AP World History
advertisement

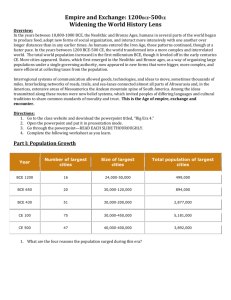
AP World History 1st Semester Unit Review Unit 1-2 Foundations (8000 BCE – 600 CE) Why start 8000 BCE: Development of farming (Neolithic Revolution) Why end 600 CE: Fall of classical civilizations. General themes: Early humans were hunters and gatherers, moved around (nomadic). Farming, animal breeding led to settlements, stability, food surplus led to job specialization (blacksmith, miller, trader, priest) gender roles emerged, craft industry (pottery, metallurgy, textiles). Copper earliest metal, led to bronze (tin & copper, 3000 BCE) and iron (carbon added, 1000 BCE) Civilizations started to develop (3500 BCE), led to population growth and cities. They had organized govt., complex religions, social structures, writing, job specialization, and marketplace. Developed along rivers. Classical Civilizations (Greece and Rome, China, India) took organization to high level. Both internal (corrupt govt., high taxes, poor leaders) and external (famine, over extensions) problems caused collapse. China recovered quickest, then India, Rome most severe. Middle East -Mesopotamia (Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, Fertile Crescent) Sumer was 1st civilization (3500 BCE), used wheel, Ziggurats (temples), writing cuneiform, kings ruled city states, priests, commoners, slaves. Silver used for money, calendar, astronomy. -Babylonians; Hammurabi’s Code 1st written law, eye for an eye - Egyptians (3000 BCE); Nile River, ruled by god like kings (Pharaohs), tombs were pyramids, mummification, calendar, hieroglyphics -Phoenicians (1300 BCE); simplified alphabet, predecessor to Greek and Latin -Judaism (2000 BCE) Nomadic group who moved from Mesopotamia to Palestine, single god (monotheistic), had covenant with God (chosen people), 10 commandments emphasized should live moral life, Romans drove out (Diaspora, 135 CE) Holy Book Torah -Christianity(4 BCE) Jesus was Jewish, born in Judea, preached kingdom of God at hand, used many of Jewish teachings. Old Testament, taught equality of souls before God, eternal life. Crucified by Romans (30 CE), Christians believed resurrected, son of God (New Testament). Religion spread by Apostle Paul. East Asia -Shang Dynasty (1500 BCE); developed along the Huang He (Yellow) River in China. First used Oracle bones (scratches) then developed ideographic symbols (pictograph) writing. Used bronze metallurgy -Zhou Dynasty (1029-258 BCE) long lasting, emperor received power from heaven (mandate of heaven) veneration of ancestors, expanded to middle kingdom (between Huanghe and Yangtze Rivers), Used iron, not powerful central govt., ruled by regional kingdoms -Confucius (551-478 BCE); philosopher, sought to bring order to end warring states, need Ren (appropriate feelings and Li (correct actions), filial piety (respect for parents, elders, need to know proper role and relationship to others, should rule by moral example, 5 key relationships; ruler-subject, father-son, husband-wife, older brother-younger brother, friend-friend. -Daoism (500 BCE); Laozi founder of school of thought, Dao is way of nature, life interdependent, humans should exist in harmony, taught concept of wu wei (act by not acting), less govt. the better, use war only for defensive reasons -Qin Dynasty (221-202 BCE); Shi Huangdi (1st emperor) brutal rule, brings order after Era of Warring States (402221 BCE), centralized rule, started Great Wall, standardized laws, currency, weights, script, built Terracotta Army for tomb. -Legalism; used by Huangdhi, man evil, needs strict laws and punishment to behave, strong central govt., absolute leader, heavy taxes -Han Dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE); retained imperial rule, tried to make lees brutal, Wu Di built roads, started civil service exams based on Confuicuisism, Silk Road began to flourish, tribute system, patriachal society, scholar gentry class, respect for family, ancestors, wheel barrow, watermils, rudder, compas, paper. Japan developed Shintoism (600 CE), worship of political rulers and the spirits of nature. Buddhism arrived in 522 CE. Southeast Asia and Oceania Polynesian people reached Fiji and Samoa by 1000 BCE, used outrigger canoes to reach Hawaii by 400 CE, bringing pigs and a caste system ruled by local kings. South Asia -River Valley civilization formed along the Indus River (2500 BCE), supported several large cities including Harrapa and Mohenjo Daro, polytheistic, traded with Mesopotamia, but had distinct alphabet, art. Nomadic Aryans (Indo-European) migrants entered from the