Geology and Earth Resources

Geology and Earth Resources
1
Outline
•
•
•
•
•
•
Tectonic Processes
Rocks and Minerals
Rock Cycle
Economic Geology and Mineralogy
Environmental Effects of Resource Extraction
Mining
-
Reclamation
Conserving Geologic Resources
Geologic Hazards
2
Review Questions
1. Describe the layered structure of the earth.
(draw a diagram)
2. What are tectonic plates and why are they important to us?
3. Why are there so many volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis along the “ring of fire” that rims the Pacific Ocean?
4. Define mineral and rock.
5. Describe the rock cycle and name the three main rock types that it produces.
3
Review Questions continued
6. Figure 14.11 maps sources of some of the most important metals. What are they, and where do they come from?
7. Give some examples of nonmetal mineral resources and describe how they are used.
8. Describe some ways metals and other mineral resources can be recycled.
9. What are some environmental hazards associated with mineral extraction?
10. Describe some of the leading geologic hazards and their effects.
4
A DYNAMIC PLANET
5
Tectonic Plates
6
Tectonic Plate Movement
7
Pangea
8
Continental Shift
9
ROCKS AND MINERALS
10
Rock Types
Rock Cycle
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
11
Rock Cycle
12
Igneous Rocks
Basalt
Granite
13
Weathering and Sedimentation
Types of Weathering
Mechanical
•
Chemical
14
Sedimentary Rock
-
Shale
-
Sandstone
-
Tuff
15
Metamorphic Rock
Marble (from limestone)
Quartzite (from sandstone)
Slate ( from mudstone & shale )
16
ECONOMIC GEOLOGY AND MINERALOGY
•
Metals
Metals consumed in greatest quantity by world industry (metric tons annually):
-
Iron (740 million)
-
Aluminum
-
Manganese
(40 million)
(22.4 million)
-
-
Copper and Chromium (8 million ea)
Nickel (0.7 million)
17
Non-Metal Mineral Resources
Gemstones and Precious Metals
Sand and Gravel
Limestone
Evaporites
Sulfur
18
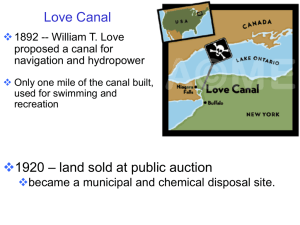
Environmental Effects of Resource Extraction
19
Placer Mining Mining
Underground Mining:
20
Strip-Mining or Open Pit Mining
-
Large scars on land surface.
-
Mountain top removal
-
Tailings
-
Toxic runoff
"Overburden Mountain", the newest of the High Peaks.
This is a huge tailings pile in the middle of the mine site.
21
Restoration
•
Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act
(1977) requires better restoration of stripmined lands, especially if land classed as prime farmland.
Difficult and expensive.
-
Complete reclamation often costs more than $10,000 / hectare.
50% of U.S. coal is strip mined.
-
Mine executives are beginning to recognize that keeping mines cleaner from the start will make good economic sense.
22
•
Processing
Metals are extracted from ores by heating or treatment with chemical solvents.
Smelting - Roasting ore to release metals.
-
Major source of air pollution.- Ducktown,
TN release clouds of sulfur dioxide resulting in a barren moonscape.
Heap-Leach Extraction - Crushed ore piled in large heaps and sprayed with a dilute alkaline cyanide solution which percolates through the pile to dissolve the gold.
-
Effluent left behind in ponds. Summitville
Mine in Colorado.
23
24
CONSERVING GEOLOGIC RESOURCES
•
Recycling
Aluminum must be extracted from bauxite by electrolysis. (expensive & energy-intensive)
-
Recycling waste aluminum consumes onetwentieth the energy of extraction from raw ore.
Nearly two-thirds of all aluminum beverage cans in U.S. are recycled. 15% 20 yrs ago.
Other metals commonly recycled:
-
Platinum, gold, copper, lead, iron, steel.
Look at Table 14.3
25
Substituting New Materials For Old
•
Reduce metal consumption by using new materials or new technologies.
Plastic pipes in place of metal pipes.
Fiber-optics in place of metal wires.
Metal alloys in place of traditional steel for cars.
Ceramic engine parts provide heat insulation around pistons, bearings, & cylinders, keeping the engine cool.
26
GEOLOGIC HAZARDS
•
•
•
•
•
Diseases kill more people than any other cause.
Drought-caused famines are the second biggest killers, including El Nino, bad weather, and bad governance.
Floods are the natural disasters that take the largest number of lives.
Wind storms cause the greatest property damage.
Look at Table 14.4
27
Earthquakes
•
Sudden movements of the earth’s crust that occur along faults where one rock mass slides past another.
Gradual movement - creep.
-
When friction prevents creep, stress builds up until eventually released with a sudden jerk.
Frequently occur along subduction zones.
Tsunami - Seismic sea swells.
28
New Madrid Fault
Information will be provided on Tuesday
29
•
Volcanoes and undersea magma vents are the sources of most of the earth’s crust.
Many of world’s fertile soils are weathered volcanic material.
Human / Environmental
Dangers
-
Volcanic Ash
-
Mudslides
-
Sulfur Emissions
Volcanoes
30
Mass Wasting
•
Materials are moved downslope from one place to another.
31
Summary
•
•
•
•
•
•
Tectonic Processes
Rocks and Minerals
Economic Geology and Mineralogy
Strategic Resources
Environmental Effects of Resource Extraction
Mining
-
Reclamation
Conserving Geologic Resources
Geologic Hazards
32
33