Climate Change
advertisement

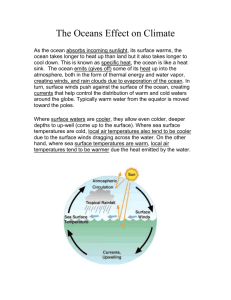
Climate Change Ch. 12 Study Guide 1. Identify 2 physical features and explain how they influence the climate. Latitude Elevation 2. List 2 geographic features and explain how they influence the climate of an area. Geographic features 1. Mountains • Precipitation – Rain shadow • Wind 2. Oceans • Humidity • Temperature- moderator 3. Lakes • Snow 3. What is the significance of growth rings in trees as indicators of environmental change? • Indicate weather – Shows the amount of growth per year • Rings close together= cold climate • Rings far apart = warm climate 4. What is the significance of ice cores from glaciers as indicators of environmental change? • • • • • Dust forms a layer each year Scientists can count layers Dark layer=winter Light layer=summer seasons Air bubbles- CO2 is high during warm temperatures 5. What is the significance of geologic sediments as indicators of environmental change? • Shells of organism spiral in one direction during warm weather and the other direction during cold weather • If shell has lots of Oxygen then the temperature was more cold 6.What is the significance of glacial sediments and landforms as evidence for climate change? • Glacier= cold climate • Glacier melts releasing dirt • Dirt is blown by the wind to nearby areas • Glacial dirt then indicates that area was close to or covered by a glacier 7. What is the significance of fossil pollen as evidence for climate change? • Certain types of trees grow during certain temperatures • Trees release pollen • Pollen layers then give clues to what the temperature was like • The thickness of the layer can indicate how long that time period lasted. 8. What is the Earth’s axial tilt? How are the Earth’s seasons related to the axial tilt? • Tilt=23.5 º • During the summer we are point toward the sun thus we have warmer temperatures • During the winter we are tilted away from the sun so we have colder temperatures. 9. What is the shape of the Earth’s orbit? How does the shape influence climate? • Earth’s orbit is elliptical • During the summer the earth is closer to the sun thus warmer temperatures • During the winter the earth is farther away from the sun, thus cooler temperatures 10. Explain how ocean currents affect regional and global climate? • Regional – Cold current causes colder weather – Warm current causes warmer weather • Global – Ocean water travels from colder north to the warmer south • thermohaline circulation– Cold salty water sinks, flows south and slowly warms, warm water is then push north and slowly sinks-thus a cycle is formed – If the circulation stops then an ice age will slowly begin 12. How is the Earth’s climate influenced by: • Plate Movements – Ice sheets only form on land close to the north or south pole • The more ice sheets the cooler the climate – Land has a lower heat capacity, as the land moves to where is gets more sun then the temperature also increases – Changes the position of the continents • Currents tend to hug along continents so as the continents move so do the currents 12. How is the Earth’s climate influenced by: • Ocean Currents • Water has a higher heat capacity if the ocean is receiving most of the sun light then the temperature remains more consistent • Thermohaline circulation, ocean conveyor belt Circulates the oceans water 13. What is the relationship between carbon dioxide and global temperature? • As carbon dioxide increases the global temperature increases as well 14. Explain why/how carbon dioxide effects global temperature. • Carbon dioxide acts like a greenhouse wall it allows heat and sun to come in but it does not allow it back out thus causing an increase in global temperature 15. List 5 causes of global warming. • Greenhouse gases – – – – • • • • • CO2- carbon dioxide CH4- methane H20- water Nitrogen Oxides- burning fossil fuels, ex. Gasoline, coal Volcanoes Cutting down forests Factories Cars Aerosol cans 16. List at least 4 effects of global warming. • ice caps melting • Global temperature increasing thus changing growing and crop seasons • Animals losing their habitat • Ocean currents changing