north(1700 BCE), had collections of hymns, songs, prayers (Vedas) written in Sanskirt, that led to the Caste system, divided into Varnas; Brahmins(priests and scholars), ksatriyas (rulers and warriors), Vaisyas (merchants), shudras (servants) and untouchables. -Hinduism; no founder, have dharma (duty) to perform in life, if followed get good Karma, which allows to move up level of samsara in next life because of reincarnation (rebirth) after death. Ultimate goal is moksha (oneness with universe), polytheistic, some gods are Brahma (creator) Vishnu (preserver) and Shiva (destroyer) -Buddhism (500 BCE); founder was Siddhartha Gautama in India, asked why so much suffering, became Buddha (enlightened one), 4 noble truths; all life is suffering, suffering is caused by desire, there is always a way out of suffering, the way out is to follow the 8 fold path and living in a righteous manner. Goal is Nirvana, release from cycle of rebirth. Don’t need Gods, seek enlightenment on own, complete equality of believers, missionaries spread message. After Buddha’s death split into Theravada (way of elders) or Hinayana (lesser vehicle) and newer Mahayana (greater vehicle) -Mauryan Empire (320BCE); Founded by Chanragupta Maurya, ended long period of decentralized rule, regional kingdoms, most famous ruler was his grandson Ashoka expanded kingdom, later converted to Buddhism, spread religion. A new line of kings, the Guptas, established a large empire in 320 CE. Left local govt. intake, reestablished Hinduism. Both empires traded through Silk Road (cotton, pepper), also used Indian Ocean. Used Algebra, pi, Arabic numbers. Both empires conquered by nomads (white Huns) Sub Saharian Africa - Mostly stateless societies. Nubia became an important trade corridor on the Nile. Kush (1750 BCE) battled Egyptians in upper Nile. Kingdom of Axum (330 BCE) defeated Kush, eventually fell to Ethiopia. Bantu became an important language based group that emerged in the Niger River basin, then migrated throughout Africa (1000 BCE) Eastern Europe/Russia - Greece (1000 BCE) Ruled by city states (polis), Athens had direct democracy, citizens, Sparta military rule, centralized, fought together in victory in the Persian War, formed Delian League, later fought against each other in Peloponnesian War. Macedonia then controlled (King Philip II, 354 BCE), his son Alexander set up empire, spread Greek culture (Hellenism) polytheistic, great philosophers (Socrates, Plato, Aristotle), Homer, Olympic games America - 1st civilization in America was Olmecs, “mother civilization” (1200 -400 BCE) in Mesoamerica. Next society was Teotihuacan near Mexico City. Mayans arose (250-900 CE) in Yucatan peninsula, Chavins (850-250 BCE in Andes mountains. Western Europe - Roman Empire (509 BCE); Monarchy changed to a Republic (govt. in which people elect representatives), dominated by wealthy class (patricians), formed Senate, common people (plebeians) gained position by winning Punic Wars with Cartage, eventually became Empire. Julius Caesar led conquest of Gaul, proclaimed dictator for life, nephew Octavian took over, given title Augustus. Had written law code (Twelve tables), great road builders, merchants valued, copied Greek culture. Initially Romans persecuted Christians, later after Emperor Constantine’s Edit of Milan, granted legal status. With the collapse of the Empire in the 400’s, Christianity split into Roman Catholic (west) and Eastern Orthodox Unit 3 Post Classical Civilization (600 – 1450) Why start 600: Fall of classical civilizations, birth of Islam Why end 1450: Beginning of European Exploration General themes: Growth of trade (Silk Road, Indian Ocean Basin, Trans-Sahara, Mediterranean Sea) Improved Technology (Shipbuilding, compass, gunpowder) Spread of Religion (Islam, Christianity, Buddhism) Middle East -Islam sprang from Bedouin society (nomads), Kaaba important in idol worship. Muhammad (570) a merchant, at 40 visited by angel Gabriel, received revelation Allah is only one true god, he was God’s messenger, preached all equal before God, will face judgment (heaven and hell). Fled to Medina (Hijra), viewed as a prophet, last in a long line of Jewish and Christian prophets. Returned to Mecca, captured city, after death followers wrote down revelations in holy book Quran. Universal religion, open to all, appealed to poor, women. 