Respiration - Harris Girls' Academy East Dulwich
advertisement

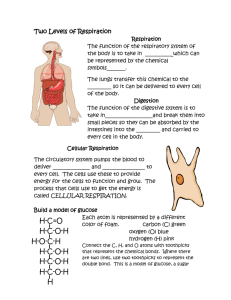
Respiration is a chemical process in which energy is released from food substances. Respiration is a series of actions in which energy is released from glucose. Glucose – A sugar made by the body from food which is used by cells to make energy in respiration. Cellular Respiration – Release of energy that happens in our cells. Respiration: glucose + oxygen – carbon dioxide + water + energy transfer. Blood also carries the glucose needed for respiration. The glucose is picked up by the blood vessels that surround our intestines. Glucose is then carried to the cells and moves around the body, all the tissues will get oxygen and glucose. Blood is mainly water and so it is very good at dissolving things. Waste dioxide is produced during respiration. This gas dissolves in the plasma. The dissolved carried by the blood to the lungs where it is released and breathed out. Blood is needed to carry fuel, oxygen and waste materials around the body. The fuel, glucose comes from food and the waste products, carbon dioxide and water, are made in the cells. Blood is a sticky red liquid that contains plasma and different types of blood cells. The red blood cells carry oxygen. Glucose and carbon dioxide are dissolved in the pale yellow liquid part of the blood, the plasma. Blood also carries many other chemicals around the body. Arteries have thick walls and take blood away from the heart. Veins have thinner walls and take blood back to the heart. Capillaries are tubes with very thin walls. There are three main types of blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries. Blood flows from the arteries into capillaries and the into veins. The heart has two pumps that work together one side pumps blood to the lungs, the other side pumps blood to the rest of the body Mitochondria are structures in cells where respiration happens. Respiration is the process that releases energy from glucose. This provides energy for life process such as movement and growth. Tissues and organs that need a lot of energy have large numbers of mitochondria in their cells. For example, liver cells and muscle cells contain a lot of mitochondria. Thin walls - to substances to pass through easily. Large surface cells – to allow many reactions to make place at once What does respiration happen? Respiration happens inside tiny structures inside your cells called mitochondria. All cells contain mitochondria, but different cells contain different amounts. Muscle cells carry out lots of respiration, so they contain large amounts of mitochondria. How does glucose get into cells? Glucose is a carbohydrate found in food. Digestion breaks down food into small molecules are absorbed by the wall of the same intestine, into the blood by the wall of the small intestine, into the bloodstream. Glucose is transported around your body in your blood. If dissolves in the liquid part of your blood. If dissolves in the liquid part of your blood called plasma. The dissolved glucose can diffuse into the cells that need it for respiration. How does oxygen get into cells? When you breathe in, oxygen fills the alveoli in your lungs. The oxygen then diffuses into your bloodstream. Oxygen is carried by the red blood cells in your body. Red blood cells contains haemoglobin (the substance that makes them red). Oxygen joins to the haemoglobin and gets carried around the body in the blood vessels. When it reaches a cell requiring oxygen diffuses into the cell. How does carbon dioxide leaves the body? If carbon dioxide remained in your body it would build up to a harmful level. You get rid of carbon dioxide when you exhale. Carbon dioxide produced during respiration diffuses out of your cells and into the blood plasma. The blood transports it to the lungs, where it diffuses into the air sacs, and is then exhaled. Sports drinks contains glucose, chemical salts and water. We sweat when we exercise because our body is trying to keep our temperature at night level. Staying alive needs energy. Our main fuel, petrol comes from the food we eat. In living cells, energy is released when glucose reacts with oxygen from the air we breathe. At the same time water and carbon dioxide are produced. This chemical reaction is called respiration. Aerobic respiration Aerobic respiration requires oxygen. It happens in cells when glucose reacts with oxygen. Word equation for Aerobic respiration: glucose + oxygen – carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) Anaerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration does not need oxygen. It happens when there is not enough oxygen for anaerobic respiration. Word equation for Anaerobic respiration: glucose – lactic acid (+ energy) Plasma- the pale yellow coloured liquid part of blood. Red blood cells- the cells in the blood that carry oxygen. Artery- thick walled tubes that carry blood away from the heart. Capillary- very thin tubes that carry blood to the tissues of the body. Vein- thin walled tubes that carry blood back to the heart. Lactic acid- A toxic chemical produced during anaerobic respiration. Oxidation- oxidation is a reaction in which oxygen combines with a substance. Oxidation also means a loss of electrons. Enzymes- a protein that speeds up chemical reactions. The act of breathing is part of the respiratory system is a process where air travels into and out of the lungs. Respiration is different, where exercise causes muscles to release energy in the form of glucose.