2013 Lesson Plans - Week of August 25, 2013
advertisement

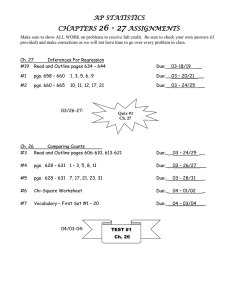
Week of August 25, 2013 Monday Tuesday Wednesday 11-12.RST.4 11-12.RST.8 N.RN.3 A.SSE.1 11-12.RST.4 11-12.RST.8 9-12.P.1.5 9-12.N.1.2 9- A.SSE.2 A.SSE.3 9-12.P.1.5 9-12.N.1.2 912.N.2.2 9-12.N.2.3A A.APR.6 A.APR.7 12.N.2.2 9-12.N.2.3A Advanced Chemistry A.REI.3 F.BF.1.a Advanced Chemistry Algebra III Thursday Friday N.RN.3 A.SSE.1 A.SSE.2 A.SSE.3 A.APR.6 A.APR.7 A.REI.3 F.BF.1.a 11-12.RST.4 11-12.RST.8 9-12.P.1.5 9-12.N.1.2 912.N.2.2 9-12.N.2.3A Advanced Chemistry Algebra III Chapter 1 - Matter and Measurement Chapter 1 - Matter and Chapter P Measurement Preliminary Section 1.1 - Chemistry: Concepts Section 1.1 - Chemistry: Principles and Principles and Section P.1 - The Applications Applications Real Number Section 1.2 - Getting Section 1.2 - Getting System Started: Some Key Started: Some Key Terms Terms Section 1.3 - Scientific Objectives Section 1.3 - Scientific Measurements Measurements Section 1.4 - Precision 1. Sets Section 1.4 - Precision 2. Union and and Accuracy and Accuracy Section 1.5 - A Problem Intersection of Section 1.5 - A Problem Sets Solving Method Solving Method 3. Absolute Value Section 1.6 - Further Section 1.6 - Further and Distance Remarks on Problem Remarks on Problem 4. Interval Solving Solving Notation 5. Order of Objectives Objectives Operations 6. Simplifying 1. Describe the usual 1. Describe the usual Variable method used to study method used to study Expressions science. science. Chapter P Preliminary Concepts Chapter 1 - Matter and Measurement Section 1.1 - Chemistry: Principles and Section P.2 Applications Integer and Section 1.2 - Getting Rational Number Started: Some Key Exponents Terms Section 1.3 - Scientific Objectives Measurements Section 1.4 - Precision 1. Properties of and Accuracy Exponents Section 1.5 - A Problem 2. Scientific Solving Method Notation Section 1.6 - Further 3. Rational Remarks on Problem Exponents and Solving Radicals 4. Simplify Objectives Radical Expressions 1. Describe the usual method used to study Assessment science. 2. Classify a sample of Assessment 2. Classify a sample of Pgs. 31-34 (1-123 2. Classify a sample of every other odd) matter as being matter as being matter as being Pgs. 15-17 (1-113 substance or mixture, substance or mixture, substance or mixture, every other odd) element or compound, element or compound, element or compound, homogeneous or homogeneous or homogeneous or heterogeneous. heterogeneous. heterogeneous. 3. Classify properties and changes as chemical or physical, and understand the differences between them. 3. Classify properties and changes as chemical or physical, and understand the differences between them. 3. Classify properties and changes as chemical or physical, and understand the differences between them. 4. Recognize and use the common SI units and 4. Recognize and use the common SI units and 4. Recognize and use the common SI units and prefixes. prefixes. prefixes. 5. Express and convert measurements using the common SI prefixes and exponential notation. 5. Express and convert measurements using the common SI prefixes and exponential notation. 5. Express and convert measurements using the common SI prefixes and exponential notation. 6. Convert, when relevant data are given, measurements between the SI and other systems of measurement. 6. Convert, when relevant data are given, measurements between the SI and other systems of measurement. 6. Convert, when relevant data are given, measurements between the SI and other systems of measurement. 7. Use the appropriate number of significant figures in writing numbers and expressing calculation results. 7. Use the appropriate number of significant figures in writing numbers and expressing calculation results. 7. Use the appropriate number of significant figures in writing numbers and expressing calculation results. 8. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision. 8. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision. 8. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision. 9. Solve problems, including those involving density, using the unitconversion method. 9. Solve problems, including those involving density, using the unitconversion method. 9. Solve problems, including those involving density, using the unitconversion method. Assessment Assessment Assessment Pgs. 27-31 (1-71 odd) Pgs. 27-31 (1-71 odd) A.REI.11 F.BF.1 F.BF.1.a Prep F.BF.1.b A.REI.11 F.IF.9 F.BF.1 F.BF.1.a F.BF.1.b F.BF.3 Algebra II Algebra II Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Pgs. 27-31 (1-71 odd) A.REI.11 Algebra II Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Section 1.1 - Collecting and Organizing Data Prep Quiz 1.1-1.4 Section 1.3 - Relations and Functions Objectives Objectives Organize data in tables, matrices, and graphs in 1. Design and use Section 1.5 - Vertical and Horizontal Translations order to analyze relationships and calculate data totals. relations and functions. Objectives 2. Determine whether a relation is a function. 