5 pillars; no God but Allah, pray 5 times a day facing Mecca, give alms, fast during Ramadan, make a pilgrimage to Mecca. After Mohammed death (632) battle over successor (caliph), Sunni (most worthy) and Shiite (descendant of Ali) split, Sunni begin the Umayyad Caliphate (661-750) and move capital to Damascus, extended empire around the Mediterranean. Jews and Christians (Dhimmi, people of the book) tolerated as long as paid taxes, and make Arabic official language of the Muslim world. Abbasid Caliphate (750-1258) follows, moves capital to Bagdad. Height of Islamic culture, pottery, rugs, Algebra, novel The Thousand and one Nights (Islamic court life), Ibn Battuta (travel journal), keep Greek ideas alive. Mongols capture caliph in 1258 and take over (Ilkhan, Hulegu). Ottomans reunify at end of period under Islamic rule.. East Asia China -Sui Dynasty (589-618); reunified after 350 year Era of Division under Wendi, and later Yangdi. Reestablish exam system and Silk Road, built Grand Canal -Tang Dynasty (618-906); expanded borders by setting up tributary system, increased silk industry and trade over Silk Road and Indian Ocean trade network. Empress Wu supported and spread Buddhism, after her anti Buddhist campaign (Emperor Wuzong) and growth of Neo –Confucianism. Poetry flourished (Li Bou), Chinese influence spread to Korea and Japan -Song Dynasty (960-1274) Most technological advanced society of its time, not as strong militarily as the Tang, developed working compass, paper money, flying cash (credit) ,gunpowder, block printing, civil service exam expanded, great rival of Confucianism (Neo), begin foot binding. -Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368) Mongols under Chingis Khan began attacking Chinese territory in 1211. After death China came under rule of his grandson, Kublai Khan, adopted some Chinese ways, adopted Mandarin as official language, adopted Buddhism, restarted trade, rebuilt Chinas, roads, canals, Great Wall, visited by Marco Polo, forced others to pay tribute. After death, poor leadership and bubonic plague resulted in overthrow by -Ming Dynasty (1368-1644); Zhu Yuanzhang was a soldier, became Emperior Hongwu, son Yongle also famous ruler. Recentralized, scholar-gentry revival, established Forbidden City in Beijing, strong army and Navy, sent Zheng He (1405-1433) on long voyages to Africa, traded porcelain, exacted tribute Japan Hein period (794) Emperior considered decendant from Shinto god, Fujiwara clan gained power, Tale of Genji (Lady Muraski) tale of court life, Taira-Minamoto war (1156)led to medieval periodEmperor became a figurehead, real power with the shogun (great general),shared power with daimyo (warlords) Had warriors called samurai (one who serves) and lived by a code (bushito) New form of Buddhism (Zen). Korea fell under Chinese influence Southeast Asia and Oceania Vietnam fell under Chinese influence, used rice paddy farming. Khmer civilazation (889-1454) emerged in Cambodia and Laos, city of Angkor Wat. Malacca became economic powerhouse in Indian Ocean Sea trading network. Polynesians reached New Zealand by the 8th century (Maori), adapted to a colder climate to reach a population of 200,000 by the 18th century. Ruled by tribal military leaders and priests, elaborate art, slaves drawn from prisoners of war. South Asia India; disunited (600-1200), Muslim invaders united a large part to Establish Delhi Sultanate (1206-1520) Mongol warlord Timur(1370-1405) conquered part of India, Middle East and Russia. Indian Ocean trade network flourished with 3 zones; Arab traded goods from Africa (ivory, hides, timber, gold, slaves) to the Middle East (textiles, carpets, glass, horses). Middle zone offered Indian gems, elephants, salt, cotton cloth and cinnamon (Sri Lanka) In the east had wood (Indonesia) and silk, porcelain, paper (China) and silver (Japan) Sub Saharian Africa - Mostly stateless societies. Small communities lived in villages, hunting, gathering farming, metalwork, lineage sometimes matrilineal, animistic, oral tradition. Ghana (West Africa thrived starting 500; part of transSaharan trade (gold, salt, ivory, slaves, hides) eventually fell to Muslim invaders. Most dedicated converts were Berbers (desert nomads, jihad) Mali 1250-1460) became a strong Muslim empire along the Niger River, founded by Sundiata, most powerful ruler was Mansa Musa(1312) went on famous hajj to Mecca spreading gold, bring back Muslims scholars and artisans to Timbuktu. East Africa was part of Indian Ocean trading network through the Swahili city states. Central Africa had Great Zimbabwe (1000-1400) city of 20,000, large deposits of gold and diamonds shipped east for trade Eastern Europe/Russia -Byzantine Empire (300-1453). Centered around Constantinople, important trading center, center of Eastern orthodox church, iconoclasm, missionaries Cyril and