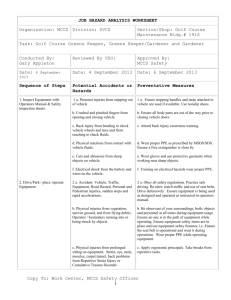
section 1 - Manatee County
advertisement

Safety Manual Manatee County TABLE OF CONTENTS SECTION 1 ..................................................................................................................................... 1 GENERAL RULES .................................................................................................................... 1 SECTION 2 ..................................................................................................................................... 3 SAFETY ORIENTATION CHECK LIST ................................................................................. 3 SECTION 3 ..................................................................................................................................... 4 ENFORCEMENT PLAN............................................................................................................ 4 SECTION 4 ..................................................................................................................................... 5 ON-THE-JOB INJURIES ........................................................................................................... 5 SECTION 5 ..................................................................................................................................... 7 COUNTY VEHICLE ACCIDENT ADMINISTRATION ......................................................... 7 SECTION 6 ..................................................................................................................................... 9 ACCIDENT AND LOSS INVESTIGATION ............................................................................ 9 SECTION 7 ................................................................................................................................... 10 GENERAL SAFETY PROCEDURES ..................................................................................... 10 SECTION 8 ................................................................................................................................... 11 OFFICE SAFETY ..................................................................................................................... 11 SECTION 9 ................................................................................................................................... 13 HOUSEKEEPING .................................................................................................................... 13 SECTION 10 ................................................................................................................................. 15 FIRE PREVENTION ................................................................................................................ 15 SECTION 11 ................................................................................................................................. 17 MATERIAL HANDLING ....................................................................................................... 17 SECTION 12 ................................................................................................................................. 20 PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AND EQUIPMENT ................................................................... 20 SECTION 13 ................................................................................................................................. 26 HAND TOOLS ......................................................................................................................... 26 SECTION 14 ................................................................................................................................. 27 OWER TOOLS ......................................................................................................................... 27 SECTION 15 ................................................................................................................................. 35 CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE SAFETY ABOVE GROUND AND UNDERGROUND .................................................................................................................... 35 SECTION 16 ................................................................................................................................. 43 WORKING IN CONFINED SPACES ..................................................................................... 43 SECTION 17 ................................................................................................................................. 46 LADDERS AND SCAFFOLDS ............................................................................................... 46 SECTION 18 ................................................................................................................................. 48 MOTOR VEHICLES AND MOBILE EQUIPMENT .............................................................. 48 SECTION 19 ................................................................................................................................. 52 FIRST AID................................................................................................................................ 52 SECTION 20 ................................................................................................................................. 53 COUNTY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS ........................................................................ 53 SECTION 21 ................................................................................................................................. 54 APPENDICIES ......................................................................................................................... 54 SECTION 1 GENERAL RULES 1.0 Goals and Objectives Employee safety is a primary Manatee County goal. Each employee has an obligation to keep safety in mind. 1.1 OBJECTIVES The primary objectives of the Safety Program are prevention of accidents, injuries and fatalities and the prevention of property damage and loss. 1.2 Safety Principles (A) Safety and loss prevention are an integral part of each employee’s daily assignments. (B) Employees are expected to conduct themselves in a safe manner at all times. (C) Safety and loss prevention are paramount considerations in selecting tools, materials and equipment to accomplish the assigned job. (D) Disciplinary action will be a likely result whenever the county determines that an employee has neglected safety practices. (E) County Safety Creed: THE NECESSITY OF THE SERVICE OR THE IMPORTANCE OF THE JOB IS NEVER SO GREAT THAT WE CAN NOT PROCEED SAFELY! 1.3 Roles (A) The Safety Manager will develop and administer the Safety Program. This includes analyzing facts to determine the cause of accidents and property damage, conducting hazard surveillance and safety assessment surveys, and communicating findings and making appropriate recommendations for corrective action to the county. (B) Risk Management Workers Compensation and Claims/ Liability Division should annually summarize all reported personal injury and property damage incidents involving County personnel and property, and report summary results to relevant county officials. (C) Employees are responsible for their safety and the safety of co-workers. They are expected to perform all job duties in a safe manner in order to prevent accidents resulting in injury and/or property damage. (D) Employees are also responsible for helping to prevent accidents by bringing unsafe working conditions to the attention of their supervisors. Safety Manual Page 1 of 54 12/2010 1.4 OPERATING PROCEDURES (A) Employee Training: The Safety Manager will provide or recommend periodic safety training to departments to ensure basic safety training is being taught to employees. (B) Effective Communication: A free flow of communication should exist between all department heads and the Safety and Risk Managers. Safety policies and practices affecting departmental operations should be communicated to the appropriate department head and/or County Administrator by the Risk Manager and or, Safety Manager. Recommendations which affect County operating policies and procedures should be communicated to appropriate individuals for approval and/or implementation. 1.5 Evaluation The Safety Manager should evaluate the Safety Manual on a regular basis and update it according as needed according to state and federal laws. 1.6 Manual not Exclusive The provisions of this manual are supplemental to any other laws, county ordinances, resolutions or policies and to the extent of any conflict, those superior authorities will control. Safety Manual Page 2 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 2 SAFETY ORIENTATION CHECK LIST 2.0 GENERAL The "New Employee Safety Orientation Check List" (see SECTION 21. E.) is designed to assist supervisors in familiarizing their employees with safety information, safe work practices, and emergency procedures. 2.1 ORIENTATION PROCEDURE (A) The immediate supervisor of each new employee, and each employee who is transferred or changes job classification, should explain the items on the check list and indicate the date discussed. Items which are not applicable should be marked "N/A". (B) The supervisor should ensure that all employees indicated in paragraph (a) above understand all items on the check list. Supervisors may conduct a group orientation, but must question each employee individually regarding his/her understanding of the information. 2.2 DOCUMENTATION Upon completion of the safety orientation meeting(s) with the employee, the check list form should be completed according to the employee job description and signed by both the supervisor and employee. The form will be retained in the employee's assigned departmental file. A copy will be forwarded to the County Administration Human Resources office for the employee’s file. Safety Manual Page 3 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 3 ENFORCEMENT PLAN 3.0 ENFORCEMENT PLAN (A) General: The enforcement of safety and loss prevention rules is not solely a matter of discipline. A supervisor's good example significantly influences employee attitudes toward safety regulations. If supervisors disregard the rules or fail to observe them consistently, employees will feel entitled to do likewise. Patience and perseverance should be exercised in all areas of enforcement. When discipline is required it must be administered according to the Personnel Policy. 1. Common Disciplinary Rules dealing with Safety include Carelessness or negligence in handling or control of County property or the improper appropriation of County property. Willful or negligent failure to follow safety rules and procedures. Horseplay, fighting, unsafe conduct or other misconduct while on duty or on Manatee County property. Unsafe driving record as determined by the Manatee County Risk Management or the loss or suspension of a driver's license when driver’s duties and/or driver's license are integral parts of the employee's job. Failure to use seat belts while driving or riding in County vehicles. (B) Accident and Violation Procedure: (1) Each motor vehicle, occupational, personal and public liability accident and each violation of safety rules or practices is subject to review and report by the Workplace Safety Committee. The report shall be submitted to the department head and shall reflect the following considerations: A. Was there negligence, carelessness or inattention as opposed to an error in judgment? B. Was there willful or knowing violation of established policy and procedure? C. Had the employee been adequately trained for the job? D. Had the employee received the necessary safety instruction? Safety Manual Page 4 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 4 ON-THE-JOB INJURIES 4.0 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following procedures are to be followed whenever an on-the-job injury occurs. 4.1 DEATH Immediately notify Risk Management if a death occurs in the workplace. 