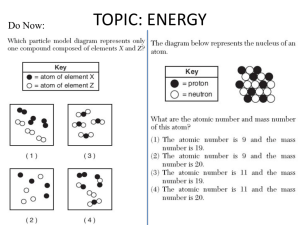
Temp, etc.. Power Point
advertisement

Temperature, Heat, Thermal Expansion, and Heat Transfer PHYSICS I Temperature defn: what a thermometer reads • Average kinetic energy reading of a substance • Fahrenheit, Celcius, Kelvin scales • Temperature Conversions °F = (1.8 x °C) + 32 °C = (°F – 32) ÷ 32 K = °C + 273.15 Heat Defn: transfer of energy from one object to another due to difference in temp. Coffee mug examples 80°C coffee sitting on counter of kitchen that is 26°C – what happens? What if cold (5°C) pop can sitting on the counter of same kitchen? Heat Internal Energy A substance contains internal energy… NOT heat There is more internal energy in a bathtub full of cold water than a red-hot pin (due to the higher number of molecules; therefore, bathtub has more kinetic energy) But! Heat flows from red-hot pin to tub water Measuring Heat Heat is a form energy (Joules) Calories: calorie Calorie Heat required to raise 1g of H2O by 1°C Kilocalorie = heat required to raise 1kg of H2O by 1°C Unit of energy Unit of energy 1 calorie = 4.184 joules Used on food labels Specific Heat Defn: quantity of heat required to change temperature of a unit mass of substance by 1° Water (discussion – see map next slides) Jet Stream? Water – What do these graphs tell us? Thermal Expansion As Temp. decreases => Substances contract (become more dense) Except Water! H2O MOST dense at 4°C From 4°C to 0°C, water expands (becomes less dense) Which is why ice floats Conduction Heat transferred by successive collisions of atoms Good conductors of heat and electricity: Metals - #1 Ag, #2 Cu, #3 Al… Poor conductors: Wool, wood, styrofoam = insulators In February you drive by a house with snow on its roof. Does the house have good insulation or poor? Explain. Convection Heat transferred due to motion of fluid Theory behind plate tectonics Global Wind Currents At night or during day? Explain. What happens during other half of earth rotation? Explain. Radiant Energy Radiant Energy in form of Electromagnetic waves