Renaissance - Fair Lawn Schools
advertisement

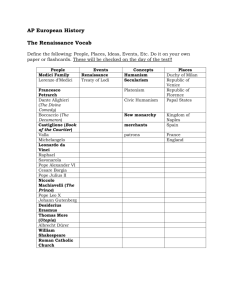
Welcome to the Renaissance! Cultural revival (change) in Europe (begins in Italy) 1300s – 1500s French for “Rebirth” Focus on learning education, history, literature and art General Overview : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4mgSPiAiBjU (2 ½ minutes) United Streaming: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HiTyTx13Clo (14 minutes) Let’s look at where it started: 1. Physical Environment: Italy Peninsula with three major rivers Mountains & mild climate Ports allowed the spread of people, goods, ideas Major trade route with the Middle East & China Money Matters! 2. Economics of the Renaissance: A switch from an agricultural system to a urban mercantile system. Related to commerce or trade Countries attempted to control as many different raw materials (resources) as possible Export raw materials & Import finished goods Goods: Wool, Shipbuilding, Silk Manufacturing, and Livestock Services: Banking and Trade Powerful Guilds (an organized group of people who have joined together because they share the same job or interest) 3.Government during the Renaissance: Wealthy merchants formed oligarchies (a small group of people having control of a country, organization, or institution) that governed each city-state Competition fueled the birth of the artistic development. Medici Family: Rulers and bank lenders in Florence Were successful because they never gave money to royalty –led to the birth of capitalism Devoted Christians and believed money lending was a mortal sin. Needed a way to save themselves from spending eternity “downstairs.” The Medici Family: Makers of Modern Art http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fwhXKvI dhWI THERE IS A WAY OUT! Money lenders could find redemption (the action of saving or being saved from sin, error, or evil) by becoming patrons (paying customers) who sponsored/funded (gave money) to many artist and architects. HOWEVER….must be the art or construction of churches or any aspect showing supporting for religion. Would have themselves occasionally added into paintings for added “insurance.” 4. Social Classes: 1. The Nobles: owned much of the land, and lived on large estates outside the city walls. 2. The Merchants: “The New Rich,” married into noble families. Built enormous gilded mansions in the city, villas in the country, and contributed to the construction of grand cathedrals. Social Classes (cont.) 3. Middle Class: shopkeepers and lived in the cities 4. The Peasants: farmers and lived in rural areas (the majority) 5. Religions & Values: Monotheism (one God) Roman Catholic Church People were encouraged to learn Latin and know the “word” of God. Theology: The study of religion and faith 6. Science and Technology: New view points and ideas were part of: Secularism Humanism Individualism 6. Science and Technology: Secularism: Topics or ideas not related to religion Law, Medicine, Philosophy, Engineering, and Science Decisions not always based on the Church or the Bible Writings were meant to inform/entertain vs. spirituality Wrote in Vernacular- everyday language Example of Secularism Writing: The Prince by Niccolo Machiavelli. Political writing aimed to manipulated others Negative view of human nature: ungrateful and selfish Leaders should be: Strong as a lion, smart like a fox Should remember ‘the end justifies the means.’ Scientific Discovery of Our Universe Copernicus: correctly placed the sun at the center of the solar system Galileo: physicist, mathematician, astronomer, philosopher Improvements to the telescope, astronomical observations Refer to Questioning of Galileo Worksheet for additional information Galileo (continued): Roman Inquisition believed the Sun and planets revolved around the Earth. Galileo believed in the idea of heliocentrism (planets evolved around a stationary sun) Put on trial for heresy (belief opinion that does not agree with the official belief or opinion of a particular religion) Book was banned and spent the rest of his life under house arrest. Humanism: Cultural change based on “Classical” works Borrowed Greek and Roman ideas Attempt to live a good life on Earth Self-worth vs. spirituality Individualism: The belief that the individual is more important than the larger community “Man is the measure of all things”- Protagoras The Printing Press Invented by Johannes Gutenberg, Germany1450 Could print copies of books quickly By 1500, twenty million books produced Increased literacy, spread ideas Literacy: The ability to read and write printed/written words Literacy and Censorship Publishers printed medical manuals, travel accounts, and broadsheets. People published criticisms of the Catholic Church. The Church began to censor what people could read. It published a list of prohibited books. Censor To remove material from published works or to prevent its publication 7.Cultural Developments: Art & Architecture: Classic ideas with realism Literature: William Shakespeare wrote about human weaknesses Books written in Vernacular Cultural Developments (continued): Painting and Sculptors: Leonardo da Vinci painted the Mona Lisa and the Last Supper Michelangelo sculpted the Statue of David and painted the Sistine Chapel Architecture: Filippo Brunelleschi created the Dome Basic Artist Styles Balance Harmony Perspective Proportion Symmetry