4.2 INJURY (A) Emergencies Supervisors must: (1) Seek immediate medical care for the injured employee; call 9 - 1 - 1. (2) Notify Risk Management as soon as possible. Submit a completed INCIDENT Report OR a VEHICLE CRASH Report as soon as possible. (B) Non-Emergencies (1) Employee immediately reports the accident/injury to his/her supervisor. (2) Supervisor, departmental designee and employee submit to Risk Management as soon as possible an INCIDENT Report OR a VEHICLE CRASH Report. (3) Supervisor, or department designee, notifies the Risk Management Division/ Workers' Compensation Claims Adjuster for authorization for medical treatment as necessary. (Ext. #3750). Risk Management will provide authorization to the appropriate medical facility (4) Supervisor may accompany the injured/ill employee to the physician's office. (5) A drug screen will be required as part of an injured employee's treatment under Worker’s Compensation, as provided in the County’s Drug Free Workplace Policy. Safety Manual Page 5 of 54 12/2010 4.3 REQUIRED WORKERS COMPENSATION FORMS (A) FIRST REPORT OF INJURY OR ILLNESS (1) Supervisors must complete a Florida Department of Labor & Employment Security -- Division of Workers' Compensation First Report of Injury or Illness (DWC-1) for each and every illness sustained by an employee of, or volunteer to, Manatee County Board of County Commissioners and its constitutional offices while on the job, regardless of the need for medical treatment. This report is required by Florida Statue to be submitted to the thirdparty administrator and to the State of Florida. Late filings are subject to a large fine per incident by the State of Florida. (2) Both the supervisor and the employee signatures are required on the DWC-1. First Reports of Injury or Illness Reports must be received by Risk Management as soon as possible following the injury. (B) WAGE STATEMENT If the injury results in an employee losing more than (1) day of work as a result from work related injury or illness, and the employee has been placed by a physician in an off work status, or restricted work status which cannot be accommodated, then the department must provide a Thirteen (13) Week Wage Statement to Risk Management as soon as possible. C. Manatee County Internal Work Related Injury or Illness Investigation Report This form must be completed for all accidents or exposure incidents. The form is utilized by Risk Management to investigate work related injuries and illnesses for safety compliance and training. Send the completed form to Risk Management as soon as possible. The Risk Management fax number is 745-3774. Safety Manual Page 6 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 5 COUNTY VEHICLE ACCIDENT ADMINISTRATION 5.0 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following procedures are established and should be followed whenever any County vehicle is involved in a Crash. 5.1 EMPLOYEE (DRIVER) PROCEDURE The driver of any County vehicle involved in an accident should refer to the insurance identification and instruction card kept in the vehicle's glove compartment and: 5.2 (1) obtain medical aid when necessary; (2) notify the police, their supervisor, and Risk Management as soon as it is safe to do so. (3) obtain names of any witnesses with complete addresses and telephone numbers; (4) get photographs of the accident scene; (5) Make no statement regarding the accident to anyone except the investigating law enforcement officer, county management, and Risk Management. (6) Complete and sign a VEHICLE CRASH Report and immediately submit it to their supervisor. (Instructions and report forms are kept in the vehicle's glove compartment.) SUPERVISOR PROCEDURE (A) Proceed immediately to the scene, if possible. Take photographs of the overall scene. Safety Manual Page 7 of 54 12/2010 (B) Immediately notify Risk Management at 745-3750, if there is a vehicle, property damage, a severe or multiple injuries, or a fatality. (C) Notify the person in the next higher level of supervision. (D) Complete the Supervisor Review portion of the VEHICLE CRASH Report and Fax a copy to the Risk Management Department at 749-3774 as soon as possible. (E) If a County employee is injured, follow the procedures outlined in SECTION 4, ON-THE-JOB INJURIES. (F) After Hours Emergency Contact: Contact the Public Safety Emergency Communications Center ( ECC) 911 and request them to Page/Text the Risk Manager and the Safety Manager if a death or serious injury occurs with a county employee or a patron utilizing a County owned property or facility. Safety Manual Page 8 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 6 ACCIDENT AND LOSS INVESTIGATION 6.0 GENERAL (A) All motor vehicle or potential public liability accidents or incidents involving a County employee will be subject to an investigation by the Risk Management Division. (B) Each investigation should be directed toward determining the cause of the accident; not placing blame or finding fault. Preventing similar accidents in the future is of primary importance. (C) A thorough investigation of every accident immediately after its occurrence will assist in: 6.1 (1) the dissemination of information to personnel on avoiding a similar accident; (2) the compilation of accident causes for identifying hazards and assessing safety training needs; (3) Which provides information for developing safer procedures and work sites. PROCEDURES (A) It is the responsibility of each employee involved in an accident, regardless of the type or severity, to report the accident at once to their immediate supervisor. (B) An INCIDENT Report OR the VEHICLE CRASH Report must be completed for ALL incidents/ accidents with, or without, an employee injury. The Original must be submitted to Risk Management as soon as possible (C) Accident and Violation Procedures as set forth in Section 3.0 (C) shall be followed. Safety Manual Page 9 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 7 GENERAL SAFETY PROCEDURES 7.0 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following general safety procedures are established and should be followed. (A) Work at a speed consistent with safety. (B) Use the hand rails on stairs and elevated places. (C) Do not jump from elevated places such as tables, benches, platforms, etc., as serious injury may result. (D) Always inspect tools and equipment before use. Do not use tools and equipment that are defective. Report defects to the supervisor and take the tool or equipment out of service. (E) Remove splinters from work benches, tables, bins, shelves and chairs. (F) Remove, cut off or hammer down protruding nails, staples and steel straps. (G) Work clear of suspended loads. If a load is being moved above your working area, stand aside until it has passed. (H) Obey warning tags and signs. They are posted to point out hazards. (I) Operate only the machinery and equipment you have been trained and authorized to operate. (J) Remove jewelry such as rings, identification bracelets, etc., when work involves climbing, materials handling or operation of mechanical equipment. (K) Never reach over moving parts of machinery or equipment. (L) Report to work in appropriate clothing and footwear suitable for the type of work you perform. Avoid wearing loose clothing and jewelry near machinery and equipment with moving parts. (M) Wear personal protective equipment as mandated. (N) Do not operate electrical appliances or machinery that does not have a grounded plug, or are not double insulated. (O) Wear a seatbelt, and require all passengers to wear a seatbelt, when operating a County vehicle. Safety Manual Page 10 of 54 12/2010 (P) Cell phones are not to be utilized while driving a county vehicle or a privately owned vehicle while on County Business unless you have a "Hands Free Device”. Text messaging while operating a Motorized Apparatus is very dangerous and can lead to termination. SECTION 8 OFFICE SAFETY 8.0 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following Office Safety Procedures should be followed: (A) Each employee is responsible for ensuring the cleanliness of his/her desk and work area. Pick up pencils and paper clips and wipe up any spilled liquids. Good housekeeping is the key to a safe office environment. (B) Be conscious of loose or rough floor covering. (C) Use caution when approaching a door that can be opened toward you. Open doors carefully and slow down when approaching blind corners. (D) Haste when walking between desks may result in bruises and falls. Proceed cautiously and watch out for electrical cords. Keep electrical cords out of aisles. (E) Keep all file, desk and table drawers closed when not in use. Close drawers before you leave them. Never open more than one file drawer at a time. (F) Overloading the top drawer of unsecured file cabinets has caused many accidents and injuries. Do not overload file drawers. If you are unfamiliar with a file cabinet, test each drawer, being careful to not pull it out too far, especially if there is no locking device on the drawer. (G) Tables, desks, chairs and other furniture should be maintained in good condition. (H) Tilting chairs can be a hazard when improperly used. Care should be taken to ensure they are in good condition. Learn the limits. Be sure your chair is behind you before you sit down. (I) Never use chairs, desks or other office furniture as a make-shift ladder. Use a step ladder. Don't overreach and lose your balance. (J) Message spindles are a frequent source of puncture wounds. When used, the point shall be protected by a suitable blunt cover or bent at a horizontal angle. (K) Keep paper cutter blades closed when not in use. (L) Carry pencils and pens point down in pockets. Safety Manual Page 11 of 54 12/2010 (M) Use caution when using scissors, paper and box cutters. (N) Paper can cut. Use a sponge or other wetting device for sealing envelopes. Use rubber finger guards when working with stacks of paper. (O) Keep razor blades covered and store paper clips, thumb tacks and pins separately. Even a minor scratch can get infected. (P) Be sure electrical equipment is grounded and that the cord is in good condition. Unplug any defective equipment, take it out of service, and report the defect to your supervisor. (Q) Extension cords should be energized from an approved receptacle outlet; used only in continuous lengths without splice or tape; connected to devices and fittings so that strain relief is provided which will prevent pull from being directly transmitted to joints or terminal screws. Extension cords may not be used as a substitute for fixed wiring. Only an approved UL Electrical Safety Strip with a Surge Breaker should be utilized. (R) All electrical space heaters should be turned off when leaving the work area. *Always alert your supervisor and the building Maintenance staff if you see a potentially unsafe condition. Safety Manual Page 12 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 9 HOUSEKEEPING 9.0 GENERAL (A) Many painful and sometimes disabling injuries are caused when employees are struck by falling objects, bump against or trip over objects they did not see. Property damage and many injuries stem from fires caused by poor housekeeping practices and improper storage of flammable materials. The best protection against these hazards is good housekeeping. (B) Accidents are prevented when materials are stored allowing proper clearance to work within the storage area and/or adequate space to move throughout the storage area. Tripping hazards can be avoided, and many sprains, fractures and bruises that result from falls can be prevented, if time is spent preplanning a job before beginning work. (C) Good housekeeping also results in more efficient job performance. When materials, tools and equipment have a place for orderly storage and are returned to the proper place after use, they are easier to inspect for damage and wear. 9.1 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following safety procedures are established and should be followed: (A) Keep work areas and storage facilities clean, neat and orderly. (B) All aisles, stairways, passageways, exits and entrances should be kept free of obstructions at all times. All spills should be cleaned up immediately. (C) Do not place supplies on top of lockers, hampers, boxes or other moveable containers at a height where they are not visible from the floor. (D) When piling materials for storage, be sure the base is firm and level. Cross tie each layer. Keep piles level and do not stack too high. Keep aisles clear with adequate space to work in them. (E) Materials stored by suspension from racks or hooks shall be adequately secured in a manner that will prevent them from falling. Route walkways a safe distance from the surfaces beneath suspended materials. (F) When storing materials on overhead balconies, provide adequate toe boards to prevent objects from rolling over the edge. (G) Do not allow trash, soiled clothes, etc., to accumulate in lockers and work places. Safety Manual Page 13 of 54 12/2010 (H) Tools, equipment, machinery and work areas should be kept clean and maintained in safe working condition. Report defective equipment and unsafe conditions to your supervisor. (I) Return tools and equipment to their proper storage place after each use. (J) Lay out extension cords, air hoses, water hoses, ladders, pipes, tools, etc., in a manner that will prevent