Performance Management Skills: Overview

Performance Management Skills:
Overview
Coaching
Coaching Styles
Coaching Process
Performance Review Meetings
Improving Your Coaching Skills
The Four-Step Coaching Process
1
2
3
4
Preparing to coach
Developing a mutually agreed change plan
Engaging in active coaching
Evaluating for feedback and follow-up
10–2
9-2
Preparing to Coach:
Applying the ABC Approach
A ntecedents
What things must come before the person does the job?
B ehavior
Can the person do the job if he or she wanted to?
C onsequences
What are the consequences of doing the job right?
10–3
9-3
FIGURE 10–1 A Short Course in Improving Interpersonal
Communications
10–4
9-4
Establishing an Effective
Mentoring Program
Require mentoring?
Provide mentoring training?
Does distance matter?
Same or different departments?
Big or small difference in rank?
10–5
9-5
Choosing a Mentor
Choose an appropriate potential mentor.
Don’t be surprised if you’re turned down.
Be sure that the mentor understands what you expect in terms of time and advice.
Have an agenda.
Respect the mentor’s time.
10–6
9-6
Characteristics of Effective Mentors
Are professionally competent
Are trustworthy
Are consistent
Have the ability to communicate
Are willing to share control
Set high standards
Are willing to invest time and effort
Actively steer protégés into important work
10–7
9-7
FIGURE 10–2
Coach’s
Self-
Evaluation
Checklist
10–8
9-8
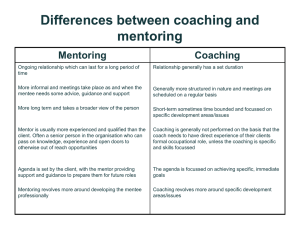
Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching
Involves educating, instructing, and training subordinates
Focuses on teaching shorter-term job-related skills
Mentoring
Is actively advising, counseling, and guiding
Is helping employees navigate longer-term career hazards
Is leading highly trained employees and self-managing teams
Supplants the need for authority and for giving orders for getting things done
Coaching and mentoring require both analytical and interpersonal skills.
10–9
9-9
Coaching: Definition (1)
Helping relationship
Manager
Interacts with employee and
Takes active role and interest in performance
Coaching: Definition (2)
Collaborative ongoing process
Directing employee behavior
Motivating employee behavior
Rewarding employee behavior
Concern with long-term performance
Understanding Successful Coaching
Guiding Principles (1 )
A good coaching relationship is essential
:
Trusting and collaborative
Willing to listen in order to understand
Looking for positive aspects of the employee
Understanding that coaching is done
with the employee, not to the employee
Understanding Successful Coaching
Guiding Principles (2)
The Employee is the Source and
Director of change
The Employee is whole and unique
The Coach is the Facilitator of the
Employee’s growth
Major Coaching Functions:
Give advice
Provide guidance
Provide support
Give confidence
Promote greater competence
Leading vs. Managing
Leading
Aim is positive change
Setting direction
Aligning people to vision
Motivating
Coaching
Managing
Aim is predictable, orderly results
Organizing
Staffing
Planning
Budgeting
Solving problems
Managers are responsible for implementing a plan. Leaders grow the dream and enroll people to help achieve it.
HEAD
HEART
Motivation
Energy
Enthusiasm
Passion
PERSONAL
ENGAGEMENT
INTELLECTUAL
UNDERSTANDING
Frameworks
Models
Tools
Examples
Demonstration
Behaviours
HAND
WALKING THE TALK
9-16
9-17
GROW steps
G – GOAL: What do you want?
R – REALITY: What is happening now ?
O – OPTIONS: What could you do?
W – WILL: What will you do?
9-18
The GROW model
GOAL
What do you want to move forward on…?
What can we achieve in the time available…? What would be the most helpful thing for you to take away from this session?
G R O
T W
TOPIC
Tell me about…
What would you like to think/talk about…?
Give me a flavour in a few short sentences...
REALITY
What is happening now that tells you…? Describe the current situation… What made you realise that you need to do something different?
OPTIONS
What could you do to move yourself just one step forward…?
What are your options…? How far towards your objective will that take you…?
WILL
What will you do next…?
How, when, with whom…?
What do you need from me?
21
9-19
Key Coaching Behaviors
Establish developmental objectives
Communicate effectively
Motivate employees
Document performance
Give feedback
Diagnose performance problems
Develop employees
The Good Coach Questionnaire
Do you listen to your employees?
Do you understand the individual needs of your employees?
Do you encourage employees to express their feelings openly?
Do you provide your employees with tangible and intangible support for development?
Do your employees know your expectations about their performance?
(continued on next slide)
The Good Coach Questionnaire
(continued)
Do you encourage open and honest discussions and problem solving?
Do you help your employees create action plans that will
Solve problems?
Create changes?
Do you help your employees explore potential areas of growth and development?
