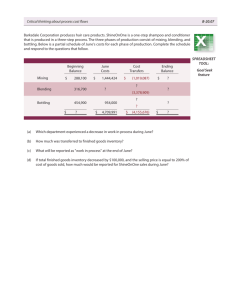
What problem in its supply chain system did Whirlpool face by 2000
advertisement

Study Guide 3 1. (ignore this question) What problem in its supply chain system did Whirlpool face by 2000? a. b. c. d. High inventory of finished goods but low availability Low amounts of finished goods High availability of goods but poor forecasting High demand but low inventories of finished goods 2. Which of the following business values of supply chain management systems did Whirlpool’s solution illustrate most effectively? a. b. c. d. Using assets more effectively Speeding product time to market Matching supply to demand Reducing costs 3. A suite of integrated software modules for finance and accounting, human resources, manufacturing and production, and sales and marketing that allows data to be used by multiple functions and business processes best describes: a. b. c. d. process management software. ERP systems. groupware. application software. 4. This type of software enables data to be used by multiple functions and business processes for organization coordination and control: a. b. c. d. groupware. application software. collaboration software. enterprise software. 5.5 You have been asked to implement enterprise software for a manufacturer of kitchen appliances. . What is the first step you should take? a. b. c. d. Select the functions of the system you wish to use. Map the company’s business processes to the software’s business processes. Map the software’s business processes to the company’s business processes. Select the business processes you wish to automate. 6.6 A network of organizations and business processes for procuring raw materials, transforming . these materials into intermediate and finished products, and distributing the finished products to customers is called a: a. b. c. d. distribution channel. supply chain. value chain. marketing chain. 7. (Ignore this question) IHOP purchased a middleware software package to integrate its data because: a. b. c. d. middleware packages are built for adaptability. packaged software is less expensive. they were able to customize their business processes to this software. this packaged software addressed their unique needs. 8. A scheduling system for minimizing inventory by having components arrive exactly at the moment they are needed and finished goods shipped as soon as they leave the assembly line best describes which strategy: a. b. c. d. just-in-time strategy. stockless inventory. ASAP inventory. replenishment-only inventory. 9. A distortion of information about the demand for a product as it passes from one entity to the next across the supply chain is called: a. b. c. d. bullwhip effect. ripple effect. replenishment effect. exponential effect. 10. Which supply chain planning function determines how much product is needed to satisfy all customer demands? a. b. c. d. Distribution management Replenishment planning Demand planning Order planning 11. Some supply chain integration can be developed inexpensively by: a. b. c. d. adapting to the business processes embedded in SCM packages. using Internet technology adapting PRM modules customizing ERP software 12. A build-to-order supply-chain model is also called a: a. b. c. d. supply-driven model demand-driven model replenishment-driven model push-based model 13. Which type of enterprise application or technique would help you best identify hidden buying patterns of your customers? a. b. c. d. OLAP using a SCM system Data mining using a CRM system Predictive analysis using a PRM system None of the above 14. The measurement of the number of customers who stop using or purchasing products or services from a company is called: a. b. c. d. switching costs. churn rate. CLTV. switching rate. 15. This metric is based on the relationship between the revenue produced by a specific customer, the expenses incurred in acquiring and servicing that customer, and the expected life of the relationship between the customer and the company. a. b. c. d. Churn rate CLTV Cost per lead Cost per sale 16. Through what channel did e-commerce first evolve? a. Online advertising sales b. c. d. Internet portals Online book sales Internet service providers 17. Which new development is helping expand B2B e-commerce opportunities? a. b. c. d. Podcasting Blogs .NET and Web services Dropping of computing and networking component prices 18. Which of the following is not one of the unique features of e-commerce technology? a. b. c. d. Information density Information asymmetry Richness Interactivity 19. Information density refers to: a. b. c. d. the complexity and content of a message. the total amount and quantity of information delivered to consumers by merchants. the total amount and quantity of information available to all market participants. the amount of information available to reduce price transparency. 20. The effort required to locate a suitable product is called: a. b. c. d. price discrimination. search costs. menu costs. transparency costs. 