00-00-Weekly Schedul..
advertisement

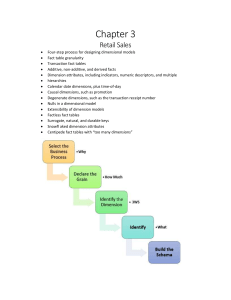
00-00-Weekly Schedule – Semester Ron Tarr Tentative schedule – meaning subject to some changes The following list of topics acts also as a schedule. The file naming/ numbering system 01-something is what is covered in week 01 and 05-something will be in week 5. The numbering system also corresponds with the numbering of the notes that will be given to you throughout the semester. Starting in the Fall of 2013, I will try to compress the lecture portion further in an effort to add additional topics at the end in the form of a project 00-00-Weekly Schedule REV: 23 March 2016 Page 1 Data Warehousing – List of topics 00-0 What is Data Warehousing (DW) Overview DW Definitions Why is it important to business Why is it important to students 01-0 Why do we need Data Warehousing Understanding the need for strategic information Recognize information crisis Difference between Operational and Informational systems What is the solution 01-2 Benefits of using DW Immediate access to information Data integration across the company Even integrating data from outside organizations Future vision from historical trends Tools to look at data in new ways Freedom from IS resource limitations Applications using a DW 01-3 What is Business Intelligence 02-0 DW Components Data modeling Definition Advantages and Disadvantages Dimensional Modeling Purpose Draw Star Schema Diagram Optimization – single join Fact table 2 components -- 3 characteristics Dimension tables Simplicity of query example Diagram from OLTP to Reporting 02-1 Additional Notes (possible reading) see 02-5 Dimensional modelling continued Dimension and measures in Data Analysis (see 02-5 page 2) Hierarchies within Dimensions (02-5) Balanced, Unbalanced, Ragged Concept of a cube 03-0 Steps in dimensional modelling 1 Choose a business process 2 Choose the grain of the fact table 3 Choose the dimensions based on the grain 4 Choose the facts that will populate the fact table 03-2 Practice exercises in dimensional modelling Case 1: Personal Expense example see 03-2.2 page 7 Case 2: Given Manufacturing Scenario grain and tables Case 3: Given statement of grain diagram Case 4: Given Fact table Draw the star schema Seneca Bookstore Case 04-0 Exercises Fact table exercise Design case 1 - order entry system Design case relationship diagram HO 00-00-Weekly Schedule REV: 23 March 2016 Page 2 Design case 2 – from access database Design Case 1 – good reading solution Design case 1 modified – reading 04-1 Time Dimension Time in DW Problems Twinkling or Temporal Inconsistencies Slowly Changing Dimension (SCD) Practice example – Seneca College FT/PT Solutions to SCD -- 1, 2 and 3 Problems – Advantages and Disadvantages 04-2 Estimating the DW size Examples demonstrating method used Other examples as exercises see 05-1 05-0 Independent study Readings 1 Surrogate key usage Snowflake Hierarchies Aggregate storage methods Partitions Data Mart Factless Fact tables Definitions to learn Readings 2 Alternate explanation that provide review 05-1 Labs – OLTP to Cubes May be started earlier in semester 05-2 Self-study/Research Review through studying/answering practice questions 06-0 Design assignment 07-0 Design Assignment Design assignment is due 08-0 Reading Week Complete labs and finish readings and review 09-0 Test 1 Test on design and theory aspects of course 10-0 Practical project part 1 Design portion 11-0 Practical project part 2 Import data to SQL server Develop a DW Develop a cube Prepare a set of reports 12-0 Practical project part 2 Continue to completion 13-0 Practical project part 3 Partition Update DW with new data 14-0 Test 2 – on the practical part of the course Test will cover going from OLTP to cube – done on-line 15-0 Exam 00-00-Weekly Schedule REV: 23 March 2016 Page 3