Coaching Styles
More assertive
Less assertive
Task & Fact oriented
People oriented
Driver
Persuader
Analyzer
Amiable
Adaptive coaches use all styles according to employee needs:
Sometimes providing direction
Sometimes persuading
Sometimes showing empathy
Sometimes paying close attention to rules and established procedures
Coaching Process
Coaching Process:
Set Developmental Goals
Identify Resources and Strategies
Needed to Implement
Developmental Goals
Implement Developmental Goals
Coaching Process:
Overview of remaining steps
Observe and Document
Developmental Behavior and
Outcomes
Give Feedback
Praise
Negative Feedback
Observe and Document Developmental Behavior and Outcomes
Constraints:
Time
Situation
Activity
Organizational Activities to improve documentation of performance
Good communication plan to get manager buy-in
Training programs
Rater error training
Frame-of-reference training
Behavioral observation training
Self-leadership training
Reasons to document performance
Minimize cognitive load
Create trust
Plan for the future
Provide legal protection
Recommendations for Documentation
Be specific
Use adjectives and adverbs sparingly
Balance positives with negatives
Focus on job-related information
Be comprehensive
Standardize procedures
Describe observable behavior
Giving Feedback
Main purposes:
Help build confidence
Develop competence
Enhance involvement
Improve future performance
Potential costs of failing to provide feedback:
Employees are deprived of chance to improve their own performance
Chronic poor performance
Employees have inaccurate perceptions of how their performance is regarded by others
To be effective, feedback should :
Be timely
Be frequent
Be specific
Be verifiable
Be consistent (over time and across employees)
Be given privately
Provide context and consequences
To be effective, feedback should:
(continued)
Provide description first, evaluation second
Cover the continuum of performance
Identify patterns
Demonstrate confidence in employee
Allow for both
Supervisor’s advice and
Idea generation by both
Employee
Supervisor
Guidelines for Giving Praise
Be sincere – only give praise when it is deserved
Give praise about specific behaviors or results
Take your time
Be comfortable with act of praising
Emphasize the positive
Giving Negative Feedback
Managers avoid giving negative feedback due to:
Negative reactions and consequences
Negative experiences in the past
Playing “god”
Need for irrefutable and conclusive evidence
Negative feedback is most useful when it:
Identifies warning signs and performance problem is still manageable
Clarifies unwanted behaviors and consequences
Focuses on behaviors that can be changed
Comes from a credible source
Is supported by hard data
Feedback Sessions should always answer: (1)
How is your job going?
Do you have what you need to do your job?
Are you adequately trained?
Do you have the skills and tools you need to do your job?
Feedback Sessions should always answer: (2)
What can be done to improve?
Job
Product
Services
How can you better serve your customers?
Internal
External
Supervisory roles in managing performance
Judge
Evaluate performance
Allocate rewards
Coach
Help employee solve performance problems
Identify performance weaknesses
Design developmental plans
Performance Review Formal Meetings
Possible types of formal meetings:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
System Inauguration
Self-Appraisal
Classical Performance Review
Merit/Salary Review
Developmental Plan
Objective Setting
Steps to take before meeting:
Give at least 2 weeks notice
Block sufficient time
Arrange to meet in a private location without interruptions
Merged Performance Review Meeting
Components
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
1.
2.
3.
4.
Explanation of meeting purpose
Employee self-appraisal
Supervisor & employee share rating and rationale
Developmental discussion
Employee summary
Rewards discussion
Follow-up meeting arrangement
Approval and appeals process discussion
Final recap
Possible defensive behaviors of employees
Fight response
Blaming others
Staring at supervisor
Raising voice
Other aggressive responses
Flight response
Looking/turning away
Speaking softly
Continually changing the subject
Quickly agreeing without basis
Other passive responses
To prevent/reduce defensive behaviors
Establish and maintain rapport
Be empathetic
Observe verbal and nonverbal cues
Minimize threats
Encourage participation
When defensiveness is unavoidable :
Recognize it
Allow its expression
Accept employee’s feelings
Ask for additional information and clarification (if appropriate)
If situation becomes intolerable
Reschedule the meeting for a later time
•
Creating a coaching culture
Build on strengths, create energy for positive change
•
•
• Value everyone’s differences and uniqueness
Have regular, consistent, structured conversations with each person
Plan and agree on stretch goals; review frequently
24
9-48
Group Exercise A
Break into groups.
Work in your groups to define
Seven features of a good coaching relationship.
Think about coaches you have admired.
"Bad habits are like a comfortable bed, easy to get into, but hard to get out of."
Unknown
9-49
Group Exercise B
Break into groups.
Work in your groups to define
Seven habits, qualities, attributes or traits of a good coach.
Think about coaches you have admired.
"Bad habits are like a comfortable bed, easy to get into, but hard to get out of."
Unknown
9-50
Group Exercise C
Break into groups.
Work in your groups to define the process of coaching
The five step process of how a coaching relationship unfolds over time; what happens first, then the rest of the sequence
"I don' like that man. I'm going to have to get to know him better."
Abraham Lincoln
9-51
The Coach in You
Current Strengths
Opportunities
9-52