with accuracy, appropriate rate, and expression on successive readings. c.
Use context to confirm or self-correct word recognition and understanding, rereading as necessary.
Fluency Benchmark: 90+ WCPM
Essential Question
I Can Statement
How should reading sound?
I can read fluently.
I can read with expression.
I can match my reading rate to the type of text.
I can recognize when I need to self correct.
Vocabulary fluent expression sight words accuracy
Timeline: May/June
Resources and
Materials
Fountas & Pinnell
6 Minute Solutions
Notes
Assessment: DIBELS Benchmark and Monthly Progress Monitoring: Nonsense Words, Oral Reading Fluency(90+ CWPM), Accuracy (Record on SOAR)
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 29
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Vocabulary
STANDARD
Common Core
RI4 Determine the meaning of words and phrases in text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
L4 Determine or clarify the meaning of unknown and multiple-meaning words and phrases based on grade 2 reading and content, choosing flexibly from an array of strategies. (A-
E)
L5 Demonstrate understanding of word relationships and nuances in word meanings.
(A-B)
L6 Use words and phrases acquired through conversations, reading and being read to, and responding to texts, including using adjectives and adverbs to describe.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
What is Vocabulary?
How does Vocabulary Grow?
* I can use context clues to figure out new words.
* I can use familiar word parts to figure out new words.
* I can use new vocabulary words
I have learned in stories read and in conversations.
Vocabulary vocabulary context clue strategy
Assessment:
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: May/June
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Teacher’s
Guide integrates vocabulary building within each story
CAFÉ vocabulary lessons build strategies
Notes
30
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Literature
STANDARD
Common Core
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Recount stories, including fables and folktales from diverse cultures, and determine their central message, lesson or moral.
3. Describe how characters in a story respond to major events and challenges.
4. Describe how words and phrases supply rhythm and meaning in a story, poem or song.
5. Describe the overall structure of a story, including describing how the beginning introduces the story and the ending concludes the action.
6. Acknowledge differences in the points of view of characters, including by speaking in a different voice for each character when reading dialogue aloud.
7. Use information gained from illustrations and words to demonstrate understanding of characters, setting, plot.
9. Compare and contrast two or more versions of the same story.
10. By end of year, read and comprehend literature including stories and poetry in grades 2-3 text complexity proficiently with scaffolding as needed at the high end of range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
I can choose good fit books.
I can read poetry.
I can identify Narrative
Elements (characters, plot, setting, theme).
I can retell stories.
I can compare/contrast two stories.
I can read diagrams, charts and graphs.
Assessment: RBA
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Genre:
Nonfiction/Atlas
Informational Book
Story
Biography
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: May/June
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Locate Information
Author’s Purpose
Narrative Elements
Predicting
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 5 Lesson 17
Book 5 Lesson 18
Book 6 Lesson 21
Book 6 Lesson 22
Fountas and Pinnell
Poetry Book
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
31
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Core Content: Comprehension/Informational
STANDARD
Common Core State
1. Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text.
2. Identify the main topic of a multi-paragraph text as well as focus of specific paragraphs within text.
3. Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text.
4, Determine the meaning of words and phrases in a text relevant to a grade 2 topic or subject area.
5. Know and use various text features to locate key facts or information in a text efficiently.
6. Identify the main purpose of a text, including what the author wants to answer, explain, or describe.
7. Explain how specific images (e.g. Diagram) contribute to and clarify a text.
8. Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text.
9. Compare and contrast the most important points presented by 2 texts on the same topic.
10. By the end of the year, read and comprehend informational texts, including history/social studies, science, and technical texts, in grades 2-3 complexity proficiently, with scaffolding as needed at the high end of the range.
Essential Question
I Can Statement
*I can understand what I am reading.
_stop and check for understanding
_reread
_cross check
_use picture clues
*I can build my reading stamina when I read to self.
_look at the pictures
_read the words
_retell the story
*I can choose good fit books.
*I can read informational text.
*I can tell what the main idea is in the story.