1. Analyze vertical and horizontal translations of a function. Assessment Assessment Pgs. 8-10 (1-22 all) Pgs. 23-25 (1-11 odd, 12, 17-29 odd, 35-41 odd) Section 1.2 - Graphical Models Objectives Pgs. 35-37 (1-41 every other odd) Pg. 37 - Checkpoint (214 even) Section 1.4 - Working with Functions Represent data graphically to make reasonable predictions about events. Objectives 1. Combine functions. Assessment 2. Add functions. Pgs. 15-18 (2-10 even, 13, 15-19 odd) Assessment Lunch Assessment Lunch Pgs. 29-31 (1-67 every other odd) Lunch Lunch Lunch 11-12.RST.1 11-12.RST.2 11-12.RST.3 1111-12.RST.3 9-12.N.2.2 9- 12.RST.4 1112.N.2.3A 12.RST.5 1112.RST.6 9Applied Chemistry 12.N.2.1 912.N.2.2 9Unit 1 - Chapter 2 12.N.2.3A Measurements 11-12.RST.1 11-12.RST.2 11-12.RST.3 1111-12.RST.3 9-12.N.2.2 9- 12.RST.4 1112.N.2.3A 12.RST.5 1112.RST.6 9Applied Chemistry 12.N.2.1 912.N.2.2 9Unit 1 - Chapter 2 12.N.2.3A Measurements 11-12.RST.1 11-12.RST.2 11-12.RST.3 9-12.N.2.2 912.N.2.3A Section 2.1 - Units of Measurement Section 2.1 - Units of Measurement Section 2.1 - Units of Measurement Chemistry Objective Write the names and abbreviations for the metric SI units used in measurements of length, volume, mass, temperature, and time. Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Chemistry Chapter Objectives Chemistry Objective Write the names and abbreviations for the metric SI units used in 1. Define all of measurements of length, the terms in the volume, mass, Chapter Glossary. temperature, and time. Chapter 1 - An Introduction to Chemistry Applied Chemistry Unit 1 - Chapter 2 Measurements Objective Chapter Objectives Write the names and abbreviations for the metric SI units used in 1. Define all of measurements of length, the terms in the volume, mass, Chapter Glossary. temperature, and time. Section 2.2 - Scientific Section 1.3 - The Section 2.2 - Scientific Section 1.3 - The Section 2.2 - Scientific Scientific Scientific Notation Notation Notation Method Method Objective Write a number in scientific notation Objective 2. Describe how science in general Write a number in is done. scientific notation Section 2.3 - Measured Section 1.4 Numbers and Measurement Significant Figures and Units Objective 2. Describe how science in general Write a number in is done. scientific notation Section 2.3 - Measured Section 1.4 Numbers and Measurement Significant Figures and Units Section 2.3 - Measured Numbers and Significant Figures Objective 3. Use the Objective 3. Use the Objective International International Identify a number as System of Identify a number as System of Identify a number as measured or exact; Measurements measured or exact; Measurements measured or exact; determine the nuber of (SI) base units determine the nuber of (SI) base units determine the nuber of significant figures in a and their significant figures in a and their significant figures in a measured number. abbreviations to measured number. abbreviations to measured number. describe length, describe length, Section 2.4 - Significant mass, time, Section 2.4 - Significant mass, time, Section 2.4 - Significant Figures in Calculations temperature, and Figures in Calculations temperature, and Figures in Calculations volume. volume. Objective Objective Objective 4. Describe the 4. Describe the Adjust calculated relationship Adjust calculated relationship Adjust calculated answers to give the between liters and answers to give the between liters and answers to give the correct number of cubic meters. correct number of cubic meters. correct number of significant figures. significant figures. significant figures. 5. State the 5. State the Section 2.5 - Prefixes numbers or Section 2.5 - Prefixes numbers or Section 2.5 - Prefixes fractions fractions and Equalities and Equalities and Equalities represented by represented by Objective the following Objective the following Objective metric prefixes, metric prefixes, Use the numerical values and write their Use the numerical values and write their Use the numerical values of prefixes to write a abbreviations: of prefixes to write a abbreviations: of prefixes to write a metric equality giga, mega, kilo, metric equality giga, mega, kilo, metric equality centi, milli, centi, milli, Section 2.6 - Writing micro, nano, and Section 2.6 - Writing micro, nano, and Section 2.6 - Writing pico. pico. Conversion Factors Conversion Factors Conversion Factors Objective 6. Describe the relationships Write a conversion between the factor for two units that metric units that describe the same do not have quantity. prefixes (such as meter, gram, and Section 2.7 - Problem liter) and units derived from Solving them by the