Lesson 1 Algebraic Expressions
advertisement

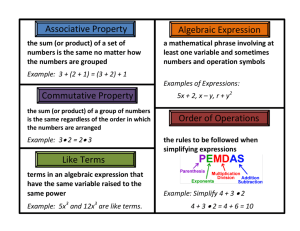
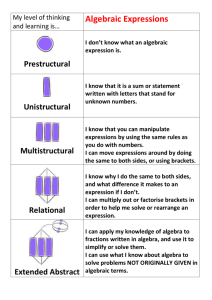
Lesson 1 Algebraic Expressions Terms To familiarize ourselves with algebra we must know some terms associated with it. Literals: The letters which are used to represent numbers are called literal numbers or literals. A literal is also called a variable Term: A numerical constant or the product (or quotient) of a numerical constant and one or more variables. Example: 5x, 3xy, -4ab Algebraic Expression: It is a combination of one or more terms. The terms in an algebraic expression are separated by either + or - signs. Example: 5pq, 7ab + 6, 6x2 - 4x - 9 Types Algebraic expressions can be classified based on the number of terms they contain. Before we get into the classification of algebraic expressions let us know some basic points. In a term like 4pq, the numerical constant 4 is called the numerical coefficient. A number without any variable is called a constant term. Types of algebraic expressions: Monomial: An expression with one term Example: -6ab Types of algebraic expressions: Binomial: An expression with two terms. Example: 9xy + 4x2 Types of algebraic expressions: Trinomial: An expression with three terms Example: -2p, +3q, 15pq Property While dealing with algebraic expressions and their simplification it is important to know about a special property called the distributive property. Distributive property Let us say we have an algebraic expression of the type, 25x + 35y, we observe that the terms of the given expressions have their coefficients 25 and 35 which are multiples of 5. We can say that they have a common factor that is 5. Hence we can simplify it as 25x + 35y = 5(5x + 7y) Distributive property Let us see another case, 32xy - 8x2y2 here we observe that not only the numerical coefficients have a common factor 8 but also the literal factors are common Hence, 32xy - 8x2y2 = 8xy(4 - xy) Distributive property Hence we can generalize these statements and frame a general rule known as the distributive property which is as follows, ax + ay = a(x + y) Substitution Introduction Generally, we see questions of the type 'evaluate' that is finding the value of an expression for a certain assigned numerical value of the variable Substitution An important technique used in algebra is substitution, the word substitute means replacing a quantity with another. Substitution is a method which is employed to evaluate an algebraic expression or express it in terms of other variables. So, if two values are equal, they can be substituted for each other. Algebraic Expressions II We are thorough with substitution method now. Let us move on to simplification of algebraic expressions. Algebraic Expressions II Like Term All the four basic operations namely addition, subtraction, multiplication and division can be performed on algebraic expressions in the same manner as we do in arithmetic. Algebraic Expressions II Before we go on to simplification of algebraic expressions, let us see what 'like terms' are: Terms that have the same literal factors are called 'like terms' otherwise they are called 'unlike terms' Algebraic Expressions II Example: 5ab, -5ab and 9ab are like terms as they have the same literal factors ab. 4x and 5y are unlike terms as their literal factors are not the same. 5p and 5q are not like terms though their numerical coefficients are equal as their literal factors p and q are not the same. Reference Online Free SAT Study Guide: SAT Guides http://www.proprofs.com/sat/studyguide/index.shtml