Internet Service Providers (ISP)
advertisement

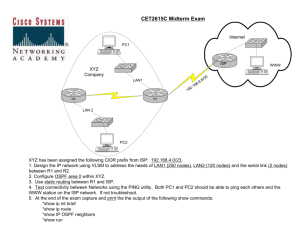
Internet Service Providers (ISP) HOW INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDERS WORK What is the role of an (ISP)? 'An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a company that provides a user with access to the Internet, usually for a fee.' Internet Service Providers (ISP) Networks There are small, medium and larger computer networks all needing access to the Internet. ‘Business Network’ Local Area Network (LAN) ‘Home’ Internet Service Providers (ISP) The Internet Packets of data are transmitted over the Internet using switched technology guided by the IP address of end computer. The Internet ‘Home Computer’ 21.34.129.86 ‘Another Computer’ Packet of data’ Internet Service Providers (ISP) 28.203.156.94 Transmitting Data packets Here is a more detailed arrangement of how data packets are transmitted across a network. Public Telephone Network Modem Modem Pool 21.34.129.86 ISP Port Server LAN ‘Another Computer’ 28.203.156.94 Router Router Router CSU / DSU Internet Service Providers (ISP) CSU / DSU Router ISP Backbone ‘Home Computer’ Internet Service Provider (ISP) Small and large networks connect to an ISP via a point of presence (POP). • • • Conventional Phone Digital subscriber line Cable Modem POP Point of Presence (POP) Internet Service Provider (ISP) ‘Home’ ‘Home Network’ Internet Service Providers (ISP) ‘Business Network’ Network Access Point (NAP) The ISP then connects to a Network Access Point via a T3 line (night data speed through put) T3 Line • • • Conventional Phone Digital subscriber line Cable Modem POP NAP Internet Service Provider (ISP) T1 Line Point of Presence (POP) ‘Home’ Internet Service Provider (ISP) Internet Service Providers (ISP) ‘Business Network’ Internet Backbone The data packets (datagrams) are then sent at high speed across the Internet backbone. • • • Conventional Phone Digital subscriber line Cable Modem Internet Backbone T3 Line POP NAP Internet Service Provider (ISP) T1 Line Point of Presence (POP) ‘Home’ Internet Service Provider (ISP) Internet Service Providers (ISP) ‘Business Network’ Internet Backbone This is a simplified diagram of how different networks interface. Local ISP Internet Service Providers (ISP) MAE Metropolitan Exchange (MAE) privately owned ‘Network Access Points’ Local ISP Local ISP Regional ISP ‘Local ISP’ NAP Internet Backbone NAP Regional ISP Local ISP Regional ISP NAP Local ISP NAP Regional ISP Local ISP ‘Regional ISP’ Internet Service Providers (ISP) Internet Backbone A backbone is typically a fibre optic trunk line (OC carrier) that can carry data at high speed. There are many companies that operate their own high capacity trunk lines (NSP), such as: - Internet Service Providers (ISP) IBM UUNet CerfNet BBN SprintNet PSINet Internet Service Providers (ISP) MAE Metropolitan Exchange (MAE) privately owned ‘Network Access Points’ NAP NAP Internet Backbone NAP NAP Following Data Packets You can follow a datagram through all the different paths taken to end up at the destination IP address. In the windows command prompt tyle in, tracert www.bbc.co.uk (or you can perform the following request online: http://traceroute-online.com/ Internet Service Providers (ISP)