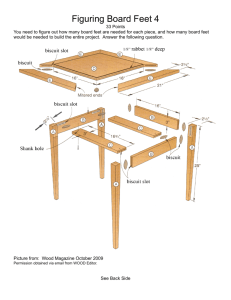
Wood I Description: Wood I will be open to all students from grades
advertisement

Wood I Description: Wood I will be open to all students from grades 9-12. This class will meet five periods per week for one semester. The students will be exposed to wood structure, blueprint reading, price figuring, shop safety, hand tool and machine woodworking, staining, finishing and other basic woodworking procedures. The students will have an opportunity to work with various woods, hand tools and machines necessary to cut, shape, form and finish these woods into an acceptable finished project. A project or projects must be completed for the amount of time spent in the shop to receive a passing grade and to be considered for enrollment in Wood II. Project material must be purchased by the students. Safety Measuring and Cutting Designing and Planning Wood Finishing Wood I Units 1. Safety a. General Safety b. Machine Safety c. Hand Tools 2. Measuring and Cutting a. Customary System b. Crosscut/Rip Saw c. Square 3. Designing and Planning a. Project Selection b. Project Sheets 4. Project Work 5. Wood a. Characteristics b. Properties 6. Finishing a. Preparing for Finishing b. Applying Stains and Clear Finishes c. Applying Paint d. Project Assembly Subject: Wood I Unit Title: Safety Grade: 9 - 12 Suggested Timeline: 3 Weeks / 15 Class Periods Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: The students will create safety handouts for the General Safety Rules for the Laboratory as well as each individual machine. They will observe the demonstration on how to safely setup and operate the machinery/hand tools. A score of 100% must be achieved before a student can demonstrate to the instructor the safe set up and operation of the machines. Essential Questions: What What What What What What What What What What What What What are the General Safety Rules that I need to follow while in the wood shop? type of special safety equipment do I need to use while in the wood shop laboratory? is an unsafe act? is an unsafe condition? type of safety device serves as an extension of the hand when using certain sawing or planning machines? are the two reasons why most accidents occur? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the jointer? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the planer? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the table saw? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the disc sander? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the oscillating sander? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the drill press? are the rules for the safe operation and set up of the scroll saw? Unit Objectives: The Student will… General Safety: Identify the General Safety Rules for the Laboratory. Comply with the safety rules established in the classroom. Organize a safe working environment. Discuss why safety is really an attitude. Discuss common woodshop hazards and how to prevent them. Describe different types of personal safety gear and state their purpose. Machine Safety: (Jointer) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the jointer. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the jointer. Safely set up and operate the jointer according to the demonstration in class. Identify the surface or face to be jointed (cup). Describe face/edge planing with a jointer. Square the fence on the infeed table according to the demonstration in class. Safely set up and joint an edge and surface of a board. (Planer) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the planer. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the planer. Safely set up and operate the planer according to the demonstration in class. Identify the surface or face to be planed. Safely set up and surface a board to a desired thickness. Plane several boards to the same thickness. (Table Saw) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the table saw. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the table saw. Safely set up and operate the table saw according to the demonstration in class. Rip stock to width with the table saw. Crosscut stock to length on the table saw. Set up and cut several boards to the same length with the use of a stop block. (Sanders) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the disc/oscillating sander. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the sanders. Safely set up and operate the disc/oscillating sander according to the demonstration in class. (Drill Press) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the drill press. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the drill press. Safely set up and operate the drill press according to the demonstration in class. Secure work to the drill press table with the appropriate clamp. Select the correct drill bit or cutting tool and fasten it securely in the chuck. (Scroll Saw) Identify the rules for the safe set up and operation of the scroll saw. Observe the demonstration on the safe set up and operation of the scroll saw. Safely set up and operate the scroll saw according to the demonstration in class. Demonstrate the ability to cut external and internal curves and designs on the scroll saw. (Hand Tools/Power Tools) Properly use a crosscut saw for a specific task, observing all the safety rules. Drill holes with a variety of hand tools as well as with a power drill. Demonstrate the correct technique for utilizing a pneumatic nail gun. Misconceptions: Being concerned about safety is not the same thing as being “chicken”. Students who work with safety in mind want to get the most from their hours in the wood shop. SAFETY IS AN ATTITUDE Concepts/Content: Machine Safety Machine Setup / Operation Competencies/Skills: Comply with the safety rules established in the classroom. Description of Activities: Create safety guides for General Safety Rules for the Laboratory. Tool Safety / Operation Organize a safe working environment. Safely set up and operate the jointer according to the demonstration in class. Safely set up and operate the planer according to the demonstration in class. Safely set up and operate the table saw according to the demonstration in class. Safely set up and operate the disc/oscillating sander according to the demonstration in class. Create Safety guides for the individual machines. Observe the demonstration on the safe setup and operation of machinery/hand tools. Safely set up and operate the drill press according to the demonstration in class. Safely set up and operate the scroll saw according to the demonstration in class. Properly use hand tools for a specific task, observing all the safety rules. Assessments: Formative Classwork: [Teacher Guided] Instruction on the safe setup and use of the above mentioned machines. Participation in discussions, following safety rules, daily work. Summative Project Work: Projects in the wood shop Interdisciplinary Connections: Mathematics Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print Subject: Wood I Unit Title: Measuring and Cutting a. Customary System b. Crosscut/Rip Saw c. Square Grade: 9 - 12 Suggested Timeline: Weeks / 3 Class Periods Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: Accurate measurement and cutting are the key process in successful woodworking. When making measurements, you must answer the questions: How thick? How wide? How long? What are the angles? Students will measure using the US customary rule (1/16th Scale). Essential Questions: What is the fractional Inch? What is meant by a “squared board”? Unit Objectives: The Student will… Measure using the English System sixteenth scale. Reduce all fractions to lowest terms. Identify the sixteen division found within an inch on the sixteenth scale. Measure with an accuracy of plus or minus one sixteenth of an inch. Develop an awareness of the importance of accurate measurement. Select and use the correct measuring tool for a specific measuring task. Correctly measure and mark stock for cutting. Properly use a crosscut saw for a specific task, observing all the safety rules. Misconceptions: There is more to measuring then just teaching the concept of how to use a ruler. Students must first identify where the measurement begins on their measuring tool. Concepts/Content: Competencies/Skills: Description of Activities: Measuring with 1/16th Scale Crosscutting Stock Accurately read measurements on a customary rule. Correctly measure and cut stock. Complete various measuring worksheets with an accuracy of plus or minus one sixteenth of an inch. Measure and rough cut boards. Assessments: Formative Classwork: Participation in discussions of the fractional inch. Observations during in-class activities and question and answer sessions during lectures. Summative Project Work: Projects in the woodshop Interdisciplinary Connections: Mathematics Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print Subject: Wood I Grade: 9 - 12 Suggested Timeline: Weeks / 2 Class Periods Unit Title: Designing and Planning a. Project Selection b. Project Sheets Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: Every step in the building process needs to be planned. Planning includes determining materials needed and figuring costs. You must first make a list called the bill of materials. Students will read the blue prints for their project plans and create a project sheet which will include the following: 1. Number of pieces 2. Name of the part 3. Finish size in thickness, width, and length. 4. Materials Essential Questions: How do you calculate the total board feet for your project? How do you calculate the total cost of your project? Unit Objectives: The Student will… Create a bill of materials for each individual part of project selected. Use a formula to calculate the total board feet needed for their project selection. Calculate the total cost of lumber selection based on the total number of board feet. Calculate the total cost for finishing (stain, fasteners & finish) project. Twenty percent of lumber cost. Calculate the cost of project by adding the cost of lumber and cost of finishing together. Misconceptions: Planning is an extremely important when using tool and materials. It helps to avoid costly errors. Concepts/Content: Competencies/Skills: Description of Activities: Observe the demonstration on how to Reading blueprints complete a bill of materials from a Project Sheet Activity/Calculating Cost Calculating cost of projects given project plan. Students will observe the demonstration on how Observe the demonstration on how to to calculate the total board feet for