tripping hazards. (K) Clean up spills immediately to avoid slipping hazards. If the spill cannot be removed immediately, the area shall be appropriately guarded, signed or roped off. (L) Nail points, ends of loop or tie wires, etc., should not be left exposed when packing and unpacking boxes, crates, barrels, etc. Nails should be removed as soon as lumber is disassembled. (M) Sharp or pointed articles should be stored in a manner that will prevent persons from coming into contact with the sharp edges or points. (N) All packing materials should be disposed of properly in order to prevent fire. (O) Wastebaskets should be emptied into approved containers only. (P) Place oily and greasy rags in a special metal container designed for this purpose. (Q) Adequate lighting in obscure areas should be provided for the protection of both employees and the public. (R) All machinery should be locked out and tagged before cleaning, greasing, oiling or making adjustments or repairs. (S) Circuit and fuse boxes should be kept closed and unobstructed at all times. (T) Extension cords should not be run across aisles or through oil or water. Inspect cords before each use for worn insulation and exposed wire. (U) A fuse that blows repeatedly is an indication of an overload or short. This condition should be reported to your supervisor. (V) Keep electrical equipment properly oiled and free of grease and dirt. (W) To prevent static sparks, keep drive belts dressed. Also, check belts for proper tension in order to prevent overloading motors. (X) Fire safety inspections should be performed and fire prevention measures shall be maintained. Safety Manual Page 14 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 10 FIRE PREVENTION 10.0 GENERAL Fire is one of the most feared and damaging disasters that can occur. Many potential fire hazards exist in the varied activities of County operations. Fires can be prevented by orderly planning, sensible arrangements of fire producing activities in relation to combustible materials, good housekeeping and by complying with and enforcing no smoking designations. 10.1 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following safety procedures and Departmental Emergency Action Plans are established and should be followed: (A) Fire equipment should be prominently displayed, labeled for usage and easily accessible at all times. (B) Know the location of fire extinguishers and how to use them. Report each use of an extinguisher immediately to your supervisor so that a replacement may be obtained or the extinguisher recharged. (C) Do not use water type extinguishers on electrical fires because of the dangers of electrocution and equipment damage. These extinguishers are intended for use on Class "A" fires only (flammable materials such as wood, paper, rags, etc.). (D) Oily rags and other flammable wastes should be placed in covered metal containers. Such debris shall be removed from buildings as soon as possible and in no case left unattended in a building overnight. (E) Flammable cleaning solvents with a flash point below 140 degrees should be kept in approved safety containers and properly labeled. Use of gasoline for cleaning parts, floors or any part of buildings is prohibited. (F) Small quantities of gasoline used for fueling engines being repaired, tested, adjusted, etc., shall be dispensed/handled in approved and properly labeled safety containers. The safety containers should be stored in a well ventilated area. Do not store near any potential ignition source. All portable fuel cans must have a self closing lid with a vapor screen to prevent ignition. (G) Fueling any type of motorized equipment while the engine is running is prohibited. When transferring flammable liquids, be sure the filler nozzle touches the container being filled in order to guard against the buildup of static electrical charge. Under no circumstances is a motor vehicle to be left unattended while fuel is being dispensed. ***Wedging or otherwise blocking open a fuel nozzle to keep it open is prohibited. (H) Never overfill a tank but rather, under fill it, to allow room for expansion of the liquid. Safety Manual Page 15 of 54 12/2010 (I) Basements, cellars and other dark places should not be entered without proper light. The use of matches for lighting purposes is strictly forbidden; flammable vapors may be present. Use only UL approved electric flashlights, or, stay out of the area completely and call the Fire Department at 911. (J) The use of fuel oil or kerosene for starting fires is allowed only in outside areas. Caution must be observed. Under no circumstances should gasoline be used for starting fires. (K) "NO SMOKING" should be enforced in all areas where hazardous/flammable substances are stored or used and in any other area where posted. A minimum distance of 100 feet should be maintained around fuel depots with an open flame. (L) Fire exits should not be locked or chained. (M) The cabs of all heavy equipment should be equipped with a "dry chemical" fire extinguisher. (Ensuring the presence of a fully charged dry chemical fire extinguisher is part of the daily vehicle safety check.) (N) A Contract Vendor should be responsible for inspecting all fire extinguishing equipment on an annual basis. Each department should have a designated person to inspect fire extinguishers on a monthly basis and appropriately mark or date the maintenance tag. Any damaged or defective fire equipment should be reported to the supervisor responsible for having the units repaired or replaced. (O) Use of unshielded halogen lights in any office is prohibited do to the high heat potential dangers generated. 10.2 EMERGENCY ACTION PLAN Each Manatee County building shall have an Emergency, Fire and Evacuation plan. The Risk Management Division and Public Safety can offer assistance to departments for establishing such a plan. In addition, individual shops and work sites that contain fire hazards should have a, “Emergency Action Plan”. The plan should include, but is not limited to, the following: (A) Adequate warning measures for alerting all persons in the area of fire; (B) Immediate reporting to the Fire Department; Telephone Contact 911 (C) Evacuation - maps designating evacuation routes must be conspicuously posted and revised as renovation changes floor plans; (D) Procedures for containing and extinguishing small fires; (E) Employee fire safety training, including plan review and extinguisher use; (F) Adequate fire extinguishing equipment that is regularly inspected by a responsible authority Safety Manual Page 16 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 11 MATERIAL HANDLING 11.0 GENERAL Many employee injuries occur while handling materials. Types of injuries experienced are strains and sprains, crushing, hernia and rupture, fractures, lacerations, bruises and contusions. Accidents can be avoided by taking time to plan ahead, using mechanical equipment whenever possible and using the proper tools for the job. 11.1 FOUR STEP LIFTING PROCESS The most important materials handling preventive safety measure is the Four Step Lifting Process. This technique will prevent pain and suffering that may extend into retirement years as well as costly medical bills. (A) STEP 1 - GET READY Size up the load. If it is too heavy or bulky, play it smart -- get help. Check the load and remove protruding nails, splinters, sharp edges, oil, grease or moisture. Wear gloves if the surface is rough. Know where the load is going and where you will put it down. Be sure the path you take is clear of obstacles. (B) STEP 2 - PICK IT UP Make sure your footing is solid. Place feet about shoulder width apart. Bend your knees to get into position. Keep your back as straight as possible. Center your body over your feet. Grip the load firmly and bring it as close to your body as possible. Tighten stomach muscles to help you back stay in balance. Lift with your legs, not your back. (C) STEP 3 - CARRY IT CAREFULLY Be sure you can see where you are going. Avoid twisting as you carry the object; turn your whole body. Move your feet, not just your hips or shoulders. Use extra caution in tight places to keep your hands and fingers safe. (D) STEP 4 - PUT IT DOWN If the receiving surface is about waist high, place the load on the edge of the surface and then push it forward. If you lower the load to the floor, bend your knees, keep your back as straight as possible and keep the load close to your body. Safety Manual Page 17 of 54 12/2010 11.2 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED In addition to knowing the proper technique for lifting, employees should follow the material handling procedures listed below: (A) Hand Trucks (1) Four wheeled hand trucks with swivel axles and tongue are to be pulled; all other trucks are to be pushed. (2) Use the right type of hand truck for the material you are handling. Special purpose trucks (such as a drum or drawbar) should be used when handling materials for which they were designed. (3) Watch where you are going when pushing or pulling a hand truck and slow down at corners. (4) Allow clearance for your hands when moving through doorways or past other objects. Use truck handles. (5) Secure help when moving hand trucks up or down inclines in order to prevent losing control of the truck. (6) When using trucks, stop at all blind intersections before proceeding. (7) Always park trucks where people will not stumble over them; leave handles in a vertical position. (8) Hand trucks with broken wheels, splintered handles and other defects must be removed from service and reported to your supervisor. (9) All hand truck operators are advised to wear steel toed shoes. (10) Watch the floor ahead in order to avoid bumps, cracks, uneven surfaces, etc. (11) Pile loads evenly. An unbalanced load may shift, causing the hand truck to overturn. (B) Power Trucks/ Forklifts (1) Only properly “Certified employees”, that are trained and checked off thru an “Approved Industrial Power Truck-Forklift Operator’s Course can utilize an Industrial Power Truck. Forklift Operators will receive re-certification annually and be issued a wallet card license to operate Industrial Power trucks thru the Safety Manager. (C) Hoisting Equipment All hoists should have the rated load capacity posted on the exterior of the hoist. Employees should not exceed the specified limit. All Man lifts, Aerial platforms and Aerial Bucket Trucks will require the user to wear a Full Body Harness with a Fall Protection Lanyard attached to a tie down point. Hard hats are required to be worn. Safety Manual Page 18 of 54 12/2010 (D) Piling Materials (1) The area where materials are to be piled should have a safe base (solid, smooth and level surface). If the floor or ground is not level, use bearing strips or timber to secure the pile from shifting. Barrels and other materials that may roll or slide should be chocked at the base. (2) Pile materials to a safe height - not so high that the pile will be unsteady. The total weight of the piled material shall not exceed the floor load limit and 36 inches shall remain between the top of the pile and any roof or sprinkler heads. (3) Cross tie each layer so that no unsteady stacks are within the pile. Piles should also be stepped back to insure stability. (4) Maintain aisle space for workers and fire equipment. Materials should not protrude beyond the face of the pile. (E) Gas Cylinders (1) The protective valve cap shall be removed only when a cylinder is to be used and shall be replaced over the valve immediately after each use. (2) Never wear gloves or allow grease or oil to be on your hands when handling gas cylinders. Keep hands away from oxygen cylinder controls. (3) Lifting cylinders is always a job for two employees. Move cylinders with a cylinder dolly if available. (4) Keep cylinders on end and strapped or chained securely so they cannot fall. Cylinders that must be transported on their sides shall be properly mounted and secured to prevent sliding. (5) Store cylinders away from salt, acids, films or other corrosive substances. (6) All cylinders will have safety caps installed protecting valve stems when not in use. (7) Separate and store volatile compressed gases cylinders away from one another. Employee failure to Utilize Safety Personal Protective Equipment: Florida Statute 440.09 (5) If injury is caused by the knowing refusal of the employee to use a safety appliance or a safety rule required by statute or lawfully adopted by the department, and brought prior to the accident to the employee’s knowledge, or if injury is caused by the knowing refusal of the employee to use a safety appliance provided by the employer, the compensation as provided in this chapter shall be reduced by twenty five (25%) percent. Safety Manual Page 19 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 12 PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AND EQUIPMENT 12.0 GENERAL The variety of work performed by County employees involves many industrial hazards. The tasks performed range from custodial services to heavy construction activities. Measures have been developed and implemented to protect employees from accidental injury. 