21 Information __________________ exists when one party in a transaction has more information that is important for the transaction than the other party. a. b. c. d. transparency asymmetry symmetry imbalance 22. Selling the same goods to different targeted groups at different prices is called: a. b. c. d. price customization. price opacity. price gouging. price discrimination. 23. Varying a product’s price according to the supply situation of the seller is called: a. b. c. d. menu pricing. supply pricing. dynamic pricing. asymmetrical pricing. 24. Reducing the business process layers in a distribution channel is called: a. b. c. d. disintermediation. BPR. market segmentation. network effects. 25. Compared to traditional goods, digital goods: a. b. c. d. have higher marketing costs. have lower production costs. have greater pricing flexibility. have higher inventory costs. 26. Which of the following Internet business models does Amazon.com use? a. b. c. d. Information broker Transaction broker Online service provider Virtual storefront 27. Which of the following businesses utilizes the content provider Internet business model? a. b. c. d. Amazon.com eBay.com CNN.com Motocross.com 28. Which of the following is an ad that opens automatically and does not disappear until the user clicks on it? a. b. c. d. Banner ad Controlled ad Portal ad Pop-up ad 29. Internet content providers: a. b. c. d. generate from directing buyers to sellers. save users money and time by processing online sales dealings. provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. create revenue by providing digital content over the Web. 30. Online marketplaces: a. b. c. d. save users money and time by processing online sales dealings. provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. create revenue by providing digital content over the Web. sell physical products directly to consumers or individual businesses. 31. A “supersite” that provides a comprehensive entry point for a huge array of Internet resources and services is called a(n): a. b. c. d. portal. online syndicator. content provider. information broker. 32. Pure-play business models: a. b. c. d. are primarily used in business-to-business electronic commerce. do not sell a physical product. are extensions of traditional bricks-and-mortar businesses. did not have an earlier existing bricks-and-mortar business before they went to the Internet. 33. eBay is an example of: a. b. c. d. a click-and-mortar business. C2C electronic commerce. B2C electronic commerce. an online exchange. 34. Consumers selling goods and services electronically to other consumers best describes: a. b. c. d. disintermediation. C2C electronic commerce. M-commerce. B2C electronic commerce. 35. Tools that record customer activities at Web sites and store them in a log for further analysis are called: a. b. c. d. clickstream tracking tools. customer tracking tools. collaborative filtering tools. filtering tools. 36. Tools that compare user behavior and interests to make purchasing recommendations to users are called: a. b. c. d. clickstream tracking tools. customer tracking tools. collaborative filtering tools. filtering tools. 37. What strategy was implemented by Stonyfield Farm’s use of blogs? a. b. c. d. Low-cost leadership Product differentiation Focus on market niche Strengthen customer and supplier intimacy 38. EDI is: a. b. c. d. the use of Internet technologies for electronic data transactions. the exchange between two organizations of standard transactions through a network. electronic data invoicing. electronic delivery infrastructure. 39. The electronic payment system in which users make micropayments and purchases on the Web, accumulating a debit balance on their credit card or telephone bill is called a(n) _______ payment system. a. b. c. d. smart card accumulated balance digital stored value digital cash 40. The electronic payment system that uses a credit card-size plastic card that stores digital information and that can be used for electronic payments in place of cash is called: a. b. c. d. digital cash. e-cash. digital wallet. smart card. 41. The electronic payment system in which users make micropayments and purchases on the Web, accumulating a debit balance on their credit card or telephone bill is called a(n) _______ payment system. a. smart card b. accumulated balance digital c. stored value d. digital cash 42. These systems digitize, index, and tag documents according to a coherent framework. a. b. c. d. Wikis CAD Document management LMS 43. The senior executive responsible for the firm’s knowledge management program is the: a. b. c. d. CTO. CIO. CKO. CEO. 44. These are specialized systems built for engineers, scientists, and other knowledge workers charged with discovering and creating new knowledge for a company: a. b. c. d. KWS LMS Wikis CAD systems 45. A collection of internal and external knowledge in a single location for more efficient management and utilization by the organization is called a: a. b. c. d. KWS. knowledge repository. document database. document management system. 