*I can find facts in the story.
Assessment: RBA
Vocabulary
Main Idea
Predictions
Inferences
Fact and Fiction
Author’s purpose
Narrative Elements
Characters
Setting
Plot
Compare/Contrast
Sequence
Cause and Effect
Mental Image
Genre:
Nonfiction/Atlas
Informational Book
Story
Biography
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012
Timeline: May/June
Resources and
Materials
Harcourt Reading
Strategies:
Locate Information
Author’s Purpose
Narrative Elements
Predicting
Comprehension Toolkit
Book 5 Lesson 17
Book 5 Lesson 18
Book 6 Lesson 21
Book 6 Lesson 22
Daily 5
Daily Café
Notes
32
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Kindergarten High Frequency Words
Good readers know many common words automatically. These words are called “sight words” or “high-frequency” words.
The Fry Instant Word Lists includes the most frequently used words for reading and writing. The words are listed in rank order.
Kindergarten students should be able to read these 30 sight words by the end of the year to be meeting benchmark.
List 1 the of and a to in is you that
List 2 he was for on are as with his they
List 3 at be this have from or one had by it I words
Ideas to help your child practice at home:
Make flashcards, sort flashcards into know/don’t know piles, you say the word they point to it, read words from bottom to top/top to bottom (mix it up), find the words in books and on signs, write the words on a whiteboard and then read them, type them and read them, use sticky notes to put around the house, practice just a few at a time, time child on a list to see how many seconds…reread to beat the time, say each word in a sentence, I spy…a word that starts with __ and ends with __, do rhymes (and band, in tin), segment the words a-n-d, practice a few minutes each day until words are mastered.
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 33
Second Grade Literacy Guide
First Grade High Frequency Words
Good readers know many common words automatically. These words are called “sight words” or “high-frequency” words.
The Fry Instant Word Lists includes the most frequently used words for reading and writing. The words are listed in rank order.
First graders should be able to fluently read the 30 Kindergarten words and 60 First Grade Words by the end of first grade.
List 4
but not what
List 5
there use an
List 6
will up other
List 7
some her would
List 8
two more she
List 9
my than first all were we when your can each which she do how their said if
2 nd Grade Benchmark Goals:
List 10-11 by the middle of December
about out many then them these so make like him into time has look go see number no way could people water been called who oil its now
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 34
Second Grade Literacy Guide
List 12-14 by middle of March
List 15-16 by the end of May
Second Grade High Frequency Words
Good readers know many common words automatically. These words are called “sight words” or “high-frequency” words. The Fry Instant Word Lists includes the most frequently used words for reading and writing. The words are listed in rank order. Second graders should be able to fluently read the
30 Kindergarten words and 60 First Grade Words at the beginning of second grade.
List 10 List 11 List 12 List 13 List 14 List 15 List 16 new sound find long down day did get come made part over give most write take only little work know place years live me back say great where very after things our just name good sentence man think same tell boy help through much before line right too means old any put end does following came want show also around form three small set why ask went another well large must big even such because turned here better fact her less since side told days now himself nothing present system didn’t given knew order room toward
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 35
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Third Grade High Frequency Words
Good readers know many common words automatically. These words are called “sight words” or “high-frequency” words. The Fry Instant
Word Lists includes the most frequently used words for reading and writing. The words are listed in rank order. Third graders should be able to fluently read the Kindergarten words, 1st Grade Words and 2 nd grade words at the beginning of third grade.
men read need house point below country page plants don’t few while group often run state once book girl
sometimes
mountains land letters last different mother home answer school father along might close move us try kind found study still learn keep trees never started something seemed next hard hand should picture American again change world high city earth eyes light open example beginning life off play spell air ever near add food away animals between own thought head under story saw left always those both paper together got important hear until stop children without side feet car miles night walked white sea began grow took river four carry second later miss idea cut young talk soon list song being enough eat leave family face watch it’s far
Indians really almost let above
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 36
Second Grade Literacy Guide
Burlington Edison Revised August 2012 37