12.1 MACHINE GUARDS All machine guards should be kept in place while machinery is in operation. Tampering with machine guards is prohibited. Guards are to be replaced immediately after the repair work that required their removal has been completed. All machinery must be locked out and tagged before being maintained or repaired. The lock and tag should not be removed until the work has been completed and the area has been cleared. 12.2 PERSONAL PROTECTIVE APPAREL When it is impractical or impossible to place a guard over the source of the hazard, it is necessary to place the guard on the worker. This is done by requiring employees to wear approved personal protective equipment such as shields, gloves, aprons, toe guards, respirators, etc. Supervisors should ensure that personal protective equipment is provided and used. Dress codes may be established within a particular department, division or section. Employees are expected to know and follow these codes. Safety is knowledge of the hazards, knowledge of the protection available and an attitude that makes use of the available protection. (A) General Clothing (1) For your safety, and comfort, invest in work clothes that are sturdy, fit well and are washable. (2) Wearing loose-flowing or ragged clothing on or near moving machinery or equipment is prohibited. (3) Do not roll up sleeves. Keep sleeve cuffs fastened or wear short-sleeve shirts as appropriate and permitted. (4) Pants legs should be cut to ankle length with cuffs sewn up. Rolled up cuffs collect dirt, and may unroll causing a trip and fall. (5) Field employees who operate machinery must wear work shoes or boots. Shoes with run down heels or torn soles are hard on the feet and can cause falls. (6) Do not wear rings, metal identification bracelets and other jewelry near high voltage electrical equipment or equipment with moving parts. Jewelry Page 20 of 54 12/2010 Safety Manual increases the danger of electric shock and can be caught in machinery causing injury. (7) Work clothes should be washed frequently, separate from the family laundry, as a safeguard against skin infections and irritations. (8) Smocks, overalls and aprons should be worn whenever possible to keep work clothes clean. (9) Oil-soaked clothes are a serious fire hazard. Keep your clothes free from oil. (10) All employees working in or alongside any public right of way should wear an orange warning vest. (B) Head Protection Many construction and maintenance activities performed by County employees involve working high above or below ground level, moving material overhead, or working near and operating construction machinery. Hard hats shall be worn while engaged in such operations to prevent head injuries. Proper protection is provided when the head harness is adjusted so that there is approximately 1 to 1 ½ inches clearance (plus or minus 1/8 of an inch) between the skull and the inside of the hat. The employees listed below should wear hard hats as prescribed by department supervision and when performing tasks, including but not limited to the following: (1) Engineering personnel while on construction or maintenance project job site. (2) Public Works and Transportation heavy equipment operators. (3) Wastewater Treatment Plant personnel when working below other employees. (4) Traffic Signal Maintenance personnel while installing, constructing or maintaining street lighting and traffic control facilities. (Personal Protective Equipment should meet approved standards for dielectric properties.) (5) Water Filtration personnel when working below ground, in booster stations or beneath other employees. (6) Employees inspecting projects involving any of the above conditions. (7) Any employee working near, or operating, construction equipment such as digging, hoisting or towing equipment. (8) All personnel working with high voltage electrical hazards. (9) All personnel engaged in climbing tasks or working from aerial lifts. (Head protection equipment must meet approved standards for dielectric properties). (C) Face and Eye Protection Safety Manual Page 21 of 54 12/2010 The possibility of eye and facial injury exists both indoors and outside. Potential injuries range from minor dust irritation to foreign bodies propelled by power tools to splashes of corrosive liquid chemicals. Many types of safety glasses, goggles, and shields are available to protect employees from these hazards. Employees must exercise sufficient care to maintain this equipment properly as dirt and scratches reduce visibility and provide a different hazard. (1) Full Face Safety Shields with Safety Goggles or Approved Safety Glasses with temple guards shall be worn when: Grinding, cutting, milling or drilling with power tools Using impact wrenches and compressed air tools Chipping, scraping or scaling paint, rust, carbon or other materials Using punches, chisels or other impact tools Cutting rivets Cutting or breaking glass Chipping or breaking concrete Cutting or threading pipe Using paint remover Using power activated tools Soldering Cleaning the dust or dirt from vehicles, machinery, etc. Performing sand blasting or air cleaning operations Using metal cutting lathes, drill presses, power back saws and other metal working tools Using power woodworking machinery both fixed and portable Tree trimming, brush chipping or removing stumps Using brush cutters Steam cleaning Washing vehicle parts with soap or solvents Working under vehicles Using power lawn and gardening tools, i.e. mowers, weed cutters Within the working area of trash compactor operations. (2) A full plastic face shield should be worn when handling acids, caustics and other hazardous substances such as Chlorine solutions, Bleach, and DeGreaser fluids (3) Spectacle type glasses should be worn when performing electrical switching operations or activating high voltage circuits where arcs may occur. Safety Manual Page 22 of 54 12/2010 ******Full Face Electrical Arc Wear Hoods, Electricians gloves, Specialized Aprons & Rubber Boots may be necessary when working on High Electrical Voltage Systems. (4) (5) A face shield, with the proper filter or welder lenses, or welder's goggles should be worn when performing all welding and cutting operations. A. Electric Arc Welding: A welder's helmet with appropriate filter lenses should be worn; Portable welding screens should be used to protect the eyes of others in the vicinity; Assistants and observers should wear safety glasses or goggles with appropriate filter lenses. B. Gas Welding and Cutting: Welder's goggles with appropriate filter lenses should be worn; Portable welding screens should be used to protect the eyes of others in the vicinity. Eye protection may be required, on other jobs not listed above, by the supervisor. (D) Hearing Protection Hearing protection (ear plugs and muffs) is provided and must be used whenever engineering controls are not sufficient to reduce the noise level or exposure duration. Employees must use hearing protection as directed by department supervision when performing tasks, including but not limited to the following: (1) Operating heavy maintenance vehicles. (2) Operating power tools. (3) At all times performing maintenance in emergency generator rooms. (E) Foot Protection Many tasks involve handling heavy tools and materials, and walking on hazardous surfaces and dangerous ground. Foot injuries, resulting in bruises, dislocations, fractures, crushes or punctures, can occur. Reinforced safety footwear can prevent foot injuries caused by falling materials and equipment, stepping on sharp objects, or exposure to power tool blades. Foot protection is a sound investment for any employee. The employees listed below should wear safety footwear as prescribed by department supervision when performing tasks, including but not limited to the following: (1) All personnel while on any construction or maintenance project job site. (2) Landfill personnel who work in the disposal area. Safety Manual Page 23 of 54 12/2010 (F) (3) Wastewater Treatment Plant maintenance personnel and plant operators when tearing down and maintaining machinery. (4) Traffic Signal Maintenance personnel while installing, constructing or maintaining street lighting and traffic control facilities. (Personal Protective Equipment should meet approved standards for dielectric properties.) (5) Water Filtration personnel and plant operators when tearing down and maintaining machinery. (6) All personnel working near construction equipment. (7) All personnel performing repair shop tasks. Hand Protection (1) Rings should be removed before performing any mechanical or construction work. (2) Gloves with leather palms should be worn when handling rough-edged or abrasive material or when hands could be cut, punctured or burned. (3) Rubberized gloves should be worn when handling skin-irritating materials. (4) Cleanse hands with soap and water--not gasoline or turpentine--to prevent skin irritation. (5) Learn to recognize poison ivy and poison oak and avoid both. 12.3 RESPIRATORY PROTECTION Exposure to harmful fumes, gases, mists and chemical dusts, and exposure to environments containing insufficient oxygen, is a potential risk associated with a number of County jobs. Injuries and illness resulting from these types of exposures can be avoided by using appropriate respiratory protection. Safe job performance is achieved when employees have adequate knowledge of the substances being handled, understand the circumstances under which harmful atmospheres may exist, know how to perform testing procedures to determine the nature of an environment before entering it, are provided the appropriate type of respiratory protection equipment and are sufficiently fit-tested and thoroughly trained in the correct use of respirators. The following rules are listed for general informational purposes. For more detailed standard operating procedures see Manatee County's Respiratory Protection Program. (A) Supervisors should ensure that all employees whose work assignments may involve exposure to toxic or oxygen deficient atmospheres have been medically evaluated for respirator use and properly trained and fit-tested. Safety Manual Page 24 of 54 12/2010 (B) The correct respiratory protection equipment should be conspicuously stored at work sites where the possibility of exposure to harmful atmospheres exists. The equipment should be kept clean and disinfected and used only for the protective function intended. (C) Each time respiratory protection equipment is used, a report should be made to the supervisor of the reason for its use, i.e. routine versus emergency. (D) Approved respiratory protection should be worn in the following instances: (1) When welding on brass, bronze or galvanized iron in confined areas where ventilation is limited. (2) When entering a permit-required confined space where tests indicate the presence of a toxic or oxygen deficient atmosphere after attempts have been made to purge and ventilate such atmosphere. (3) When determined by a supervisor to be advisable due to the presence, or suspected presence, of hazardous substances or the lack of oxygen in the environment. (4) Wherever chlorine, ammonia or other hazardous gas leaks are suspected or detected. (E) Respirators should not be worn when conditions prevent a good face seal. Such conditions may be a beard, sideburns, temple pieces on glasses or a cap that projects under the face piece. It is essential that employees be able to obtain a good face seal on short notice. (F) Each time a respirator is worn a fit check must be performed to ensure a good face seal. If a proper seal is not achieved the supervisor must be notified. The employee is NOT to enter the environment; protection is inadequate. (G) Wearing contact lenses in contaminated atmospheres with a respirator is prohibited. (H) Respirators shall be cleaned and disinfected after each use. Disinfection is accomplished by washing the mask inside and outside with a mild detergent and water. Dry thoroughly before storage and place mask in a vinyl storage bag. 12.4 OTHER PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT (A) A safety harness with a lifeline should be worn by any employee entering a permitrequired confined space. An attendant worker should be stationed outside the permit space to monitor and protect the entrant. (B) Vehicle Safety Seatbelts should be properly fastened by all occupants whenever a motorized