46. Which of the following is a collaboration tool used to support knowledge management systems? a. b. c. d. Blogs Wikis Social bookmarking All of the above 47. Which of the following is used for knowledge discovery? a. b. c. d. Expert systems Transaction processing systems Case-based reasoning Data mining 48. Technology that consists of computer-based systems that attempt to emulate human behavior is called: a. b. c. d. fuzzy logic. neural networks. AI technology. genetic algorithms. 49. Forward chaining is: a. b. c. d. a strategy for searching the rule base in an expert system that begins with information entered by the user. the programming environment of an expert system. a method of organizing expert system knowledge into chunks. a strategy for searching the rule base in an expert system that begins with a hypothesis. 50. Backward chaining is: a. b. c. d. a strategy for searching the rule base in an expert system that begins with information entered by the user. the programming environment of an expert system. a method of organizing expert system knowledge into chunks. a strategy for searching the rule base in an expert system that begins with a hypothesis. 51. An inference engine is: a. b. c. d. a strategy for searching the rule base in an expert system that begins with information entered by the user. the programming environment of an expert system. a method of organizing expert system knowledge into chunks. a strategy used to search through the rule base in an expert system by forward chaining or backward chaining. 52. Hardware and software that attempts to emulate the processing patterns of the biological brain best describes: a. b. c. d. neural network. expert system. case-based reasoning. fuzzy logic. 53. Genetic algorithms: a. b. c. d. develop solutions to particular problems using fitness, crossover, and mutation. represent knowledge as groups of characteristics. do not work for most problems. are based on logic. 54. Software programs that work in the background without direct human intervention to carry out specific, repetitive, and predictable tasks for individual users, business processes, or software applications, are called: a. b. c. d. intelligent agents. intelligent techniques. business intelligence. AI hybrid systems. 55. Where there is no well-understood or agreed-on procedure for making a decision, it is said to be: a. b. c. d. undocumented. unstructured. documented. semistructured. 56. The type of decision that can made by following a definite procedure is called a(n): a. b. c. d. structured decision. unstructured decision. semistructured decision. procedural decision. 57. Which type of decision is deciding whether to introduce a new product line? a. b. c. d. 58. Structured Unstructured Recurring Nonrecurring Which type of decision is most common at higher levels of management? a. b. c. d. Semistructured Unstructured Structured Undocumented 59. Which phase of decision making finds or recognizes a problem, need, or opportunity? a. b. c. d. Design Intelligence Choice Implementation 60. Mintzberg’s classification of managerial roles defines three main categories: a. b. c. d. interpersonal, informational, and decisional. symbolic, decisional, and interpersonal. symbolic, interpersonal, and technical. technical, interpersonal, and informational. 61. These systems support decision making by enabling users to extract useful information that was previously buried in large quantities of data: a. b. c. d. GSS. ESS. TPS. DSS. 62. Which type of model is used to help managers use historical data to estimate future conditions and sales figures resulting from these conditions? a. b. c. d. Optimization Sensitivity analysis Statistical Forecasting 63. This information system uses data visualization technology to analyze and display data for planning and decision making in the form of digitized maps. a. b. c. d. GIS DSS MIS TPS 64. Dell Computer’s online tools for selecting and customizing a new PC are a type of: a. DSS. b. c. d. CDSS. Web-based GIS. Intelligent agent. 65. (ignore this question) As discussed in the chapter case, the COMPSTAT system developed by the New York City Police was a type of: a. CDSS. b. PDSS. c. GIS. d. GDSS. Answer: C 66. (ignore this question) Electronic questionnaires in a GDSS: a. b. c. facilitate the organized integration and synthesis of ideas generated during brainstorming. document group agreement on definitions of words and terms central to the projects. use structured approaches to evaluate the impact of an emerging proposal on the organization. d. aid the organizers in pre-meeting planning by identifying issues of concern. Answer:D 67. Which of the following features of an ESS supplements traditional financial metrics with measurements from additional perspectives, such as customers, or learning and growth? a. b. c. d. Balanced scorecards Digital dashboard Graphic visualization tools Drill-down capabilities 68. The information system used by Caesar’s Entertainment, which combines data from internal TPS with information from financial systems and external sources to deliver reports such as profit-loss statements, impact analyses, is an example of: a. b. c. d. DSS ESS CDSS MIS 69. The concern that data values of an information source fall within a defined range reflects which quality dimension of information? a. b. c. d. Accuracy Integrity Validity Consistency