File
advertisement

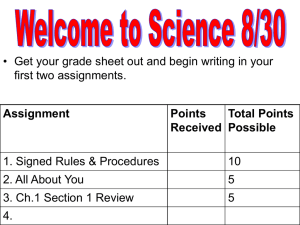
MGMT 580 FINAL PROJECT: S. BATCHELDER WP INC: SPRAY NOZZLE BLUES What’s the problem? Spray nozzle on the parts washer is clogging Integral part of the manufacturing process Each part manufactured goes through washer Creates time delays Only alternative for cleaning parts to maintain quality system The causes could be… Nozzle installed incorrectly Debris in water causing clog From water in tank From water fed through line Buildup from hard water Debris from parts Soap interaction Malfunction in nozzle Mineral deposit The Fishbone: Cause & Effect. MACHINE PROBLEMS No filter system Malfunction Operator Error WATER PROBLEMS Water in tank not optimal temperature Evaporation causes level variation Residue in tank Soap/water Mixture Flakes SOAP PROBLEMS CLOGGED WATER NOZZLE Mitigate the causes. Machine problems Operator training Investigate adding filtration system Audit of parts and performance Mitigate the causes. Soap and water problems Operator training Revise operational processes Explore alternative brands of cleaning solution Temperature control system Supply fill water to counter evaporation Force Field Analysis 1. DRIVING FORCES RESTRAINING FORCES Simple process adjustments Low cost solution Higher Morale Motivation Operator Training Inconsistent Time to implement Force Field Analysis 1. DRIVING FORCES RESTRAINING FORCES Better technology (filter, temp control) Process better, more reliable Spend money to save money Expensive Overhaul Machinery/ New Equipment Compatibility Learning curve Force Field Analysis 1. DRIVING FORCES RESTRAINING FORCES Added steps to process Could be lower cost Opportunity for new partnership Fill water/ New brand of cleaning solution Availability Additional cost to implement Follow up the Force Field. The low cost option is to correct the temperature control issue OR explore alternatives to cleaning solution that may dissolve at lower temp Both would involve an element of incorporating clean fill water to alleviate evaporation Last resort is new equipment or modifying existing equipment for cost reasons Corrective actions could be… Incorporate a fill water system AND… Operator training Maintain temperature Use water only to fill after evaporation Investigate alternate brand of cleaning solution or adding a filtration option for existing machine Corrective Action Plan ISSUE SOLUTION Water temp. not optimal Solution used to fill tank when evaporation occurs TIMEFRAME SUCCESS EVALUATION Train ops to 2 weeks to monitor reach all and adjust operators as needed Consistent results in temp samples If success Ops fixes Supervisors problem, /Manager completed. Implement clean fillwater solution Soap deposits reduced in tank If success Above plus fixes facilities. problem, completed. After results of item 1 determined No filtering Explore After Filtering system options to results of system add system items 1 and installed 2 determined If success fixes problem, completed. PERSON RESPONSIBLE Operations supervisor, purchasing, controller Implementing the CAP… Each action is determined by success or failure of previous action Action 1 (training): Document what process is for achieving and maintaining correct temp range and acceptable variations. Establish training schedule for all operators to educate Two weeks should cover all shifts/employees Implementing the CAP… Action 2 (clean fill water) Evaluation and testing of water supply to ensure no negative reaction with cleaning solution Determine water delivery system and storage methods Establish guidelines and process on when and how to use the clean fill water Any additional process changes to include this step in washing parts Implementing the CAP… Action 3 (install filter) Determine if existing machine can be fitted with filter If so, find cost, installation procedure and downtime expected for machine Additional training, process steps may be needed If unable to modify existing machine, explore purchasing new machine Follow up. Action 1 (training): Sample water temp regularly Compare with instances of nozzle clogging before implementation of action If action remedies problem, further analysis could be done to determine the exact temp at which the nozzle starts to experience clogging Follow up. Action 2 (clean fill water): Sample water in tank regularly to determine presence of particulate matter Gather data to further evaluate effects of fill water temp and volume on cleaning solution Evolve process for water storage and delivery as needed to increase efficiency in process Follow up. Action 3 (install filter): Determine best option for modifying or purchasing new equipment, contact manufacturer of machine Evaluate efficiency and any changes in initial costs as well as total cost of ownership of this action after implementation Conclusion Action 1 is very low cost, low impact solution to try that has seems to have a high probability of working. Temp affects both the functionality of the machine as well as the soap used in the solution. The build up of non-dissolved soap is prime suspect Training the operators and making small adjustments to operational process could be solution. Conclusion The fill water option is still lower cost, but involves a lot of testing for compatibility and best practices for introducing a new variable to the process. This solution would also add to the operational process, but could easily be implemented with the proper instruction. The next step up would be to modify the machine, or take it a step further and replace it. Conclusion Adding a filter could be expensive, so could replacing the machine. Additionally, the time lost and any additional training with new equipment could be taxing. In the long run, it could result in a more efficient process. A quick search shows that the machine type described could retail for around $8,000. A considerable chunk of money, but not usually a back-breaker. With a three-tiered action plan, there is no pressure to spend a lot of money right away, the first two options are the easier ones. References “Cause & Effect Diagram.” (2014). Retrieved from http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/templates/cause-and-effect-diagramTC006082737.aspx “Force Field Analysis.” (2014). Retrieved from http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newTED_06.htm “Spray aqueous parts washers.” Retrieved from http://www.safetykleen.com/products-services/parts-cleaning-technologies/aqueous-partswasher/spray Summers, D. (2010). Quality/5e. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. “Writing an effective corrective action plan.” (2014). Northwestern University Research [online]. Retrieved from http://irb.northwestern.edu/policies/compliance/corrective-action-plan