vehicle is in motion. Safety Manual Page 25 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 13 HAND TOOLS 13.0 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED Injuries resulting from improper use and care of hand tools are a common occurrence. The following safety procedures for the use of hand tools shall be followed: (A) Select the right tool for the job. (B) The cutting edges of hand tools shall be sharpened as necessary. Tools should be carried with the sharp edge/point down. (C) Wooden handles of shovels, rakes, malls, etc., should be sanded periodically to prevent splinters. (D) Before using any tool check the handle to ensure it is tight and secure. (E) Check the head of all hand tools (hammers, chisels, punches, malls, etc), before use for burrs, chipped edges and mushroomed conditions. Do not use the tool if such conditions are present. Remove the tool from service and report it to your supervisor. (F) Wear shatter proof, clear goggles when using chisels, punches and wedges. Be sure the work area is clear of other persons before using such a tool. (G) Use only properly insulated tools (screwdrivers, wire cutters, etc.), when working near energized electrical circuits or equipment. Avoid using metal measuring tape, fabric tapes containing woven metal strands, rope with wire cord or other tools and equipment that have conductive properties. (H) Return tools to their proper place after use to prevent loss, and injuries from tripping and other hazards. Safety Manual Page 26 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 14 POWER TOOLS 14.0 GENERAL Power tool hazards range from electrical shock to being struck by debris. The following safety procedures for using power tools shall be observed: (A) Never operate power tools without the protective guards provided. (B) All electrical tools should be grounded by connecting a three wire cord with a polarized three prong plug to a properly grounded three-hole receptacle or must be double insulated if it is a two prong plug. (C) Electrical tools and machinery should be inspected for damaged cords and ground connections before each use. The most common defects occur at points where the cord is attached to the tool or where the cord is attached to the plug. Be sure to check for a secure connection that allows for an insulation plate on the inside portion of the plug. (D) When electrical equipment is to be used at a wet location, use low voltage equipment and wear rubber boots and rubber gloves. 14.1 GRINDERS (A) Grinding wheels should be mounted only by those employees who have been trained in the procedure. Fixed mounted Safety Signage will be displayed, “Wear Safety Shields & Goggles”. (1) A ring test should be performed on each new grinding wheel before installation. (A ring test is made by supporting the wheel freely on a rod through the arbor hole and tapping it lightly with a wooden object. A clear metallic ring indicates absence of cracks.) (2) The wheel must fit easily onto the spindle -- too loose or too tight is dangerous. (3) After the wheel is mounted, stand aside -- out of danger -- while allowing it to develop full operating speed, for at least one minute. (B) Grinding wheels are most subject to breakage when they are cold. Therefore, apply work gradually to a cold wheel at the beginning of each work period. (C) Never store a grinding wheel on damp or cement surfaces. Do not put oily rags on the wheels. (D) Every grinding tool must be securely fastened to the shaft before beginning work. Safety Manual Page 27 of 54 12/2010 (E) Grinding wheels should not be operated in excess of the maximum operating speed as given by the manufacturer on the wheel label. (F) The work rest on all grinders should be kept adjusted closely to the wheel with a maximum opening of 1/8 inch to prevent the work from being jammed between the wheel and the rest. The distance between the wheel periphery and the adjustable tongue or the end of the peripheral member at the top should never exceed 1/4 inch. Never attempt these adjustments while the machine is in motion. (G) Do not use the side of an emery wheel for grinding unless it is specifically designed for side grinding. Side grinding weakens the ordinary wheel and may cause it to burst. (H) Only grind aluminum on wheels designated for aluminum grinding. (I) Use the cutting surface of a grinding wheel uniformly. A grooved cutting surface can dangerously weaken the wheel. (J) Grinder bearings should be kept properly oiled and adjusted. This will help prevent hot bearings and spindles which are sometimes responsible for melted bushings. (K) Do not abuse the wheel by applying excess pressure. (L) Be particularly careful when grinding narrow tools or other objects as they are easily caught between the work rest and the wheel. (M) Grinder operators should wear a Full faced Safety Shield & Goggles at all times when the grinder is in use. 14.2 DRILL PRESSES Warning Safety Signage will be mounted at each drill press “Wear Safety Shields and Safety Goggles at all times during operation" (A) Adjust the work table to allow plenty of room for the jig, and keep hands away from the revolving drill. Never run the point of the drill into the table. (B) Be sure that both the chuck and the drill are tight on the spindle and that any circular tables are tightened before beginning to drill. (C) A sluggish drill is usually the result of incorrect grinding. Be sure the drills are sharpened properly for the particular material to be drilled so that the cut will be the right size. (D) Materials should be clamped or otherwise fastened to the drill press bed -- not held in the hand. (E) Never run a drill faster than the rated speed as this may result in broken drills, damaged material and serious injury. Safety Manual Page 28 of 54 12/2010 (F) Do not remove broken drill pieces with a center punch and hammer. (See your supervisor for additional instruction.) (G) Never leave the key in the chuck after tightening a drill. Report any protruding set screws to your supervisor so that the drill may be repaired or replaced. (H) Lower the spindle close to the table before removing the chuck so that it will not cause injury or damage to the material as it falls. (I) Reduce the pressure if there is any backlash in the spindle. Listen carefully for the distinctive noise made when the drill comes through work so that you can ease the pressure when necessary. (J) Set the safety stop to prevent the over arm of a radial drill from swinging out where it may cause an injury. (K) Do not wear gloves and loose clothing while operating a drill press. 14.3 LATHE OPERATIONS Safety Signage will be affixed & mounted at each lathe stating, Wear Safety Shields and Safety Goggles at all times during operation”. (A) Lathe tools should be ground so that the chips will break off instead of curl. Only lathe dogs that are equipped with safety set screws shall be used. (B) Be sure that all gear and belt guards are in place. This includes back-gears and ingears especially. (C) Whenever chucks or face plates are changed, they shall be started on the spindle by hand power. Keep hands off chuck rims when the lathe is in motion. (D) Be sure to remove the chuck wrench immediately after adjusting a chuck. Also be sure that the tailstock, tool holder and material are properly clamped before turning on power. (E) For external work, never set the lathe tools below the center of the work being turned. (F) Use a brush to remove chips. Do not use compressed air. (G) When near the chuck end or head stock, file with the right hand over the lathe stock instead of the left hand, holding the file in such a position that in case it is forced back, the hand will not be forced against the body. (H) Do not wear long sleeves while operating a lathe. (I) Lathe operators should wear safety goggles during all lathe operations. Safety Manual Page 29 of 54 12/2010 14.4 COMPRESSED AIR (A) Using compressed air for cleaning purposes is prohibited. Brushes should be used for cleaning machinery. (B) Check the air hose of compressed air equipment before each use for leaks, tears or other defects. Do not use defective equipment; take it out of service. Report all equipment and machinery defects to your supervisor. (C) Remove the piston or tool of an air hammer whenever it is not in use to prevent it flying out and striking someone. (D) Always close the valve on the air line and release the air from the hose before cleaning, repairing, inserting any tool or leaving any air powered unit. (E) Maintain a secure hold on the handle of the air motor to prevent it from flying around and striking you. (F) Be sure the discharge end of an air hose is secure before releasing compressed air into it so that it will not swing around and cause injury. (G) The use of safety goggles and hearing protection, in the form of ear muffs, is required when operating compressed air equipment. 14.5 WOODWORKING MACHINERY Warning Safety Signage will be affixed and mounted at each piece of equipment “Wear Safety Shields and Safety Goggles during operation”. (A) Machine guards on woodworking machinery should be permanently attached. (B) When running short or narrow stock, use a block to protect your fingers. (C) Before using a circular saw, check all materials for possible warping. If a concave edge is found, place it away from the straight edge guide of the table saw. (D) Saws should be turned off before attempting to dislodge lumber. (E) A rip saw should not be used for crosscutting nor shall a crosscut saw be used for ripping. A spreader and kickback fingers are required when using a rip saw. A spreader is required when using a crosscut saw. (F) Learn to stand clear of possible "kickbacks" and to avoid the danger of being struck by small pieces that are frequently thrown from a circular saw. (G) Safety glasses should be worn by any employee operating woodworking machinery. Safety Manual Page 30 of 54 12/2010 14.6 GAS WELDING (A) All gas welding equipment and connections should be kept free of grease and oil. Oxygen will explode upon contact with oil or grease. Oily and/or greasy gloves may bring about the same effect and cause difficulty in handling the cylinders. (B) Never roll tanks on the floor. Do not attempt to carry them by hand or hoist unless properly secured. Use the skid provided when unloading cylinders from the truck. The cylinders must be securely chained after unloading. (C) Acetylene and oxygen tanks should be securely fastened with a chain in an upright position where there is no danger of their falling or being bumped. (D) Use only standard green oxygen hose with right hand couplings and red acetylene hose with left hand threads. (E) Blow out the tank valve before attaching the regulator. Never use compressed air for blowing out equipment as it may contain oil and moisture. Use oxygen to blow out oxygen hoses and acetylene to blow out acetylene hoses. (F) When exchanging an empty tank for a full one: (1) Shut off the valve on the empty tank. (2) Release the thumb screw on the regulator. (3) Disconnect the regulator, blow out the tank valve and connect the regulator to the full tank. (4) Stand on the opposite side of the tank and point the acetylene valve outlet away from the gauge while opening the tank valve. (5) Adjust the thumb screw on the regulator to the proper pressure, making sure there is no excess oxygen which causes unnecessary sparks in operations. (G) Clean the end of the torch before lighting it. Use only friction lighters. (H) Do not place materials in a position that will permit sparks, hot metal or a severed section of metal to fall on the gas supply hose or employees' feet. (I) Once work is completed, the welder should make a careful inspection of the job site to ensure that hot articles, which could develop into a fire, have not been left smoldering. (J) Proper safety goggles and gloves should be worn when performing gas welding operations. Safety Manual Page 31 of 54 12/2010 14.7 ELECTRIC ARC WELDING (A) Welding operations should be performed inside a regular welding booth, whenever possible. If work must be performed outside a booth, the arc should be effectively screened to prevent injury to eyes and other parts of the body. (B) Before entering a welding area, be sure the operator is aware of your presence (shout, if necessary), so that s/he can guard against sudden flashes and injury to you. (C) Any person entering a welding area should wear required welding eye protection. (D) When welding galvanized material, the operator should use a specially designed airline respirator which fits under his/her helmet. (E) Deposit short ends of welding rods in containers provided for that purpose in order to prevent burning holes in shoes and/or starting fires. (F) When not in use, place the electric holder