Being a Vascular Surgery PA
advertisement
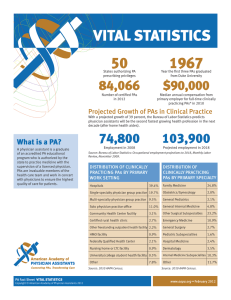
Kimberly Nicole Kurtz, MPA, PA-C Personal Background Tips on Getting Into College and Grad School Explaining Physician Assistant Role and Career Outlook Specifically what I do as a Vascular Surgery PA Questions Benicia High School, 2002 • Cumulative GPA 4.33, Senior Year 4.5 • SAT score 1250 • Cheerleader, Key Club/Honors Club, Part-time job Diablo Valley College, 02-03 Santa Barbara City College, 03-04 • William Oliverius Scholarship for Excellence in Biology • Volunteered 4-6hrs week at Cottage Hospital Cancer Research Internship, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI – Summer 2004 University of California, San Diego, 2006 • • • • • • • BS – Human Biology, GPA 3.6 Kappa Alpha Theta Sorority Crew Team Teacher’s Assistant, Into to Nutrition Class MCAT score 29R Part-time job, Customer Service Representative Observed Surgical Procedures What to do next?? • • • • • Medical School? Physician Assistant School? Pharmacy School? Podiatry? Optometry? Masters of Nursing? Medical Device/Pharmaceutical Rep? PA school • Approx $50,000/year X 2.5yrs = $150,000 • Master’s Degree • Can start working as soon as you pass PANCE exam Medical School • Total average cost of attendance $67,000/yr • X 4yrs= $268,000 • Average residency pays $50,000 - $80,000/yr X 5 yrs • At least 2 years of fellowship for surgical specialties Front Office Medical Assistant, ENT and Medical File Clerk for Pain Management Clinical Back Office Medical Assistant, Bay Area Surgical Specialists, Walnut Creek, CA GRE Anatomy class CASPA application Visit Schools, School Interviews Samuel Merritt University, Oakland, CA • Master Physician Assistant Degree, 2010 • Didactic Curriculum – 1.5 yrs, condensed medical school • Clinical Rotations – 1yr, nine 5-week long rotations Geriatrics, Pediatrics, Women’s Health, Internal Medicine, Family Medicine, Emergency, Surgery 2 electives – Vascular Surgery and Plastic Surgery NCCPA Certified - Jan 2011 California State Medical License – Jan 2011 DEA Certified • Controlled Substance Course ACLS/BLS Certified “A physician assistant (PA) is a medical professional who works as part of a team with a doctor. A PA is a graduate of an accredited PA educational program who is nationally certified and state-licensed to practice medicine with the supervision of a physician.” - AAPA “By design, physicians and PAs work together as a team, and all PAs practice medicine with physician supervision. Supervision does not mean, though, that a supervising physician must always be present with the PA or direct every aspect of PA-provided care. PAs are trained and educated similarly to physicians, and therefore share similar diagnostic and therapeutic reasoning. Physician-PA practice can be described as delegated autonomy. Physicians delegate duties to PAs, and within those range of duties, PAs use autonomous decisionmaking for patient care. This team model is an efficient way to provide high-quality medical care. In rural areas, the PA may be the only healthcare provider on-site, collaborating with a physician elsewhere through telecommunication.” – AAPA Prescribe medication, including narcotics Order labs, tests, radiologic scans, nursing care, etc. First- assist in surgery Perform in-office surgical procedures under his/her scope of practice See patients in the office and hospital independently Not much difference from the patient perspective Nurse practitioners are trained in the nursing model • Patient care centered Physician assistants are trained in the medical model • Diagnosing and treating disease NPs tend to stick in family practice, women’s health, pediatrics PAs are more widely distributed among specialties PA profession was created to improve and expand healthcare First PA program at Duke University • Graduating class 1965 • Navy corpsman from Vietnam More common on east coast Currently 86,500 nationally certified PAs First-year PA students – 6,630 Graduating PA students – 5,964 In California, 6,723 practicing PAs 20% of US population lives in rural areas • Only 10% of doctors are in rural areas • 17% of PAs practice in Rural areas The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that PAs will be the second-fastestgrowing profession in the next decade, increasing from 74,800 in 2008 to 103,900 in 2018. Growing physician shortages Aging Population More people seeking medical care with the Affordable Care Act US News and World Report – in Top 50 Careers of 2011 Money Magagzine, Nov 2010 – 2nd Best Job in America Forbes.com ranked physician assistant first in its list of best master’s degrees for jobs. Kiplinger’s named PA as one of its great careers for your future. According to the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA), the average annual compensation for physician assistants is $84,326 in primary care, and $97,207 for surgical specialties. CA SLRP Loan repays students loans up to $60,000 for 2 years in a rural area “Would you become a PA if you had to do it all over again?” • “Yes!” – 88% • “Definitely” – 52% • “Probably” – 36% Source: 2009 AAPA Census Vascular Surgery PA • Washington Township Medical Foundation • Hired Jan 2011 2 Supervising Physicians • John Thomas Mehigan, M.D • Gabriel Herscu, M.D. First-assist in OR First-assist in Cath Lab Rounding on inpatients Write post-op orders and note See patients in office • New pts, f/u, post-op, pre-op Dictate History and Physical Reports Consult new patients in hospital/ED Wound Care Clinic On Call 24/7 for nursing orders/questions 7:15AM – Arrive at hospital, meet up with SP discuss plan for the day 7:30 – Preround on the computer looking up lab results and other doctors’ notes 7:45 See a critical pt in ICU, write new orders 8:00 – Scrub into the first surgery, prep pt, and first-assist, carotid endarterectomy 10:00 – Accompany pt to PACU and write post-op orders and post-op note 10:10 – Meet up with SP and start inpt rounds 10:45 – Go to Cath lab and obtain ultrasound-guided percutaneous access into femoral artery, assist in angiogram 11:45 – Scrub into AVF creation, first assist 1:00 – Post-op orders/note 1:15 – Find family and discuss case, give further instructions 1:20 – Pre-op next pt/mark site 1:30 2:00 – Finish inpt rounds – Revisit critical pts, f/u on ordered labs, return phonecalls 2:15 – Scrub into toe amputation and foot debridement 3:00 – Post- op orders/note 3:15 – Check on Cath lab pt, and discharge pt 3:30 – Wound debridement, lower extremity 4:00 – Post- op orders/note 4:15 – Go home Including limb savage – lower extremity revascularization, bypass procedures Amputations Carotid endarterectomy Fistula creation and revision Embolectomy AAA repair Aneurysmectomy Wound debridement/Wound VAC placement Temporal artery biopsy Fasciotomy Line placement arterial and venous Dialysis catheter placement, CAPD catheter Ultrasound guided percutaneous access Intra-operative fluoroscopy(I do not step on pedal) Angioplasty and stenting Vein stripping and ligation IVC filter placement, Mediport placement Tunneled cuffed hemedialysis catheter placement and removal Peripheral Vascular Disease /Atherosclerosis End Stage Renal Disease Diabetes, Type 2 Chronic Wounds Hypercoaguable states Giant Cell Arteritis Venous Insufficiency Pelvic Venous Compression Syndrome Aortic Aneuyrsms Strokes Renal Artery Stenosis Hypertension Infectious Diseases Superior Vena Cava Syndrome www.aapa.org www.capanet.org https://portal.caspaonline.org Rodican, Andrew J. Getting into the Physician Assistant School of Your Choice. 2003 www.vascularweb.org