their project. calculate the total cost of their project. Complete project sheet according to the demonstration in class. Rough cut projects according to dimensions on their project sheets. Safely set up and use machinery according to the demonstration in class. Students will begin work on individual projects. They will then calculate the total cost of their project according to the demonstration in class Assessments: Formative Classwork: Instruction on how to complete a project sheet. I will walk around and observe students completing their project sheets. [Teacher Guided] Summative Project Work: Projects in the woodshop Interdisciplinary Connections: Mathematics Subject: Wood I Unit Title: Project Work Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print Grade: 9 - 12 Suggested Timeline: 13 Weeks / 65 Class Periods Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: Students will begin work on their individual projects. I will walk the students through each step of the bluebird house. The demonstrations will consist of the proper procedure for squaring a board. We will utilize the jointer, planer, table saw and drill press. The project will be on going through out the semester. We will stop to cover additional topics as needed. Unit Objectives: The Student will… Comply with the safety rules established in the classroom. Organize a safe working environment. Misconceptions: When squaring rough cut lumber there is no set procedure. Concepts/Content: Competencies/Skills: Description of Activities: Safe set up and operation of: Jointer Planer Table Saw Sanders Drill Press Project Work (bluebird house) (Jointer) Safely set up and operate the jointer according to the demonstration in class. (Planer) Safely set up and operate the planer according to the demonstration in class. (Table Saw) Safely set up and operate the table saw according to the demonstration in class. (Sanders) Safely set up and operate the disc/oscillating sander according to the demonstration in class. (Drill Press) Safely set up and operate the drill press according to the demonstration in class. (Scroll Saw) Safely set up and operate the scroll saw according to the demonstration in class. (Hand Tools/Power Tools) Properly use a crosscut saw for a specific task, observing all the safety rules. Assessments: Formative Classwork: [Teacher Guided] Instruction/demonstration/observation on the above mentioned machines. Summative Project Work: Projects in the woodshop Interdisciplinary Connections: Mathematics Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print Subject: Wood I Grade: 9 - 12 Suggested Timeline: Weeks / 4 Class Periods Unit Title: Wood a. Characteristics b. Properties Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: Students will learn about different wood properties and characteristics. The will also learn about the two different classifications of wood. Essential Questions: What is a coniferous tree? What is a deciduous tree? What is the difference between hardwoods and softwoods? What are the two different types of grading systems for hard wood and soft woods? What are the advantages and disadvantages of different species of wood? How does moisture content and defects affect the strength of lumber? What are the three parts of a tree and their function? How can you determine the age of a tree? How does each layer of the trunk of a tree affect its growth? What four things can affect the growth of a tree? What are the two most common methods of drying lumber? What are the different types of natural wood defects? What are the four types of warps? What are the two woods with best decay resistance? What is the procedure for preparing a stack of lumber for drying? What does S4S mean? What are the common wood properties generally considered in Wood I? What are the three planes on a piece of wood in the order of hardness? Unit Objectives: The Student will… Identify the physical properties of a wood. Identify the two main classifications of wood. Identify the different types of wood defects. Identify the different grades of hard woods and soft woods. Name the three surfaces of a board. Describe the two main factors that influence the strength of wood. Understand the growth process of a tree. Identify the different types of natural wood defect. Identify the different parts of a tree and state their purpose. List the four factors that influence the growth of a tree. Identify the trunk layers of a tree and state their function. List the two methods for drying lumber. Describe the process for kiln and air drying lumber. Identify the two most decay resistant woods. Misconceptions: The classification of wood has always been either hardwood; any leaf bearing tree, and softwood; any cone bearing tree. These terms can be confusing since some leaf bearing trees can have very soft wood and some coniferous trees can have very hard wood. Concepts/Content: Competencies/Skills: Description of Activities: Take the appropriate notes to complete a study Different species of wood. Examples of the common types of wood defects guide for the Wood Properties quiz. Different grades of hardwoods & will be shown to help students grasp the softwoods. concepts. Take the appropriate notes to complete a study Parts of a tree. Physical properties of wood. Factors influencing the