where it cannot cause an arc. (G) Prevent injury to yourself and others from short circuits by using only welding cables that are in good condition. (H) Only properly trained and authorized operators should use welding equipment. Never attempt to repair welding equipment. Take broken or defective equipment out of service and report it to your supervisor. (I) Proper helmets and shields should be worn during all electric arc welding operations. Do not remove your helmet while bending over a hot weld. (J) WARNING: Remove butane lighters from clothing pockets and store with other personal items. No butane lighters are allowed in welding work area. 14.8 TREE TRIMMING AND CHAIN SAW SAFETY (A) An employee should not be assigned to work in a tree unless s/he has been trained as a climber and is: (1) Able to use a climbing rope and saddle. (2) Able to tie all necessary ropes & knots. (3) Able to use necessary hand tools. (B) Before beginning any tree operations, check the trees in the surrounding area for any dangerous conditions. Safety Manual Page 32 of 54 12/2010 (C) Except in cases of emergency, tree work will be avoided when trees are wet, during high winds or during extreme low temperatures. (D) Tree trimmers will ask only crew members for assistance. Never ask bystanders for help. (E) Danger signs and barriers should be placed around areas where tree work is to be done. (F) Supervisors are responsible for crew instruction, tool inspection, and enforcement of all safety rules and determination of suitable clothing for work activities. (G) Ropes should be used for raising and lowering tools. (H) Ropes of suitable strength should be used for lowering large limbs. (I) Safety or climbing ropes should not be used for lowering limbs. (J) Ladders should not be used unless they can be set on a firm foundation. (K) Ladders should be frequently inspected for damage. All ladder safety rules shall be observed. (See SECTION 17: LADDERS AND SCAFFOLDS.) (L) Climbers should always call a warning before dropping limbs. (M) Never leave hangers or tools in trees during lunch hour or overnight. (N) Special precautions should be taken when working near live wires. (See SECTION 15.8: AERIAL PLATFORMS and Bucket Trucks) (O) All wires broken or damaged during tree work should be reported to the proper utility company. (P) Fallen wires should be guarded until service workers arrive. (Q) Do not touch a victim who has come in contact with a live wire. S/he must be separated from the wire by the use of non-conductive materials. Call 911 for emergency assistance at once. (R) Pull ropes should be used to guide the fall of large trees. Once the notching has begun, the tree must not be left unguarded. (S) Only one-man saws should be used in trees. All chain saws should be roped with their own rope. Either a taut line hitch or a ground person should secure the rope during tree trimming operations. Safety Manual Page 33 of 54 12/2010 (T) Turn the saw motor off and point the guide bar to the rear before walking or changing work locations. (U) Never walk or change work locations while the saw motor is running. (V) Always stand behind the saw when cutting - never at the side. (W) Avoid using the tip of the saw for cutting to prevent kick back. (X) Never replace the chain in the guide rail groove while the saw motor is running. (Y) Clean and check saws thoroughly and lubricate as required. Maintain proper tension on the chain. Always inspect the saw for sharpness as a sharp saw will reduce maintenance costs and provide faster, safer and easier cutting. (Z) Refuel the saw before it runs out of gasoline to avoid a "bound saw" which is difficult to refuel and start, and to avoid the danger of fire when starting a saw at the refueling site. (AA) Hard hats, safety footwear, chaps, and safety goggles / glasses should be worn when performing tree trimming when utilizing a chain saw. Additional Personal Protective Equipment may be required based on identified hazards. 14.9 LAWN MOWERS (A) Do not leave a power lawn mower unattended while the motor is running. (B) Safety goggles or glasses should be worn by employees operating a push type rotary lawn mower. (C) Areas to be mowed should be inspected for foreign objects. Wires, stones, bottle caps, sticks, etc., shall be removed before mowing. (D) Mower operators should warn bystanders of the danger of flying objects. Extreme caution should be taken when children are in the immediate area. (E) Operators should keep hands and feet away from the undercarriage of the mower. (F) The spark plug wire should be disconnected from the spark plug during maintenance repairs. (G) After mowing is completed, disconnect the spark plug wire from the spark plug, remove dirt, grass, etc., from the top of the mower and store the mower in a dry location under a protective cover. Safety Manual Page 34 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 15 CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE SAFETY ABOVE GROUND AND UNDERGROUND 15.0 GENERAL (A) Public Works and Transportation employees are often involved in jobs related to the heavy construction industry. Public Utilities are often installed in or near the work site area of projects being completed by County employees. Safety precautions, related to public utilities, must be a part of job planning. Overhead lines are a hazard and must be considered when operating machinery beneath them. Underground services are a hazard when damaged in a dig up. For safety sake, employees cannot assume they know what utilities are where. Contact with an electrical service or rupture of a gas service are the most immediate dangers to County Employees engaged in construction and maintenance activities. Such accidents can be prevented by advanced planning. However, should they occur, prompt reporting to the utility concerned is of prime importance. Escaping natural gas constitutes an explosion potential and the leak must be stopped by trained personnel as soon as possible. Contact with a primary electrical circuit constitutes a shock hazard. If an injured employee is still at the point of contact or rescuers are attempting to remove the victim, the reactivation of the circuit poses additional hazards. An immediate report to the utility affected will avoid compounding the hazard. (B) Some of the principal hazards affecting employees and/or public safety are: (1) Dig ups resulting in gas explosion, electrocution, flash burns, etc. (2) Rupture of gas, water and sewer facilities from using mechanical compaction, boring or digging equipment. (3) Electrocution resulting from contact with overhead electrical wires. (4) Interruption of electrical service or communication lines from dig ups, pole collapse, etc. (C) Construction accidents can be prevented by considering safety in planning every job, coordinating with other utilities to locate services near the job site, instructing workers about the hazards involved as each job is explained to them, using approved protective clothing and equipment and adhering to approved safe job procedures. Safety Manual Page 35 of 54 12/2010 15.1 SEE: Sunshine State One-Call Florida, Inc. "Professional Excavators Guide" (Current version of) available from Public Works Department. 15.2 IF A GAS PIPELINE IS DAMAGED (A) Immediately call the gas utility service and repair office to report the damage. (B) Shut off all motors in the area; do NOT start motor vehicle engines. (C) Remove all flares AND sources of ignition from area. (D) Enforce NO SMOKING in the area. (E) Do not cover a damaged pipeline. (F) Do not operate gas valves. (G) Check buildings in the immediate area for gas odors. (H) Request occupants to leave the area if gas odors are detected. (I) Reroute traffic from the immediate area and notify the supervisor, department head and Risk Management of the situation. (J) Stay near the area until relieved by police or gas company personnel. 15.3 ELECTRICAL TRANSMISSION SERVICE (A) Accurately locate any electrical service in the work area and contact Florida Power & Light (FPL) when work is to be done near any such service. (B) When excavating near pole or guide-wires, and the possibility of damage to cables or collapse of a pole line exists, contact FPL. (C) Before excavating beneath buried conduit or cables, arrangements concerning maintenance of electrical services, proper support of exposed conduit and/or suitable compacting of backfill should be planned in advance with the proper utility service. (D) All wires and conduit should be considered energized and dangerous. (E) Booms and protruding parts of construction machinery should not be operated closer than twenty five (25) feet from overhead electric power lines. When construction machinery is operated in close enough proximity to energized lines that a full traverse of the moving parts could result in contact, a signal person should be provided to direct the operator. Signal persons should watch carefully and give signals to the operator to prevent movement of the machinery any closer than the twenty five (25) foot minimum clearance. Safety Manual Page 36 of 54 12/2010 (F) Employees in contact with machinery and/or handling suspended loads, slings or cables are in a most hazardous position should accidental contact with energized electrical lines occur. Supervisors should warn ground crews of this hazard and ground crews should be especially careful to prevent such contact. ***Fall Protection Full Body Harness & Safety Lanyards will be utilized for all above ground work by employees utilizing all types Aerial Devices including Aerial Baskets, Platforms, etc. The utilization of Safety Belts has been outlawed since 1998 according to OSHA and are not authorized devices for county employees. 15.4 IF MACHINERY CONTACTS ENERGIZED WIRES: (A) Immediately contact FPL. (B) The operator should attempt to swing the boom clear. (C) Persons on the rig are usually safe. If necessary to leave the rig, jump entirely free, being careful that no part of the body is in contact with the machine and the ground at the same time. (D) When jumping clear of energized equipment, try to land on dry ground. (E) Once clear of energized equipment, do not return to it, and keep others away from it. 15.5 TELEPHONE SERVICE (A) Notify the telephone company when work is to be done near any telephone service. Telephone circuits operate on low voltage and are not an electrical hazard. However, they can become energized with higher voltages when accidentally crossed with power lines at points which may be far removed from the job site. Consider ALL lines hazardous. Observe the precautions listed for ELECTRICAL TRANSMISSION SERVICE (Section 15.3). (B) Do not cut or disturb guide wires. Sudden release of tension may cause an entire pole line to collapse. (C) Underground telephone cable is usually buried with a minimum cover of 24 inches. Subsequent grading may reduce this minimum. Pipe pushers, trenchers, boring tools, air hammers, pins for paving and curb forms, etc., should not be used until after the location and depth of any buried telephone cables and conduit in the work area has been determined. Safety Manual Page 37 of 54 12/2010 15.6 DIGGING AND TRENCHING OPERATIONS HARD HATS and Reflective Safety Vests are required to be worn by all personnel on all excavation sites. (A) Approved guards such as cribbing, barricades, warning signals or flag persons should be in place when workers are engaged in any excavation or street repair work or when removing or replacing manhole covers. Open manholes should be properly guarded with warning devices. (B) A signal person should be posted on the surface of the excavation to assist the machinery operator. This person should be stationed where he/she can be easily seen by the operator (outside the range of movement and hazardous area of loads), and should warn the operator of the presence of others who enter the area. (C) Manhole covers not equipped with lifting devices should be raised slightly on one edge and slid off the hole. Reverse the procedure to replace the cover. (D) All tools, materials and equipment should be kept a reasonable and safe distance from the edge of trenches, curbs or embankments. (E) When chains, ropes, cables, slings, etc., are placed under tension, employees and observers should be warned to stay beyond the range of whipping strands should the chains, ropes, etc., break from the tension. (F) The public should be directed away from hazardous areas and material piles. 