Methodius spread religion, spoke Greek, Justinian most famous emperor, issue Justinian Code based off the Roman 12 tables, built Hagia Sophia, used Greek fire, 1st lost land to Sejik Turks, then fell to Ottoman Empire. -Kiev Rus; Danish Prince Rurik established (855), Vladimir I converted, began separate Russian Orthodox church , highly decentralized under Boyars (aristocrats), Yarsoslav last great Kievan prince established law codes. Mongols (Taters) under Batu (Chingiss Khan’s grandson) and the Golden Horde (1236) Power shifts to Moscow as the Mongols increase trade, eventually Golden Horde defeated in Battle of Kulikova in 1380. America -Mesoamerica; Toltecs (968-1156) followed Mayas, gave many legends to the Aztecs (1300-1520) Chief city was Tenochtitlan, built on a lake, had chinampas (floating islands) to feed the people, city ruled by calpulli (kin group) warlike, ruled over an empire of 10 million through a tribute system, pyramids built as temple to the gods for human sacrifice -South America; Incas (1400-1540), lived on rugged terrain (Andes Mountains), built roads with way stations (tambos), terrace farming, irrigation, bred Llamas, large cities like Machu Picchu, used labor tribute system (mita), no written language, recorded information on knotted strings (quipu) Western Europe - Dark Ages (50-100) and high Middle Ages (100-1450) Feudal system, Monarchs and Lords(nobles) awarded land (fiefs) to loyal vassals, manor protected by knights, had a code of chivalry, serfs worked the land, portion had to be given to lord in exchange for protection (manorialism). Catholic Church had much power, Monks controlled learning , held Inquisitions, launched crusades (Pope Urban II) to recapture holy land, Charles Martel defeated Muslims in Spain and Portugal (Battle of Tours, 732) Charlemagne (768-814) crowned Holy Roman Emperor, enlarged kingdom. Late in the period (1300’s) centered in Italy trade and commerce increased, urbanization was a trend, guilds were formed, a cultural rebirth took place (Renaissance), with a emphasis on humanism and classicism. Technology learned from Chinese and Muslims lead to the start of exploration, Prince Henry set up navigation school and sponsored voyages (1394-1460) Unit 4 World Shrinks (1450 - 1750) Why start 1450: Global network, rise of Europe Why end 1750: Beginning of Industrialization General themes: America becomes part of Global trade network through Colombian Exchange (goods, disease, culture). Old world provides: wheat, sugar, coffee, horses, cattle, pigs, sheep, goats. New world provides: corn, potato, beans, tomatoes, pepper, peanuts, avocadoes, pineapple, tobacco Africans trade captured slaves with Europeans across Atlantic to work in America (Middle Passage) America colonized, natives decimated by disease (90%), new society based on race forms. Portugal/Spain divide up New World, later Dutch, French and British join in. Economically exploit Asia and Africa. Renaissance spreads north, along with reformation and enlightenment challenge Church, change life. Middle East Ottoman Empire (1300-1923), Sultan Memed II (1453) led the capture of Constantinople, expanded after Mongols declined, strong army using captured Christian boys (Janissaries), Most famous Sultan was Suleyman, built magnificent mosques and palaces. Slow decline started in 17th century. Safavid Empire (1501-1723) Devoted Shiites, enemies of Sunni Ottomans, Ismail led troops in battle of Chaldiran (1514), lost because he didn’t have muskets. Greatest ruler was Abbas the Great (1587-1628), added gunpowder, built public works projects, mosques, schools. Declined rapidly after his death East China China Europeans first began to arrive during Ming period. China too powerful to conquer, but Europeans established trading ports, trading with silver. Late Ming rulers were weak, along with famine caused revolts, and Manchus, led by Nurhaci and the banner armies from the North invaded and set up the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911). Limited foreign trade to the port city of Canton, traded silk, porcelin, and tea. Most famous ruler was Kangxi, skilled general and lawgiver, used Confucian ideals of respect for authority. Japan By 150 Japan was in a period of chaos, Europeans missionaries and traders from Portugal and Holland gained much influence, included Francis Xavier. Tokugawa Ieyasu (1603) finally reunified Japan and appointed himself Shogun, moved capital to Edo. Began period of isolationism, Christians’ persecuted Southeast Asia and Oceania Buddhism and Hinduism were dominant religions, with Islam importand