strength of wood. Factors that affect the growth of a tree. Tree trunk layers and their function in the growth of a tree. Common types of warps. Methods of drying lumber. Size of standard lumber. Common defects in lumber. guide for the Wood Theory quiz. Participate in the discussion on the Wood Properties and Wood Theory. Assessments: Formative Observations during in-class activities/project work. Question and answer sessions during lectures. Summative Project Work: Projects in the woodshop Wood Properties Quiz Wood Theory Quiz Interdisciplinary Connections: Science Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print Subject: Wood I Grade: 9 - 12 Unit Title: Finishing a. Preparing for Finishing(Abrasives) b. Applying Stains and Clear Finishes c. Applying Paint d. Project Assembly Suggested Timeline: Weeks / 2 Class Periods Unit Overview/Essential Understanding: Students will learn about the two reason that stains and finishes are applied to wood. The will learn that the most important rule to remember when preparing the project for finishing as well as throughout the finishing process is “Don’t be in a hurry”. The finishing process could take just as long as it did to build the project. Essential Questions: What are the two purposes of sanding? What are the two types of classifications for abrasives? What are the two most common natural and man-made abrasives? What was the first type of abrasive used? What are the different types of abrasives and their uses? What is the difference between gravity method and electrostatic process for applying the abrasive to its backing? What are the different types of backing to which abrasive grits are attached? What is the difference between open and closed coat? What is the proper procedure for sanding stock? What are the four shapes that abrasives may be purchased in? What type of abrasive is used between finish coats? Why is finishing a necessary step in wood project construction? What types of finishes are applied to furniture? Which stain raises the grain of the wood? What are the two reasons for using finishes? What does NGR stand for? What can be done to a piece of wood before oil staining to ensure even staining? When using water based stain, what additional step must be added to ensure even staining? What are the two reasons for using stains? What are the four basic types of stains used in the wood industry? What are the two basic types oil stains? What are the two classifications of wood finishes? What are examples of common types of transparent finishes? What are examples of common types of opaque finishes? What is the difference between penetrating and build up finishes? What are common types of penetrating and build up finishes? What are the different methods for applying stains and finishes? What is the composition of different types of stains and finishes? Where does the best bristle for a brush come from? Unit Objectives: The Student will… Abrasives Sand the three surfaces of stock using proper sanding procedures. Take the appropriate notes to complete a study guide for the Abrasives quiz. Participate in the discussion on abrasives. Identify the two purposes for sanding. Identify the different types of abrasives and their use by their definition. Identify the two classifications of abrasives. List the four shapes that abrasives can be purchased in. Identify the two types of backing materials for abrasives. Identify difference between gravity method and electrostatic process for applying the abrasive to its backing. Stains and Finishes Take the appropriate notes to complete a study guide for the Stains and Finishes quiz. Identify the two reasons why wood is stained. Identify the two reasons for applying finishes. Classify finishes as either penetrating or build-up. Classify finishes as either transparent or opaque. Identify stain and finishes according to their composition. Describe the extra step that can be done to oil based and water based stains to ensure an even coat. Misconceptions: Stains can be a cost-effective option to add color to less expensive woods like poplar or pine. Choosing what stain/finish to use is important, but that is really the easiest part. Preparing the surface correctly is crucial to achieving a fine finish. Concepts/Content: Competencies/Skills: Description of Activities: Types of Abrasive (grading system, Safe set up and operation of Select the proper abrasives to use for preparing shapes of abrasives, material machinery and hand tools. project for stain/finishing. Select the proper backing, types of sandpaper, and Perform processes necessary for the stain to enhance the grain and achieve the methods for applying abrasives to assembly and finishing of individual desired color. Apply a topcoat of lacquer to backing) projects. project. Usually, two or more coats are needed Types of Finishes (application process) and the surface must be sanded between coats. Types of Stains (application process) Assessments: Formative Observations during in-class activities/project work. Question and answer sessions during lectures. Summative Project Work: Projects in the woodshop Abrasives Quiz Stains and Finishes Quiz Interdisciplinary Connections: Science Additional Resources: Feirer, Mark D. Wood Technology & Processes. Columbus: McGraw Hill Companies, 2011. Print