15.7 MATERIALS HANDLING MACHINERY (A) When heavy objects are to be moved with a crane, be sure the load to be suspended is properly secured by slings and grips with sufficient strength to hold the load. (B) Always use non-conductive rope or nylon tag lines when guiding a suspended load into position. This will reduce shock hazards if accidental contact with an electrical service occurs. The rope or tag lines should be of sufficient length to maintain a safe working distance from the drop zone in case a suspended load should fall. (C) Never crawl under mobile construction machinery during rest or lunch breaks. (D) Avoid moving a suspended load over persons on the ground or above persons working in an excavation. 15.8 AERIAL PLATFORMS AND BASKETS (A) County employees use several kinds of mobile equipment with platforms or baskets and genie lifts on which they are mechanically lifted for work high above ground level. Full Fall protection is required at all times while in a lift. Safety Manual Page 38 of 54 12/2010 (B) This equipment is used by line persons and tree trimmers and in various public service maintenance tasks. Possible hazards include: (1) contact with electrically charged overhead wires; (2) falls; (3) dropping tools and other objects on workers below; (4) being caught in, on or between equipment parts. (C) Extreme care should be exercised when operating this equipment near overhead lines. With certain exceptions, aerial platforms or baskets should not be positioned closer than twenty five (25) feet to overhead lines. These exceptions are: (1) when maintenance personnel must work on overhead lines; (2) when traffic signal maintenance personnel must service a traffic signal installation. (D) A raised platform or basket becomes unstable if jarred by a collision to the base vehicle, when not operated smoothly or if mechanical controls fail. To prevent falling hazards, any employee who works from an aerial platform or basket should use a safety Full Body Harness with Lanyard attached. Safety lines should be connected to a fitting or harness secured to the platform, basket or boom tie in and to a Full body Harness worn by the employee. (E) Equipment used by County crews to operate outriggers, booms, power takeoffs, etc., has controls located in various parts of the basic machine. There is little standardization even on equipment of the same general type. The operator who activates such controls should ensure all persons in the vicinity of the equipment are clear of any moving equipment parts before power is applied. The supervisor or lead person in charge of the crew will ensure all precautions are taken and warnings are given. (F) Always lower outriggers before raising the basket. Most machinery now in use is equipped with an interlock which prevents raising the basket until outriggers are down. (G) Before lowering outriggers, the operator should give adequate warning to persons near the equipment. If the automatic audible signal is inoperative or unavailable, a verbal warning should be given. Safety Manual Page 39 of 54 12/2010 15.9 WORKING IN PUBLIC RIGHT OF WAY (Roadside work activities) Tree trimming, curb site planting, landscaping tasks, utility service repairs, street sweeper operation, trash pick-ups, light fixture cleaning, traffic signal repair and other construction, maintenance and repair activities often require County employees to work in or alongside rights of way normally used for vehicle or pedestrian traffic. These activities may interfere with normal traffic flow in the form of standing or slow moving vehicles and equipment or occasional movement of equipment into the normal right of way. The following safety procedures should be followed utilizing the U.S Highways Administration: Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) (A) A DOT, Department of Transportation orange or green High Visibility Warning Vest should be worn by all employees working in or alongside any public right of way. DOT approved Class Three High Visibility Vests must be worn at night. (B) Warning signs and barricades should be used whenever construction, maintenance or repair work performed by County crews obstructs any public right of way. (C) Whenever possible, maintain work site traffic flow, interfering as little as possible with normal traffic patterns. (1) Protect employees from being struck by vehicular traffic. (2) Assist the public to safely avoid hazards that interrupt the flow of vehicular and pedestrian traffic. (D) Notify the proper law enforcement agency before any County street is completely closed for maintenance or repair work. (E) When a portion of a street has been closed and equipment must be operated in lanes left open to traffic, a flag person should be provided to control traffic. (F) When County work crews must perform emergency work in a posted traffic lane during peak traffic periods, the proper law enforcement agency should be notified of the work location, the time work began and the estimated time of completion. (G) When road surfaces are to be repaired, manholes opened or excavations dug, adequate hazard warnings shall be posted before work is begun. A minimum amount of the right of way (consistent with safety requirements) should be blocked and that traffic efficiently rerouted. (H) If repair work obstructs a traffic lane and thus compresses several lanes of traffic into fewer lanes, adequate warning signs and barricades should be placed so as to warn motorists well in advance of the obstruction. If manhole openings and excavations constitute a hazard to pedestrians, adequate barricades and rerouting of walkways should be provided. Safety Manual Page 40 of 54 12/2010 (I) If an open cut is left in a posted traffic lane when work is stopped or suspended for any reason, a cover of sufficient strength to sustain normal traffic loads should be placed over the cut and anchored. If the cut cannot be covered and must be left overnight, adequate warning signs and barricades should be used, adequate lighting shall be provided and the Police Department should be notified. (J) Mobile equipment used for maintenance or repair of County streets should be equipped with flashing or rotating lights and any combination of the following warning lights: turn signal lights flashing lights rotating lights oscillating lights flashing arrow signs mounted on the vehicle or equipment Simultaneous flashing of all warning lights available should be implemented whenever any mobile equipment is operated in or alongside any public right of way. (K) In addition to the foregoing, staff should comply with all requirements of the county’s Right of Way Ordinance, at 82-21-28, et seq. of the Manatee County Code. 15.10 TRAFFIC WARNINGS AND BARRICADESU.S. Reference: U.S. Highway Administration: Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices ( MUTCD) (A) Hazard Prevention/Warnings: (i.e. large holes, soft patches, windrows, etc.) (1) Place signs (plus flashing lights at night) well in advance of the hazard. (2) Mark windrow ends with a warning flag during the day and a flashing light at night. (3) Gravel windrow should not be left in the middle of the road overnight. (4) Protect holes and patches with wooden horses or fence barricades and add flashing lighted barricades at night. (5) Replace flags used to mark a hazard with warning signs as soon as possible. (B) Barricade Lighting: The employee in charge of work requiring the lighting of a barricade should ensure the lights are operable, properly placed and adequate for the job. Safety Manual Page 41 of 54 12/2010 (C) Removal of Temporary Signs: (1) Signs placed solely for the protection of workers (Men Working, etc.), should be removed at the end of the day's work. (2) Signs placed to warn of temporary hazards (Bump, One Way Traffic, etc.), should be removed as soon as the hazard has been eliminated. (D) Protection of Employees Working on a Roadway: (1) "Workers Ahead/Construction Ahead" signs should be placed well in advance of the work zone, in both directions, during operations. (2) When patching and/or filling cracks, etc., work should be done on one-half of the roadway at a time. (3) Flag persons should be used whenever the situation warrants. 15.11 FLAG PERSON PROCEDURES (A) Flag persons should: (1) stand near enough to the workers being protected so there is no doubt as to the flag person's purpose; (2) stay not less than 100 feet from the workers unless conditions make this impossible; (3) Stand on the shoulder of the roadway and to the right of approaching traffic. (B) To Stop Traffic: The flagger should face the traffic and extend the STOP sign paddle in a stationary position with the arm extended horizontally away from the body. The free arm should be raised with the palm toward approaching traffic. (C) To Direct Stopped traffic To Proceed: The flagger should face traffic with the SLOW sign paddle held in a stationary position with the arm extended horizontally away from the body. The flagger should motion with the free hand for traffic to proceed. (D) To Alert or Slow Traffic: The flagger should face traffic with the SLOW sign paddle in a stationary position with the arm extended horizontally away from the body. The flagger may motion up and down with the free hand, palm down, indicating that the vehicle should slow down. (E) To Flag Traffic at Night: Safety Manual Page 42 of 54 12/2010 (1) Class III (3) Garments and STOP/SLOW paddles should be retro reflective visible at a distance of 1,000 feet. (2) Flagger stations should be illuminated. SECTION 16 WORKING IN CONFINED SPACES 16.0 DEFINITIONS All employees assigned to a Confined Space Operation must be certified through the County Safety Manager and must have received a minimum of 20 hours CSET training and possess a current CSET Certification Card. Eight (8) Hours of Annual Re- training and CS Entry is required to maintain your certification through Manatee County Government and OSHA. All CSET members must possess a current CPR and First Aid card. (A) Confined Space means a space that: is large enough and so configured that an employee can bodily enter and perform assigned work; and has limited or restricted means for entry or exit (for example, tanks, vessels, silos, storage bins, hoppers, vaults, and pits are spaces that may have limited means of entry); and is not designed for continuous employee occupancy. (B) Non-permit Confined Space means a confined space that does not contain or, with respect to atmospheric hazards, have the potential to contain any hazard capable of causing death or serious physical harm. (C) Permit-required Confined Space (permit space) means a confined space that has one or more of the following characteristics: contains or has a potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere; contains a material that has the potential for engulfing an entrant; has an internal configuration such that an entrant could be trapped or asphyxiated by inwardly converging walls or by a floor which slopes downward and tapers to a smaller cross-section; or contains any other recognized serious safety or health hazard. 16.1 GENERAL Protection against hazards involves adequate precautionary measures. Testing instruments must be used to detect the presence of explosive gases or vapors, other toxic gases or vapors, and oxygen deficient atmospheres. If tests indicate danger, the area Safety Manual Page 43 of 54 12/2010 should be purged of dangerous atmospheres, ventilated and then tested again. The source of contamination should be closed off if possible. Whenever it is necessary for a worker to enter a space that is potentially hazardous, appropriate respiratory equipment should be used. (See Section 12.3: RESPIRATORY PROTECTION.) 