Terrestrial Planets
advertisement

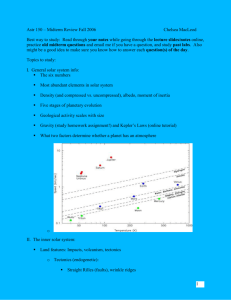
Mercury Closest planet to sun Surface similar to Moon heavily cratered no atmosphere Only one spacecraft flyby Mariner 10 flew by 3 times in 1974-75 New mission Messenger is in planning stages Mercury Mass = 0.055 MEarth Radius = 0.38 REarth Surface Temp: -300 - +800 C Orbital period = 88 days Rotation period = 59 days (Exactly 2/3 of Mercury’s year!) Mercury - Structure Smallest of planets by mass and size Density 5.4 g/cm3 Mass 1/18 of Earth’s mass Radius less than half of Earth’s denser than Earth’s mantle quite different from Moon Dense iron-nickel core 60% of total mass almost size of Moon! Mercury - Surface Moonlike: Surface craters, no atmosphere No evidence of tectonic activity Scarps (cliffs) in middle of craters crust shrank and cracked (after craters formed) Question How do we determine the rotation rate of a planet? Determining rotation rate of a planet • Use reflected radio waves to determine line of sight doppler shifts. We always see the same face of the Moon. So period of orbit = period of rotation Why? Tidal Locking If orbit period faster than spin period, bulge moves around surface of Moon => friction Moon Top view of Moon orbiting Earth Earth What does this have to do with Mercury? Mercury’s Rotation • Highly eccentric orbit => Mercury’s speed changes as it orbits the sun => no synchronous rotation • Next best thing - presents same side to sun every other time around. Earth-Like Planets: Venus and Mars Chapter 7 View from Earth Venus shows phases otherwise featureless • Obscured by clouds Mars appears red due to iron oxides (rust) polar ice caps surface markings • Seasonal changes Highlights Venus: seems a “twin” of Earth (but not!) massive atmosphere • large greenhouse effect due to high CO2 • surface temp about 750 K Mars: quite cold • once much warmer very thin atmosphere • once much thicker had flowing water in past • possibility of life? Radar Map of Venus Venus: General Properties Mass 82% of Earth’s mass Radius about same as Earth Density (5.3 g/cm3) about same as Earth Surface of Venus Problem: how to see through cloud cover? Spacecraft exploration Venera 7 (USSR) • landed on surface (1970) • lasted 23 minutes! Magellan Orbiter (USA) • use radar imaging (from orbit) • mapped surface at 100m resolution Surface of Venus Surface features produced by volcanic and tectonic activity but no plate motion 75% low lava plains • produced like lunar maria • very “young” surface (few craters) 25% mountains/mountain ranges Craters on Venus Few small craters small objects burn up in dense atmosphere Use large (>30 km) craters to estimate age lava plains 500-600 million yrs • vast geologic activity then • not much since Atmospheric Conditions Extreme atmospheric pressure / density 100x greater than Earth Very high surface temps around 750 K little day/night variation • due to thick atmosphere Generally hot and dry no water Occasional “acid rain” Atmosphere of Venus Layers of sulfuric acid clouds Composition 30-60 km above surface 96% carbon dioxide 3% nitrogen remove CO2, then atmos. like Earth’s Runaway greenhouse effect Greenhouse gasses -> high temps water evaporates carbon dioxide CO2 released from rocks increases greenhouse Venus About how far from the Sun (in AU) is Venus? How long is its orbital period (Venutian year)? How long is its rotational period (Venutian day)? Venus Mass = 0.82 MEarth Radius = 0.95 REarth Average distance from Sun = 0.72 AU Orbital period = 225 days Rotation period = 243 days (longer than orbital period, and retrograde!) Anomalous rotation of Venus • • • Extremely slow - Venutian day longer than Venutian year! Retrograde - Sun rises in the west and sets in the east! Most likely due to a collision during solar system formation Venus • Thick clouds prevent viewing of surface. (UV Image) • High temperatures and pressures, acidic gases • Led to much speculation. • How did we get info "Radar Echo" technique measures altitude space probe time for signal to return tells you the altitude of surface feature. Planet Surface Venera 14 photo of surface. Lander destroyed after about an hour! Venus' Atmosphere - Hot at surface - 750 K! (Room temp. on Earth about 300K) - Why so hot? Runaway Greenhouse Effect 1) Water and CO2 evaporate from oceans into atmosphere. 2) Greenhouse effect more efficient. 3) Temperature rises. 4) More evaporation (back to #1). => complete evaporation of oceans. Thick atmospheric blanket. Atmospheric Comparison • How does Venus lose its interior heat? We don’t know! No plate tectonics => no interior convection • Possible volcanic activity, but … • • • Distribution of craters on surface is uniform • Surface of Venus is same age everywhere: 500 Million yrs. old Cataclysmic resurfacing? • Geologically dead rest of the time Mars: General Properties radius density 3.9 g/cm3 less than Earth; more than Moon mostly silicates possible metal core Rotation about 1/2 of Earth’s period 24 hours, 37 min (like Earth) tilt of axis about 25º; orbital period 1.88 years seasons similar to Earth’s duration ~ 6 months (instead of 3) Surface Conditions Temperatures Summer: • • • • Day 240 K (-33 C) Night 190 K (-83 C) Coldest 173 K (-100 C) Water frost deposits Surface winds mostly moderate but giant dust storms can occur Mars Atmosphere & Climate Composition: 95% carbon dioxide (CO2) 3% nitrogen (N2) similar to Venus! Atmospheric pressure 100x smaller than Earth’s Surface Pressure 0.006 that of Earth's atmosphere (thin air!) equiv. to 30 km above Earth surf. Clouds dust clouds water ice clouds dry ice (CO2) crystals Polar Caps At both N and S poles change with seasons seasonal ice caps • composed of dry ice (frozen CO2) permanent ice caps • composed of water ice Seasonal Changes Channels and Flood Plains Evidence liquid water existed on Mars highlands runoff channels • from ancient rainstorms? • older than 3.9 million yrs outflow channels • much larger • carved by huge floods Martian Canals Schiaparelli (1877) reported canale on Mars Led to suggestion of intelligent Martian civilization Italian = “channels” English = “canals” War of the Worlds (H.G. Wells) Percival Lowell primary American proponent Eventually shown to be optical illusion Climate Change Evidence indicates Mars had liquid water (warmer) much denser atmosphere What happened? “Runaway refrigerator effect” atmosphere began to escape into space (low gravity) • • • • • less dense atmosphere -> less greenhouse surface cools water freezes -> less greenhouse more cooling carbon dioxide freezes -> less greenhouse happened over 3 billion yrs ago Mars Mass = 0.11 MEarth Radius = 0.53 REarth Average distance from Sun = 1.52 AU Rotation Period = 24.6 hours Orbital Period = 687 days Olympus Mons Largest known volcano in Solar System – 3X the height of Everest! Question What is the main reason that many scientists think Mars may have once harbored life? Evidence for Past Surface Water "runoff channels" or dry rivers "outflow channels" standing water erosion in craters? teardrop "islands" in Mars' Moons Phobos and Deimos Deimos: 16 x 10 km Phobos: 28 x 20 km Properties similar to asteroids. They are probably asteroids captured into orbit by Mars' gravity.