Formulating objectives, general and specific
advertisement

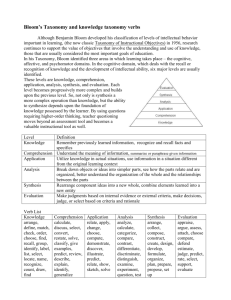
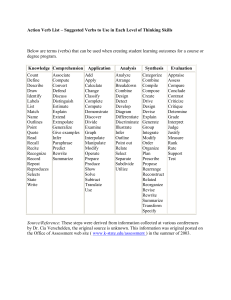
In planning effective curriculum, the objectives of different courses of study are to be clearly defined and laid down, so that courses are well guided Before formulating the objectives of nursing educational program, the needs of learners, organization, society, community and nation to be considered The result sought by the learner at the end of the educational program, ie, what the students should be able to do at the end of a learning period, that they could not do beforehand - J J Guilbert Desired end results or goals are expected or anticipated end results The statement of those changes in behavior which are desired as a result of specific learner and teacher activity which is a two way process. To prepare the nurses for rendering community services through primary health To prepare nurses for providing care at institutional level To prepare nurse educators to handle teaching learning situations in all clinical areas Cognitive (knowledge) Conative (practical skills) Affective (communication skill) Recall of facts Interpretation of data Problem solving Imitation Control Automatism Receptivity or attention Response internalization The 5 levels of Bloom's taxonomy are: Knowledge and Comprehension This is the lowest level on Bloom's cognitive domain. It is associated with the recall of information, knowledge of subject matter as well as understanding basic facts. Application Application relates to the using and applying of information. Problem solving methods are utilized and information is recorded, reported and manipulated. Analysis Analysis specifically refers to the identification of patterns and the organization of ideas. It is strongly linked to the recognition of meaning. There is an emphasis towards examination, classification, investigation and comparison of ideas. Synthesis Synthesis focuses strongly on the creation of new ideas and the concept of invention, imagining, prediction, estimating, modifying, inferential thinking and hypothesizing. Ideas are combined and new concepts emerge. Evaluation Evaluation is the highest order of thinking on the taxonomy. It involves the assessing of theories, the use of higher order reasoning skills and the comparison, judgment and evaluation of ideas. By using Bloom's Taxonomy as a guide, one is assured of an upward movement from lower level recall of information (Knowledge and Comprehension) to higher level synthesis and evaluation. Level 1 - Knowledge (Memory) This level includes definitions, terms, categories, and "boomerang-back" information. Level 2 - Comprehension This level includes interpretation, putting ideas in one's own words. Level 3 - Application This level involves using knowledge to solve problems when no directions or methods are specified. Level 4 - Analysis This level involves the ability to outline major points, to break down material into its component parts. Level 5 - Synthesis This level involves putting together the parts to form something that is new. Level 6 - Evaluation This level involves the ability to make a judgment based on criteria. Verbs using levels of understanding for use in formulating questions for oral or written use or for stating learning objectives arranged according to Bloom's Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain. KNOWLEDGE The student recalls or recognizes information. define, name, memorize repeat, label, record list, recall, relate COMPREHENSION The student changes information into a different symbolic form/language. restate, report, express describe, tell, locate explain, discuss, review identify, recognize translate, interpret APPLICATION The student solves a problem by using the knowledge and appropriate generalizations. apply, show, illustrate use, demonstrate, schedule practice, dramatize, employ operate ANALYSIS The student separate information into component parts. distinguish, debate, compare differentiate, question, diagram calculate, solve, inspect test, analyze, inventory contract, appraise, relate criticize, experiment, examine SYNTHESIS The student solves a problem by putting information together that requires original, creative thinking. compose, set up, collect propose, manage, create formulate, plan, organize assemble, design, prepare construct, arrange EVALUATION The student makes qualitative and quantitative judgments according to set standards. estimate, value, measure evaluate, predict, select/choose compare, appraise, assess score, rate condition Behavior Criterian/level Health needs/ demands of society Services to the patient Services to the community The profession itself The students Progress in sciences Scientific methods Statement of school’s philosophy Levels of professional competencies to be attained Student’s background, level of education Statutory minimum requirements Teaching, physical and clinical resources available Future demands on nursing Expected responsibilities for different nursing positions General Intermediate Educational objectives Specific/ insructional institutional Correspond to the functioning of the types of health personnel trained in an establishment The course objectives must be in harmony with general curriculum objectives of program of school Eg: providing preventive and curative care to the individual and the community in health and sickness It is made possible by breaking down general objectives into components, which together indicate the nature of those functions Eg: planning and carrying out blood sampling session for a group of adults in community The graduate of nursing program will be prepared to function as generalist with beginning competencies in a specialized area of nursing Eg: the graduate will be prepared to function in a variety of settings and be able to obtain health histories and make health assessments Instructional objectives are descriptions of performance the instruction is expected to produce Relevant Logical Unequivocal Feasible Observable measurable Behavioral terms Reflect the condition Reflect the standard Reasonable in number of behavioral changes expected Consistent with unit theme Relation to each other and unit Approximately of some level of generality and specificity Distinctive and discriptive