Objective 6. Describe the relationships Write a conversion between the factor for two units that metric units that describe the same do not have quantity. prefixes (such as meter, gram, and Section 2.7 - Problem liter) and units derived from Solving them by the Objective Write a conversion factor for two units that describe the same quantity. Section 2.7 - Problem Solving Objective addition of prefixes. Objective addition of prefixes. Use conversion factors to change from one unit 7. Given a metric to another. unit, write its abbreviation; Section 2.8 - Density given an abbreviation, Objective write the full name of the Calculate the density of unit. a substance; use the density to calculate the 8. Use everyday mass or volume of a examples to substance. describe the approximate size of a millimeter, a Assessment centimeter, a meter, and a Worksheet Packet kilometer. Use conversion factors to change from one unit 7. Given a metric to another. unit, write its abbreviation; Section 2.8 - Density given an abbreviation, Objective write the full name of the Calculate the density of unit. a substance; use the density to calculate the 8. Use everyday mass or volume of a examples to substance. describe the approximate size of a millimeter, a Assessment centimeter, a meter, and a Worksheet Packet kilometer. 9. Use everyday examples to describe the approximate size of a milliliter, a liter, and a cubic meter. 9. Use everyday examples to describe the approximate size of a milliliter, a liter, and a cubic meter. 10. Describe the relationship between cubic centimeters and milliliters. 10. Describe the relationship between cubic centimeters and milliliters. 11. Describe the relationship between mass and weight. 11. Describe the relationship between mass and weight. 12. Name the two factors that cause the weight of an object to change. 12. Name the two factors that cause the weight of an object to change. 13. Use everyday examples to describe the approximate size 13. Use everyday examples to describe the approximate size Objective Use conversion factors to change from one unit to another. Section 2.8 - Density Objective Calculate the density of a substance; use the density to calculate the mass or volume of a substance. Assessment Worksheet Packet of a gram, a kilogram, and a megagram. of a gram, a kilogram, and a megagram. 14. Describe the relationships between metric tons, kilograms, and megagrams. 14. Describe the relationships between metric tons, kilograms, and megagrams. 15. Describe the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales. 15. Describe the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin temperature scales. 16. Describe the relationship between a degree Celsius, a degree Fahrenheit, and a kelvin. 16. Describe the relationship between a degree Celsius, a degree Fahrenheit, and a kelvin. Section 1.5 Reporting Values from Measurements Section 1.5 Reporting Values from Measurements 17. Given values for a series of measurements, state the precision of the measurements. 17. Given values for a series of measurements, state the precision of the measurements. 18. Report measured values so as to show their degree of uncertainty. 18. Report measured values so as to show their degree of uncertainty. 19. Given a value derived from a measurement, identify the range of possible values it represents based on the 19. Given a value derived from a measurement, identify the range of possible values it represents based on the A.REI.11 Algebra II Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Section 1.1 - Collecting and Organizing Data assumption that its uncertainty is ±1 in the last position reported. assumption that its uncertainty is ±1 in the last position reported. Assessment Assessment Pgs. 27-31 (15-47 Pgs. 27-31 (15-47 odd) odd) A.REI.11 F.BF.1 F.BF.1.a SRB A.REI.11 F.IF.9 F.BF.1 SRB F.BF.1.b F.BF.1.a F.BF.1.b F.BF.3 Algebra II Algebra II Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Chapter 1 - Models, Functions, and Permutations Quiz 1.1-1.4 Section 1.3 - Relations and Functions Objectives Objectives Organize data in tables, matrices, and graphs in order to analyze relationships and calculate data totals. 1. Design and use relations and functions. 2. Determine whether a relation is a function. Assessment Section 1.5 - Vertical and Horizontal Translations Objectives 1. Analyze vertical and horizontal translations of a function. Assessment Pgs. 8-10 (1-22 all) Section 1.2 - Graphical Models Objectives Represent data graphically to make reasonable predictions about events. Pgs. 23-25 (1-11 odd, 12, 17-29 odd, 35-41 odd) Section 1.4 - Working with Functions Objectives 1. Combine functions. Assessment 2. Add functions. Pgs. 15-18 (2-10 even, 13, 15-19 odd) Assessment Pgs. 29-31 (1-67 every other odd) Assessment Pgs. 35-37 (1-41 every other odd) Pg. 37 - Checkpoint (214 even)