Electric Heating ,Advantages of Electrical Heating ,Requirements of
advertisement

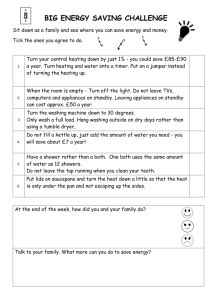
Department of Technical Education Andhra Pradesh Name of the faculty Designation Branch Institute Year / Semester Subject Sub. Code Topic Duration Sub. Topic Teaching Aids Revised By : V. Narsimha Reddy : Lecturer in EEE : E.C.E. : GMR. Polytechnic Gajwel : VI Semester : Electrical Utilization & Automation : EE605A : Electric Heating : 50 Mins : Advantages and Requirements of Electric Heating : PPT, Animation : K. Chandra Sekhar, L/EEE, GPT, HYD 9EE605A.11 1 Known to Unknown • What is the necessity of heat in our lives? • What is meant by electric heating? 9EE605A.11 2 Objectives On completion of this topic you would be able to know • Electric Heating • Advantages of Electrical Heating • Requirements of Good Heating Element • Materials for Heating Element 9EE605A.11 3 Introduction of Heating • Heat plays an important role in everyday life • Heat or fire and wheel are the basis for human civilization • Without fire and wheel, man wheel go back to stone age • Man used fire to cook food • In present days heat is used to extract the metals from the ores 9EE605A.11 4 Electric Heating • Heat and electricity are interchangeable • Heat can be produced by passing the current through a conductor • This method is superior compared to other methods 9EE605A.11 5 Advantages of Electrical Heating • Cleanliness • High Efficiency • No Pollution • Localized Heating. • Ease of Control • Uniform Heating 9EE605A.11 6 Advantages of Electrical Heating Contd… • Better working conditions • Less floor area is required • No carrying expenses • Low attention and maintenance cost • Economical • Safety 9EE605A.11 7 Modes of Heat Transfer The heat is transferred from a hot body are • Conduction • Convection • Radiation 9EE605A.11 8 Modes of Heat Transfer Conduction • The heat transferred depends on the difference • • • between the temperature of the two points The heat transfer by conduction takes place in solids, liquids and gases In solids, heat is transferred from one molecule to adjacent molecule and so on There is no actual motion of molecules 9EE605A.11 9 Modes of Heat Transfer Convection • Heat is transferred from One point to the other point due to motion of molecules . • Heat dissipation: H = 3.875 (T1-T2)1.25 w/m2 • T1 = Temperature of the heating surface (0K) • T2 = Temperature of the Air (0K) 9EE605A.11 10 Modes of Heat Transfer Radiation • The heat transfer is confined to surfaces • The radiant energy is emitted and absorbed by different surfaces. • Heat dissipation: H=5.72Ke [(T1/100)4 – (T2/100)4] w/m2 T1 = Temperature of source (0K). T2 = Temperature of absorbing surface (0K) . 9EE605A.11 11 Modes of Heat Transfer where e = emissivity = 1 for black body = 0.9 for resistance heating element k= radiating efficiency or a constant =1 for single element = 0.5 to 0.8 for several elements placed side by side 9EE605A.11 12 Requirements of Good Heating Material The material used for heating element should posses the following properties • High specific resistance • Low temperature coefficient of resistance • Free from Oxidation • High melting point • Non corrosive 9EE605A.11 13 Requirements of Good Heating Material The material used for heating element should posses the following properties • Ductile • Positive temperature Coefficient of Resistance • High mechanical strength • Economical 9EE605A.11 14 Materials for Heating Elements The materials normally used as heating elements are • Nickel-chromium • Nickel-chromium iron • Nickel-chromium aluminum and • Nickel-copper 9EE605A.11 15 Properties of Heating Elements SI. NO TYPE OF ALLOY COMPOSITION 1 Nickelchromium 2 Nickelchromium Iron 3 Iron chromium 65-75% Fe Aluminum 20-30% Cr. 5% Al. 4 Nickel- Copper 80% Ni 20% Cr. 60% Ni 16% Cr. 24% Fe 45% Ni 55% Cr. COMMERCIAL SPECIFIC SPECIFIC MAXIMUM 0 NAME RESISTANCE AT 20 C GRAVITY TEMPERAT URE Nichrome - 1.03 μΩ-m 1.06 μΩ-m 8.35 11500C 8.27 9500C Kanthal 1.4 μΩ-m 7.2 1150 to 13500C Eureka 0.49 μΩ-m 8.88 4000C 9EE605A.11 16 Reasons for failure of Heating Elements The reasons are • Formation of hot spots • Oxidation of elements and intermittency of operation • Embrittlement caused by grain growth • Corrosion 9EE605A.11 17 Summary In this class we have discussed about • Advantages of Electrical Heating • Modes of Heat Transfer • Requirements of Good Heating Element • Materials employed for Heating Element 9EE605A.11 18 Quiz 1. Electrical Heating is a) Uniform b) Non-uniform c) Both a & b d) None 9EE605A.11 19 Quiz 2. The heating element should posses a) High melting point b) Low melting point c) Both a & b d) None 9EE605A.11 20 Frequently Asked Questions 1. State the advantages of electric heating 2. What are the requirements of good heating element ? 3. What are the materials employed for heating element ? 9EE605A.11 21 THANK YOU 9EE605A.11 22