16.2 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following safety procedures for working in confined spaces are established and should be followed: (A) Before entering a permit space, test(s) as should be made to determine whether explosive or toxic gases or vapors are present and if oxygen deficiency exists. Atmospheric Testing by the utilization of a Calibrated Gas Monitor Detector should be conducted & recorded before entry into the space. The Competent Person & Confined Space Entry Team should review the results of the Atmospheric readings. (B) Whenever possible, venting of hazardous atmospheres should be accomplished before entering a permit space. Air Monitors will be utilized continuously during the Confined Space Entry operation by a Certified Confined Space Entry Technician, known as the Outside Attendant. (C) Adequate ventilation should be maintained. (D) When using portable blowers to ventilate, be sure the air intake does not pick up carbon monoxide fumes from the engine. (E) Appropriate respiratory equipment should be used and all users shall be instructed in the proper use of such equipment. (F) No employee should enter a permit-required confined space without a safety harness and attached lifeline tended by another employee at the point of entry. (G) Smoking or open flames in any underground operation or in other confined spaces is prohibited. (H) Confined space exits should never be blocked. (I) Before opening manholes, barricades and warning signs should be properly placed to protect vehicular and pedestrian traffic. (J) Ladders should be used to enter manholes if there is any doubt about the safety of the manhole steps. Safety Manual Page 44 of 54 12/2010 Only lights approved and provided by the County shall be used in manholes and sewers. (K) When changing air tools, the air supply shall be shut off at the supply source. It shall not be shut off by bending or pinching the airline hoses. (L) Lift Station Entry (See Lift Stations Section & Sewer Collections Section Safety Policy). Safety Manual Page 45 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 17 LADDERS AND SCAFFOLDS 17.0 GENERAL Electrical shock and falls are the two most critical types of injuries sustained while working from ladders and scaffolds. The following safety procedures concerning ladders and scaffolds should be followed: 17.1 LADDERS: See OSHA 1910.25 Ladders (A) Metal ladders should not be used in the vicinity of electrical circuits. (B) Wooden ladders should be inspected periodically. Wooden ladders shrink over time which may loosen the steps or back bars. To maintain the strength and steadiness of a ladder, hold each rod beneath the steps with pliers and tighten the nut at the end with a wrench. (C) (Wooden ladders or scaffold planks should not be painted as defects in the wood may be covered by the paint. A good grade of spar varnish or a mixture of linseed oil and turpentine shall be used to preserve the wood. (D) Ladders shall not be placed against a window sash. (E) Ladders form a triangle when placed against a wall or other object to be climbed. When properly placed, your shoe tip should touch the bottom of the side rails & your arms out stretched shall touch the rung in line with your shoulders. (F) All ladders should be long enough to extend at least (3) three rungs above the level to which the user is climbing. A Heel Man should be utilized to stabilize the ladder to prevent slipping. If a heel man is not available the ladder should be tied off & secured. (G) Stepladders should not be used as straight ladders -- they are not designed for this purpose. (H) If the bottom of a ladder is placed on an unsecured surface, the ladder should be secured by the use of hooks, ropes, spikes, cleats or other anti-slip devices or by stationing an employee at the base of the ladder to hold it in position. (I) Never stand on the top step of a stepladder. (J) Only one person at a time should be on a ladder. (K) Never carry articles in hand while climbing ladders. Use a hand line to raise and lower tools and materials or suspend tools in a belt. (L) When ascending or descending a ladder, always face the ladder and have free use of both hands. Safety Manual Page 46 of 54 12/2010 (M) Clean muddy or slippery shoes before climbing any ladder. (N) Keep ladder rungs clean and free of grease and oil. (O) When it is necessary to place a ladder near a door or other traffic area, establish warning signals, display warning signs, or take other precautions to prevent accidental contact that might upset the ladder. 17.2 SCAFFOLDS (A) Planks and other materials used to build scaffolds must be sound and free of knots. Keep planks in good condition through periodic application of a spar varnish. Never use paint on planks. (B) Planking shall have cleats.. Scaffolds over ten feet high shall have Toe Boards, Mid Rails and Hand Rails. (C) When working from a scaffold, keep tools in a bucket or box that is secured to the scaffold in order to prevent injuries caused by falling tools. (D) Full Body Harness with Lanyard & attached safety lines is required on all scaffolds. Safety Manual Page 47 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 18 MOTOR VEHICLES AND MOBILE EQUIPMENT 18.0 GENERAL County vehicles are easily identified and have what is often called "high exposure". They constitute a traveling advertisement seen by many citizens. County vehicle drivers' behavior effects the public's perception of Manatee County Government. Courteous and considerate driving habits combined with defensive driving principles prevent accidents and build good public relations. 18.1 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following safety procedures are established and should be followed: (A) Vehicle Safety Check: (1) Employees are responsible for a DAILY vehicle safety check. (2) Safety checks should include: Lights Power steering and fluid reservoir Horns Windshield washers and wipers Tires Directional signals Clutch travel Brakes and brake fluid Motor oil Hydraulic systems Fire extinguisher Vehicle damage (Brakes should be tested by putting the vehicle in gear and applying the brakes to bring it to a stop.) (3) Perform all safe driving adjustments (seat, inside and outside mirrors and sitting position) before putting the vehicle into gear. (B) County vehicle drivers must possess a valid Florida Driver's License and must be thoroughly familiar with state and local regulations governing motor vehicle operations. An employee operating an emergency vehicle is not absolved from civil or criminal liability for the consequences of wantonly reckless driving. The driver must be in a position to satisfy a jury that he/she used reasonable care and prudence in operating an emergency vehicle. Even though emergency vehicles have warning devices, drivers are expected to PROCEED WITH ALL CAUTION. (C) All slow moving equipment operated in public rights of way should be equipped with a triangular shaped reflecting sign and flashing lights in accordance with the State of Florida Motor Vehicle Code. Safety Manual Page 48 of 54 12/2010 (D) Load Security: (1) Supplies transported in motor vehicles should be secured in such a manner that they will not dislodge, fall out or fall forward, during transit or sudden stops. (2) Truck drawers should be secured before the truck is driven. (3) All tower equipment (ladder trucks, aerial buckets, etc.) should be checked and secured before the vehicle is moved. (E) Manatee County Government prohibits the use, by any employee, of alcohol or any illegal drugs, or the misuse of legally obtained drugs, when operating County vehicles or equipment. (F) All persons who drive or ride in County vehicles shall wear seat belts. (G) No more than three persons shall ride in the front seat of any vehicle. Persons should not be transported in any vehicle unless safe and secure seating is provided for each person. All occupants will wear seat belts. (H) Parking Vehicles: (1) On arrival, whenever possible, back INTO the parking place. Backing IN on arrival prevents having to back OUT after surrounding conditions may have changed. (2) If pulling in forward is the only parking option, when leaving either: use a spotter, or walk all the way around the vehicle to ensure clearance. (3) Except when working conditions require otherwise, turn off the engine, remove key from ignition, set emergency brake and leave in gear. (4) When parking on a downgrade, turn the front wheels of the vehicle towards the curb. When parking on an upgrade, turn the front wheels away from the curb. Set the brakes and put the transmission in "PARK" before leaving the driver's seat. (I) Backing Vehicles: When backing a vehicle, be sure the way is clear. Get out of the vehicle and inspect the area. Back slowly and sound horn or audible reverse signal if necessary. When backing a vehicle or equipment the size of a pickup truck or larger, another employee should serve as a safety guide, or spotter, and should direct the backing operation from outside the vehicle. (J) Never leave a vehicle unattended while the motor is running. (K) Drivers must be particularly alert when driving in areas where children are known to gather. Children must be kept from playing in or near County owned vehicles. While working in areas such as schools, parks, playgrounds, swimming pools or Safety Manual Page 49 of 54 12/2010 community centers, drivers should be especially watchful for children and should drive carefully and slowly at all times. (L) Stay within posted speed limits. Slow down when conditions warrant. (M) Do not assume the right of way. The driver who has the last chance to avoid an accident may be the driver in the legal right. (N) Keep the Three (3) second rule in effect when following other vehicles to avoid tailgating. Do not allow others to tailgate. Slow down, pull over to the roadside and let the tailgater pass. The Three Second Rule Stay three (3) SECONDS BEHIND THE CAR IN FRONT OF YOU. You will keep the correct distance no matter what your speed if you: Watch the vehicle ahead pass some definite point on the highway, such as a telephone pole. Count to yourself "one thousand, two thousand, three thousand". If you reach the mark before you finish saying those words, you are following too closely. (O) Signal intentions at least 100 feet in advance before changing lanes or directions. Avoid sudden braking. (P) Headlights: Turn on low beam headlights during dark periods of the day such as during rain storms and fog. When driving at night, headlights should be on from one-half hour before sunset until one-half hour after sunrise. Parking lights designate a vehicle is parked. Never drive with only the parking lights on. Utility vehicles and other mobile equipment the size of a pickup truck or larger should have the headlights ON when operating in or alongside any public right of way. NOTE: 1. Red Light Camera’s- County Vehicles Running Red Lights. All Manatee County Driver Operator(s) while operating a county vehicle will be responsible for any Moving Violations or Infractions caused by them. They will be responsible for all fines levied against the County’s motor vehicles while under their control. (Q) Fueling Tanks: (1) Safety Manual Turn the engine OFF. Page 50 of 54 12/2010 (2) Do not smoke near gasoline pumps. (3) Keep the hose nozzle against the edge of filler pipe. (4) To avoid spilling gasoline, do not fill the tank too fast or too full. (R) In the event of an accident involving a County owned vehicle, follow the procedures outlined in SECTION 5, COUNTY VEHICLE ACCIDENT ADMINISTRATION. Safety Manual Page 51 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 19 FIRST AID 19.1 PROCEDURES ESTABLISHED The following first aid rules are established and should be followed: (A) First aid cabinets or kits should be maintained in all County buildings. (B) Supervisors should inventory and restock first aid supplies monthly, and after each use. The supplies maintained should be those specified by the kit's manufacturer. (C) Minor first aid treatment for cuts, scratches, etc., should be self-administered whenever possible. Be sure that open wounds are thoroughly cleansed with soap and water to prevent infection. 19.2 ON-THE-JOB INJURIES All on-the-job injuries, no matter how minor, should be reported to the supervisor immediately. Procedures outlined in SECTION 4, ON-THE-JOB INJURIES, should be followed. (A) Animal Bites: Due to the possibility of rabies, animal bite cases should be referred immediately to an emergency hospital facility for prompt medical attention. The Animal Control Division will be contacted and an attempt to confine the animal should be made. (B) Life or Limb Threatening Injuries: Whenever a life or limb threatening on-the-job injury occurs, call Emergency Dispatch, 9 - 1 - 1. This decision rests with the injured employee's immediate supervisor. Some examples of life or limb threatening injuries are: (1) employee unconscious or apparently in shock; (2) employee cannot get up from floor or seated position; (3) an apparent fracture; (4) severe bleeding; (5) severe abdominal pain; (6) chest pain; (7) breathing difficulty Safety Manual Page 52 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 20 COUNTY REPORTING REQUIREMENTS The Manatee County Attorney Office, Risk Management Division, recommends all Departments maintain a record of each workplace injury, illness, occupational disease, and fatality. The purpose of the record keeping is to assist the Risk Management Division, and other governmental agencies, in tracking frequency and severity of workplace injuries and illnesses. The following criteria should be met to comply with the record keeping responsibilities: All departments are to maintain, for each Division or Section, by location or physical address or cost center, a "Log and Summary of Occupational Injuries, Diseases and Illnesses." Safety Manual Page 53 of 54 12/2010 SECTION 21 APPENDICIES A. FIRST REPORT OF INJURY OR ILLNESS B. WAGE STATEMENT C. VEHICLE INCIDENT REPORT/REVIEW D. INCIDENT REPORT E. SAFETY ORIENTATION CHECKLIST All documents are available on the INET under FORMS - Risk Management. Safety Manual Page 54 of 54 12/2010