in Indonesia and the southern part of the Philippines. Strong states in the region included Thailand, Vietnam, and Burma. Indonesia was important economically until the Europeans (1st the Portuguese, then Dutch, French and English) came. They conquered what they could, trade elsewhere. British mariner Captain Cook(1770) charted the coast of Australia and New Zealand South Asia Mughal Empire (1526-1739) Begun by Babur, a Mongol warlord who led invasion, Muslim gunpowder empire, booming cotton trade, allowed Hinduism and caste system to continue, including sati. Reached its peak during rule of Akbar(1556-1605), grandson of Babur, great warrior who swore off violence, efficient bureaucracy and tax code, very tolerant of other faiths. Shah Jahan built Taj Mahal in memory of his wife. Aurangzeb(1658-1707) Akbar’s great grandson was not tolerant fo non-Muslim, led to revolts from groups like the Sikhs, eventually collapsed after arrival of Europeans. Sub Saharian Africa - Muslim Kingdom of Songhai (1493-1590) arose under Sunni Ali after Mali fell. Muhammad the Great extended the boundaries into Sudan, sponsoring art and scholarship -West Africa; Portuguese pushed down the coast of west Africa and established forts and trading posts with African merchants (factories) Most important was El Mina(1482) on the Gold coast. Europeans changed character of Slave trade from east (Arab, female) to west (Atlantic, male) by working with local powerful kingdoms (Asante, Dahomey) in trading guns for slaves captured from neighboring tribes. These slaves were taken in horrible conditions (middle passage) to America to work on plantations and mines. This became part of the triangular trade, up at least 12 million Africans until the 19th century. - East Africa; Continued to be important part of the Indian Ocean trade network, but Portuguese began to exert increasing influence over Swahili City states, even setting up some plantations on offshore islands along with Arabs and Indians. Trade for gold, ivory and increasingly slaves continued with the interior. -South Africa; little effected by slave trade, Portuguese then the Dutch arrived along the coast. Dutch East India Company set up a provisioning station at the Cape of Good hope(1652)and settlers began to arrive (Boers), coming into conflict with the local Zulu tribe. Eastern Europe/Russia Expand to great land empire ruled by Tsar, also head of church. Ivan the Great help end Mongol rule and free Moscow (1480), Ivan the Terrible continues expansion by killing many Boyars. After Time of Troubles the Romanov dynasty appeared (1613-1917), started by Michael and his son Alexis. Peter I and Catherine the Great both started the process of Westernization, moved capital to St. Petersburg, limited enlightenment, expanded serfdom America Treaty of Tordesillas divided up world between Spain and Portugal. Helped by horses, gunpowder, and divide and conquer tactics, Spanish conquistadores led invasion of Aztecs (Hernan Cortes, 1519) and Incas (Francisco Pizarro, 1531), eventually setting up New Spain, Natives died in massive numbers due to smallpox and measles, others died because of forced labor in gold and silver mines, or sugar plantations. Encomienda system forced natives to work as slaves, reduced numbers led to escalation of the Atlantic slave trade for workers. King ruled new Spain through two viceroyalties, which were divided up into 10 audiencias (courts) Rigid class structure was imposed with peninsularies (Spanish born) on the top, followed by creoles (pure Spanish born in New World), then mestizos (Spanish/native mix, mulattos (Spanish/African mix) and zambos (Natives/African), at the bottom were Natives and slaves. Same trends applied to Portuguese Brazil, which came to have an even more slave based economy centered on Sugar plantations. Western Europe - Age of Exploration, motivated by power, money and spread Christianity. Desire to trade with the Far East and bypass Muslims and Italian city states led to voyages Christopher Columbus (1492) sponsored by King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain and Vasco da Gama (1497), Ferdinand Magellan(1519) from Portugal. French, Dutch and British later concentrate on North America and set up trading companies in East India. - Renaissance expands influence north; Martin Luther’s Protestant Reformation splits church. Enlightenment emphasizes intellectual though, human reason, culminates in Scientific revolution. See the emergence of Nation-States that unlike empires share a common culture and language, ruled by absolute or parliamentary monarchies.