What's a Region?
advertisement

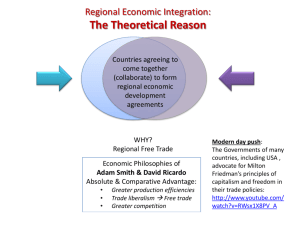
GO131: International Relations Professor Walter Hatch Colby College Regionalism Defining Terms Regionalization (an economic process) market integration associated with the cross-border flow of capital, labor, and technology within a specific area or region Regionalism (a political process) cooperation among states to create institutions to help bring about or support economic integration in a region What’s a Region? An area encompassing three or more nations that have Shared sense of political or cultural identity and/or Potential for economic complementarity and/or interdependency Which comes first? Intra-Regional Exports (US$ billion) 1985 European Union 353 North America 143 East Asia 49 1990 828 226 137 1996 1249 437 390 Growth in RTAs (average number of notifications to GATT/WTO per year) 25 20 15 10 5 0 1948-94 1995-2000 Growth in RTAs Why the new interest in regionalism? Multilateral (WTO) negotiations slow “Everyone else is doing it” Competing blocs demonstration effect Hierarchy of RTAs Free Trade Agreement Customs Union Common Market Economic Union A World of RTAs IR Puzzle #1 Why do states agree to “pool” sovereignty in the form of RTAs? Liberals: integration begets further integration Realists: powerful states (regional hegemon) Constructivists: regional identities IRA Puzzle #2 Why do RTAs differ so much from region to region? Europe North America Asia European Union History in Brief Treaty of Paris (1951) to create a European Coal and Steel Community Treaty of Rome (1957) to create a customs union (the EEC) Single European Act (1986) to create a common market Treaty of Maastricht (1992) to achieve monetary union A Highly Institutionalized EU European Commission European Parliament Council of the EU Court of Justice Court of Auditors Free Markets or Social Welfare? Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) Reduced tariffs on intra-regional trade But spends about $63 billion a year to subsidize farmers Social policy Labor standards Regional policy Structural funds ($250 billion in 2006) Cohesion fund ($23 billion) EU Expansion EU expanded from 15 to 25 (May 1, 2004) Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovak Republic, and Slovenia EU will expand again (2007) Bulgaria and Romania And then again (with Turkey)? NAFTA NAFTA History in Brief 1989: US and Canada set up US-Canada Free Trade Area 1992: Mexico agrees to join the two others to create NAFTA (beginning January 1st 1994) 1994: Negotiations begin on plan to expand NAFTA to create hemisphere-wide Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA) What NAFTA Did Reduced tariffs over 10 years Created rules for investment National treatment Intellectual property rights Financial regulations Established procedures for resolving disputes What NAFTA Didn’t Do No large bureaucracy No economic union, common market or even customs union No powerful court Asia High level of regionalization Low level of regionalism but rising steadily APEC APEC: Brief History Created in 1989 Reinvigorated by Clinton in 1993 1994 “vision” (but no treaty) of free trade by 2010 and 2020 1997: failed EVSL of trade in forestry and fish products ASEAN “The ASEAN Way” Consensus decision-making Policy of non-interference Standing secretariat, but limited staff Delayed timetable for AFTA Building on ASEAN East Asian Economic Group Asean + 3 China-ASEAN FTA Japan-ASEAN EPA? Explaining Asia Economic Disparity in Asia (2005) 5 4.5 4 GDP (trillion $) 3.5 3 2.5 China 2 1.5 1 Indonesia 0.5 0 Japan South Korea Thailand HK Singapore Malaysia Vietnam Philippines Burma Brunei Laos Cambodia Other Explanations US bilateralism Asian nationalism Security externalities Illiberal states Cultural diversity No need