Classical Macroeconomics
advertisement

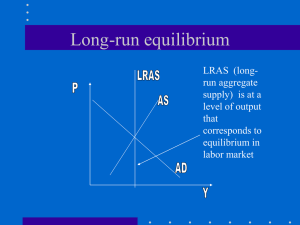
Module 35/19- Classical and Keynesian Macroanalysis J.A.SACCO Classical and Keynesian Macroanalysis Section 4A was a “cliffhanger” for section 4B. In Section 4A we examined what happens after an aggregate demand or aggregate supply shock What we didn’t analyze is the effect of those shocks on the determination of equilibrium output, employment and the price level (inflation). Classical Analysis Keynesian Analysis Two different methods of explaining the macroeconomy and the flexible nature of prices. Helps to explain equilibrium levels of GDP and employment. The Classical Model 1770’s- First attempt to explain the determinants of the price level and the national levels of output, income, employment, consumption, saving, and investment. Adam Smith J.B.Say David Ricardo Thomas Malthus The Classical Model Beliefs: I. II. III. All wages and prices are flexible and that competitive markets exist throughout the economy (supply/demand) Economy is self-regulating– economy always capable of achieving the natural rate of real GDP output and full employment (LRAS) The price level of products and input costs change by the same percentage, that is proportionally, in order to maintain full employment level of output The Classical Interpretation Say’s Law Supply creates its own demand Producing goods and services generates the means and the willingness to purchase other goods and services Example- Economy produces 7 trillion GDP (final goods/services) simultaneously produces the income with which these goods/services can be demanded. Actual Aggregate Income = Actual Aggregate Expenditure Total National Supply Equals its own Demand 5 Say’s Law and the Circular Flow 6 The Classical Model Assumptions of the Classical Model *In order to study the classical model must accept the following assumptions 1) Pure competition exists- no single buyer or seller of a good or service can influence price 2) Wages and prices are flexible- All prices and wages are determined by supply/demand. Buyers/sellers cause prices to rise and fall to equilibrium levels 7 The Classical Model 3) People are motivated by self-interest- Businesses want to maximize profit. Households want to maximize standard of living. 4) People cannot be fooled by money illusionBuyers and sellers recognize the change in relative prices, that is the understand inflation and lost purchasing power. 8% rise in wages/ 8% rise in price level (inflation) You are not better off!!! The Classical Model Consequences of the Assumptions 1) Minimize the role of government in the economy 2) If disequilibrium (unemployment/inflation) occurs it will be temporary 3) The power of market forces will keep the economy at full-employment in the long-run Role of Government is minimal! 9 Houston, We May Have a Problem! What is the problem with the assumption that all income will be spent to purchase all goods and services produced by an economy? Saving The Problem of Saving The Problem of Saving While it is true that the income obtained from producing a certain level of real GDP must be sufficient to purchase that level of real GDP, there is no guarantee that all of this income will be spent. Some of this income might be saved Saving is a type of leakage in the circular flow of income and output Therefore aggregate demand will be less than aggregate supply. This goes against the economy achieving the natural level of real GDP . 11 The Problem of Saving Full employment/No savings Below full employment, because of savings Leakage The Classical Model Question If saving increases won’t AD fall as consumption is reduced? Classical Answer No, because Saving (S) = Investment (I) Remember, investment (I) is a component of GDP. So any income saved would be invested by businesses so that the leakage of saving (less “C”) would be matched by the injection of business investment (more “I”). 13 Equating Desired Saving and Investment in the Classical Model Question How does the market adjust to changes in investment? In other words, what happens when demands of aggregate investment (a right shift) is greater then the supply of all savings in the economy? CREDIT MARKET 14 Equating Desired Saving and Investment in the Classical Model At 10% interest rate, an Interest Rate (percent) 14 12 10 Saving increase in investment creates a shortage (gap), Investment>Savings. The increase in interest rate returns the market to equilibrium 8 6 Investment2 Investment1 4 2 0 600 700 800 900 Investment and Saving per Year ($ billions) 15 Equating Desired Saving and Investment in the Classical Model Summary Changes in saving and investment create a surplus or shortage in the short-run. In the long-run this is offset by changes in the interest rate. This interest rate adjustment returns the market to equilibrium where S = I. *The credit market is entirely flexible based on supply and demand. 16 Equilibrium in the Labor Market Flexibility of the wage rate keeps the labor market in equilibrium. If supply of workers > Demand for workers Then wage rate decreases to reach “full employment” 17 Equilibrium in the Labor Market Hourly Wage Rate ($) 16 Unemployment S Supply of labor 14 Full-employment equilibrium 12 10 8 6 D 4 Demand of labor 2 0 105 115 125 135 145 155 Employment (millions or workers) 18 Changes in the demand for Labor Market Question How does the market adjust to changes ( left shift) in the demand for labor? 19 Equilibrium in the Labor Market Hourly Wage Rate ($) Unemployment 16 S 14 Wages adjust to eliminate the unemployment 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 D1 D2 105 115 125 135 145 155 Employment (millions or workers) 20 Equilibrium in the Labor Market Once again, just as with the credit market , the labor market is also flexible. If unemployed (surplus labor) accept lower wage than all workers can be put back to work (equilibrium reached) Classical economists believe that any unemployment that occurs in the labor market or any other resource market is “voluntary unemployment”. Classical Price Level and Output Determination LRAS Long term involuntary Price Level unemployment is impossible Say’s Law- Flexible interest rates, prices, wages will keep all markets in equilibrium The LRAS (vertical) is the only aggregate supply curve that exists in equilibrium Any shift of AD will soon cause a change in the price level Any AD shock will cause only “temporary” disequilibrium. Q0 Real GDP per Year 22 Classical Theory and Increases in Aggregate Demand Price Level LRAS Observations Initial equilibrium at P=100 and Q0 100 E1 AD1 Q0 Real GDP per Year 23 Classical Theory and Increases in Aggregate Demand Price Level LRAS 100 Observations Increase in AD creates disequilibrium At PL 100- greater than full employment exists (shortage) A1 E1 AD2 AD (Q1) > LRAS (Q0) AD1 Q0 Q1 Real GDP per Year 24 Classical Theory and an Increase in Aggregate Demand Price Level LRAS 110 100 E2 A1 E1 Observations Classical theory believes the economy adjusts back to equilibrium Wages/resources are bidded up. Price level increases to E2 returning the economy to equilibrium AD2 AD1 Q0 Q1 Real GDP per Year P = 110, Real GDP = Q0 Only the price level changes Real GDP supply determined 25 Classical Theory and an Increase in Aggregate Demand Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium Effect of a Decrease in Aggregate Demand in the Classical Model 28 Figure 19.5 Short-Run Versus Long-Run Effects of a Negative Demand Shock Ray and Anderson: Krugman’s Macroeconomics for AP, First Edition Copyright © 2011 by Worth Publishers Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium Classical Price Level and Output Determination Conclusions In the long run, everything adjusts so fast that the economy is essentially always on or quickly moving back to equilibrium. Economy is at or soon to be at full employment/equilibrium. In the classical model, equilibrium level of real GDP is supply determined by the LRAS. Changes in AD only effect the price level. It does not effect the output of real goods and services.